"Healthy and Delicious: Why the Mediterranean Diet Should Be Your Go-To"
Have you ever heard of the Mediterranean diet? This popular way of eating has gained a lot of attention in recent years for its health benefits. In this blog post, we'll explore the history, components, and benefits of the Mediterranean diet, and provide some tips for adopting this delicious and nutritious way of eating.
History and
Origins of the Mediterranean Diet
The
Mediterranean diet is based on the traditional eating habits of people who live
in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, Spain, and
Morocco. The diet has been around for centuries and is rooted in the cultural
and historical factors of these regions. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes
whole foods and minimizes processed foods, which are prevalent in Western
diets.
Key
Components of the Mediterranean Diet
The
Mediterranean diet is primarily plant-based and includes a high consumption of
fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil. Fish, poultry,
and dairy are also part of the diet, but in moderation. Red meat and sweets are
kept to a minimum. Herbs and spices are used to flavor food instead of salt. Herbs
and spices not only add flavor to food but also have health benefits. For
example, garlic and onions contain compounds that may help lower blood pressure
and cholesterol levels. Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory
properties and may help protect against chronic diseases, such as cancer and
Alzheimer's disease.
In addition
to using herbs and spices, the Mediterranean diet also emphasizes drinking
water as the main beverage. This is because sugary drinks, such as soda and
juice, can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes
and heart disease. Drinking water, on the other hand, can help hydrate the
body, promote digestion, and support overall health.
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the importance of eating a variety of foods to ensure a balanced nutrient intake.
Health
Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
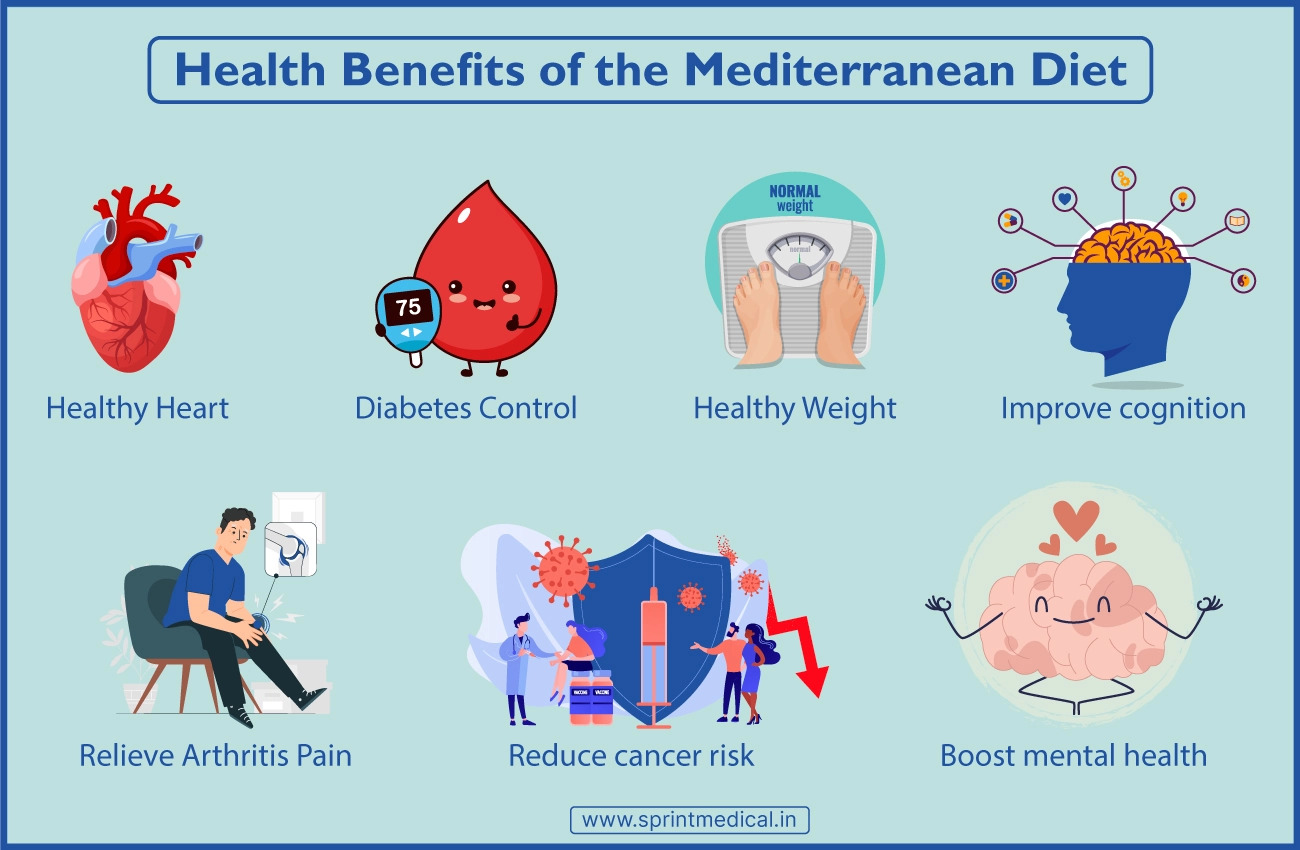
Research supports the health benefits of consuming the Mediterranean diet. It has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease and helps in weight management, digestion as well as mental health.
Reduced Risk of Heart Disease: The Mediterranean diet has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, which is the leading cause of death worldwide. A meta-analysis of 50 studies found that the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 29% reduced risk of heart disease, including a 57% reduced risk of coronary heart disease. This may be due to the high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The Mediterranean diet also emphasizes healthy fats, such as olive oil, and minimizes unhealthy fats, such as trans fats and saturated fats.
Reduced
Risk of Diabetes: The Mediterranean diet has also been associated with a
reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, which is a major public health concern. A
systematic review of 17 studies found that adherence to the Mediterranean diet
was associated with a 23% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. This may be due to
the high intake of whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, which are rich in
fiber and have a low glycemic index. The Mediterranean diet also emphasizes
healthy fats, such as olive oil, which may improve insulin sensitivity.
Reduced
Risk of Cancer: The Mediterranean diet has been associated with a reduced risk
of various types of cancer, including breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer.
A meta-analysis of 12 studies found that the Mediterranean diet was associated
with a 10% reduced risk of overall cancer incidence and a 15% reduced risk of
breast cancer. The high intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which
are rich in antioxidants, may help protect against cancer. The Mediterranean
diet also emphasizes moderate intake of fish and poultry, which are good sources
of protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
Reduced
Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: The Mediterranean diet has been associated with a
reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease, which is a progressive neurodegenerative
disorder. A systematic review of 11 studies found that adherence to the
Mediterranean diet was associated with a 33% reduced risk of Alzheimer's
disease. This may be due to the high intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole
grains, which are rich in antioxidants and may help protect against oxidative
stress and inflammation. The Mediterranean diet also emphasizes moderate intake
of fish and poultry, which are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which may
protect against cognitive decline.
Improved
Weight Management: The Mediterranean diet has been associated with improved
weight management, which is important for overall health. A meta-analysis of 32
studies found that the Mediterranean diet was associated with a significant
reduction in body weight, body mass index (BMI), and waist circumference. This
may be due to the high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts,
which are low in calories and high in fiber, and the moderate intake of fish
and poultry, which are good sources of protein.
Research has shown that the Mediterranean diet has many health benefits. These benefits are likely due to the high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and healthy fats, and the moderate intake of fish and poultry. The Mediterranean diet is a delicious and nutritious way of eating that can improve overall health and well-being.
Tips for Adopting the Mediterranean Diet:
If you're interested in adopting the Mediterranean diet, start by making small changes. Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your meals. Switch to olive oil instead of butter or other oils. Add herbs and spices instead of salt for flavor. Plan your meals ahead of time to ensure a balanced nutrient intake. You can also experiment with Mediterranean recipes to add variety to your meals.
A sample
menu is provided below for reference.
Breakfast:
Greek
yogurt with fresh berries and a drizzle of honey
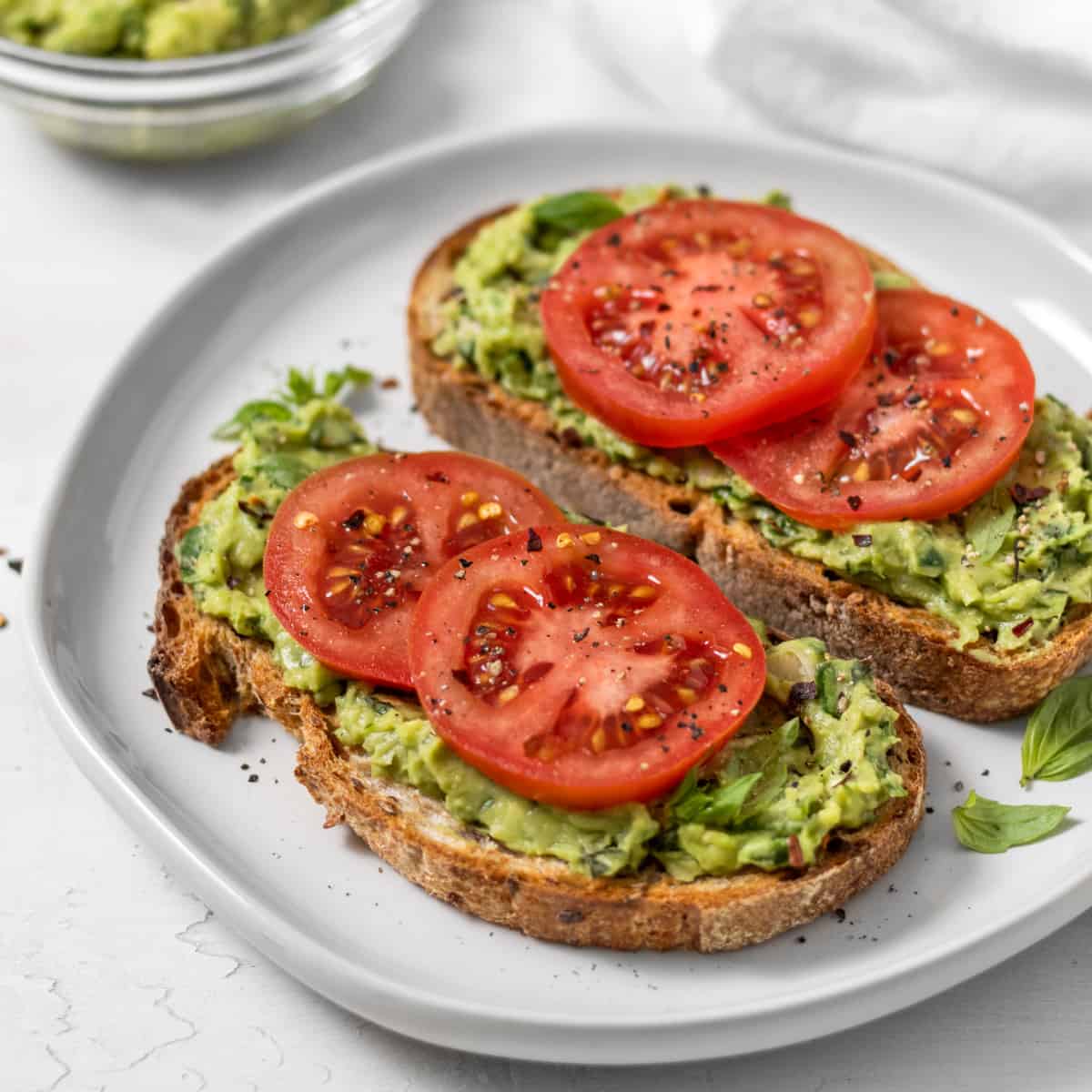
Whole grain toast with avocado and sliced tomato
Snack:
Handful of
almonds
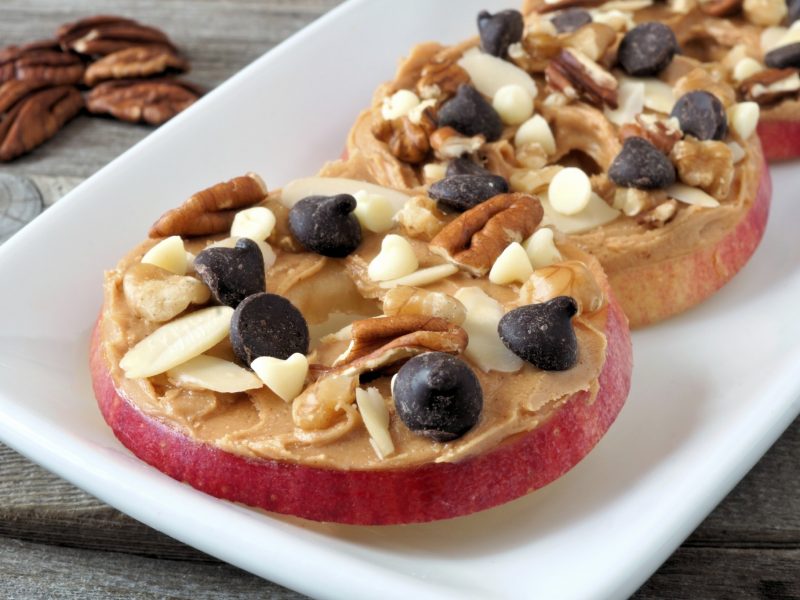
Apple slices with almond butter
Lunch:
Grilled
chicken salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and feta cheese,
dressed with olive oil and lemon juice
Whole grain
pita bread
Snack:
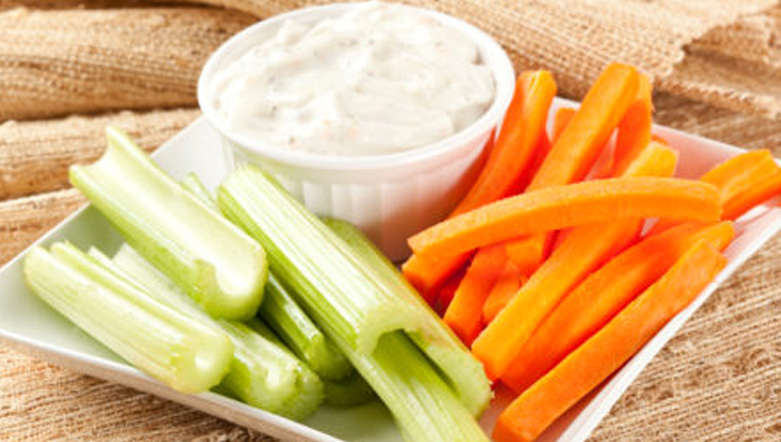
Carrots and celery sticks with hummus
Dinner:
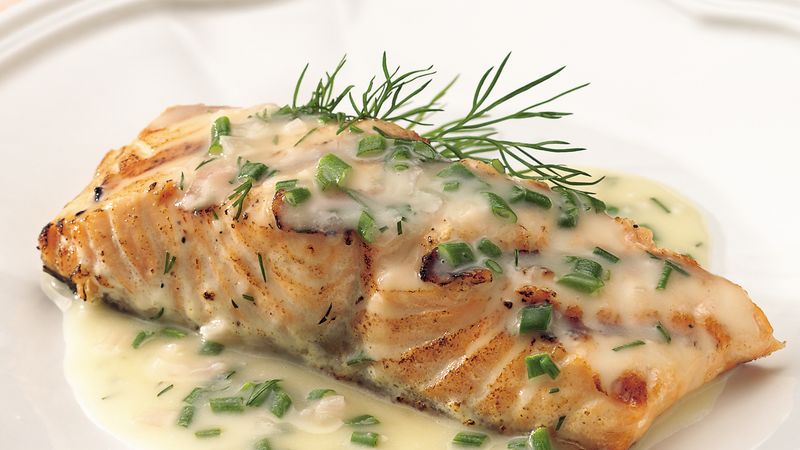
Grilled
salmon with lemon and herbs
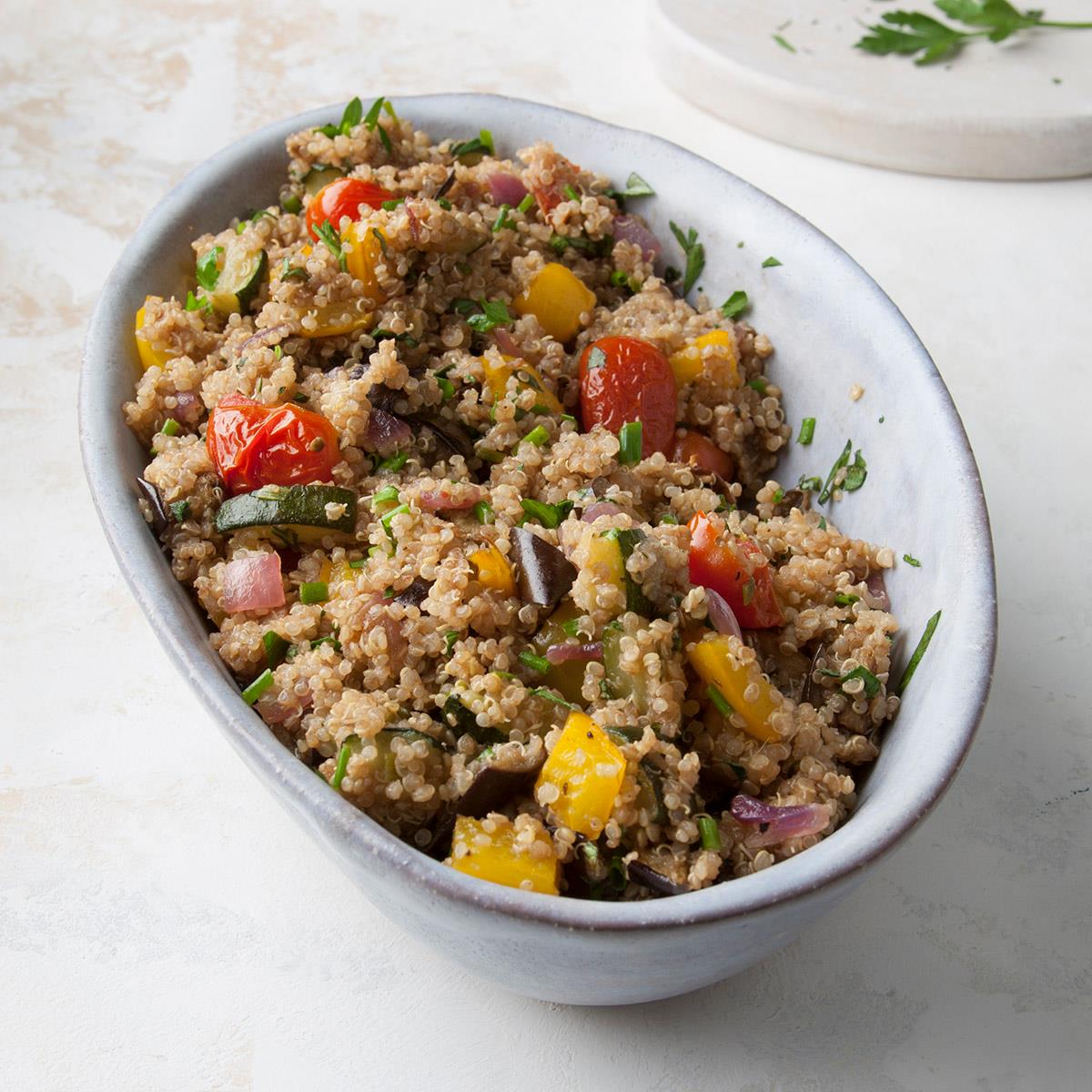
Quinoa
pilaf with roasted vegetables (e.g., zucchini, eggplant, bell peppers)
Roasted
garlic green beans
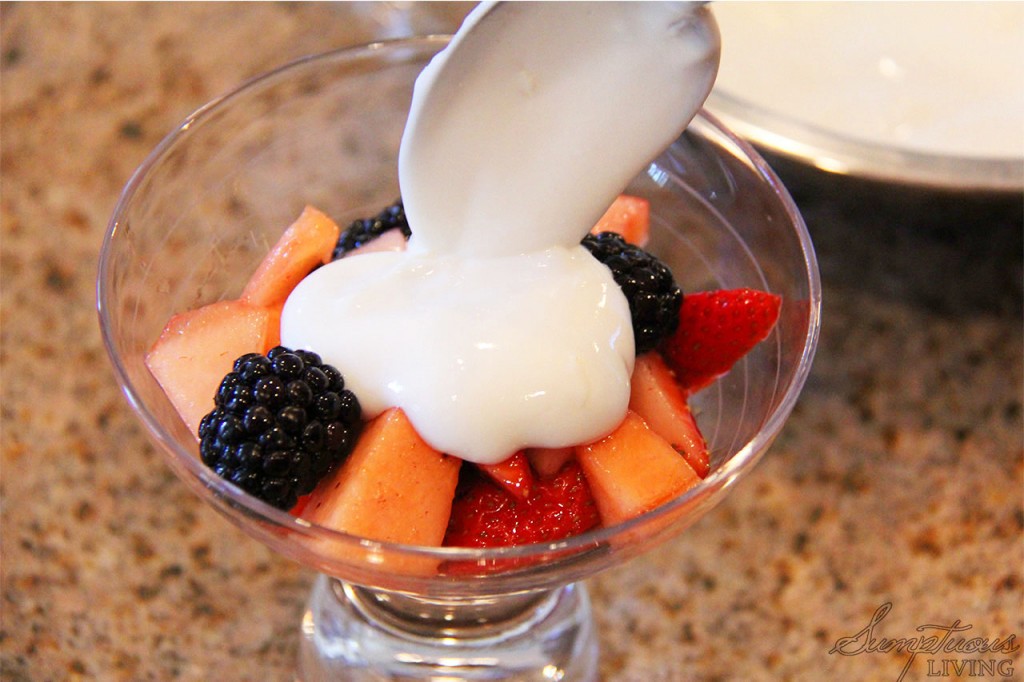
Dessert:
Fresh fruit salad with a dollop of Greek yogurt
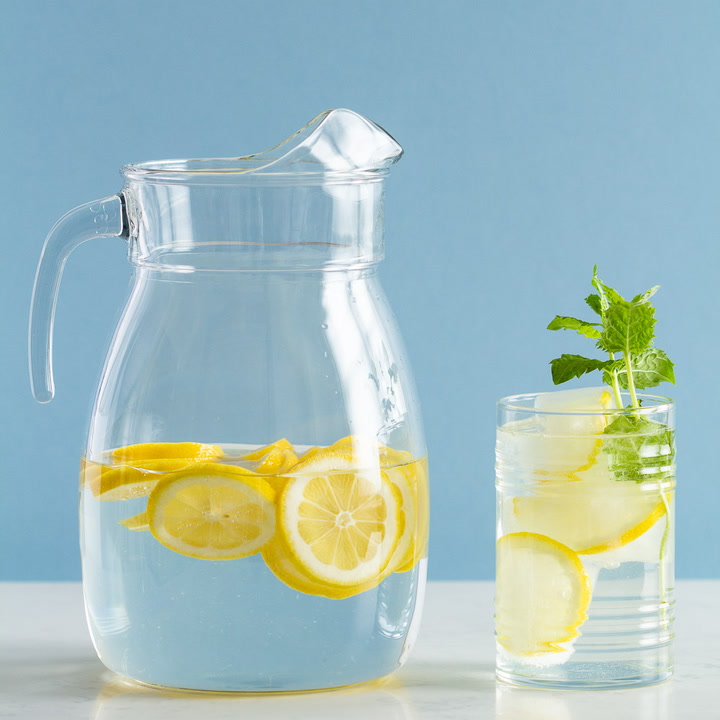
Beverages:
Water with
lemon slices
Herbal tea
This sample menu includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods that are typical of the Mediterranean diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Let's watch this yummy video.
Conclusion
The
Mediterranean diet is a delicious and nutritious way of eating that emphasizes
whole foods and minimizes processed foods. It has been associated with many
health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease, diabetes, cancer,
and Alzheimer's disease. If you're looking for a way to improve your health and
enjoy delicious food, the Mediterranean diet may be the perfect choice for you.

















Comments
Post a Comment