Solar Marvels: 12 Fascinating Things You Didn't Know About the Sun
Introduction
The Sun,
our nearest star, has captivated human imagination since time immemorial. Its
warm glow, life-giving energy, and mesmerizing beauty have made it a celestial
object of wonder. But did you know that the Sun holds many secrets and surprises
beyond what meets the eye? In this article, we're going to take a closer look
at our extraordinary Sun and uncover 10 fascinating facts that will leave you
in awe of this blazing celestial giant.
1. The Sun
is Mostly Hydrogen and Helium
While the Sun appears to be a glowing ball of fire, its composition is primarily made up of hydrogen (about 74%) and helium (about 24%). These two elements, forged in the furnace of the Sun's core, fuel the immense energy that radiates into space.
2. The Sun is a Giant Thermonuclear Reactor
At the Sun's core, temperatures soar to about 15 million degrees Celsius (27 million degrees Fahrenheit). Through a process called nuclear fusion, hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing an incredible amount of energy in the process. This continuous fusion reaction sustains the Sun's luminosity and warmth.
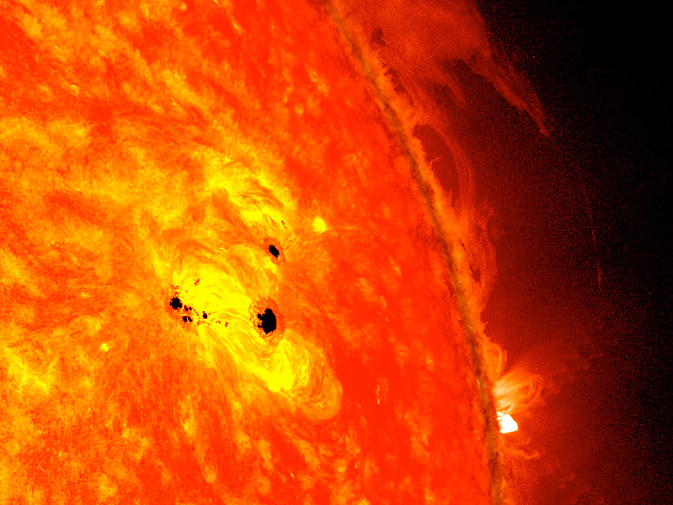
3.
Sunspots: Dark Blemishes on the Sun's Surface
Sunspots are cooler regions on the Sun's surface that appear as dark spots. They are caused by intense magnetic activity and occur in cycles that last about 11 years. Sunspots can be many times larger than Earth and have temperatures lower than their surroundings.
4. The
Sun's Atmosphere Has Layers
During a total solar eclipse, these layers become visible, creating a breathtaking celestial spectacle.
5. Solar Flares and Prominences
Solar flares and prominences are explosive events on the Sun's surface. Solar flares release a tremendous amount of energy in the form of intense bursts of radiation, while prominences are huge, looping structures of glowing gas that extend outwards from the Sun's surface. These phenomena are a result of the Sun's magnetic activity and can have significant impacts on space weather.
6. The
Sun's Energy Reaches Earth in About 8 Minutes
Despite
being about 93 million miles away from Earth, the Sun's energy travels at the
speed of light. This means that the light we see and the warmth we feel from
the Sun actually took around 8 minutes to reach us. So, when you bask in the
sunlight, you're experiencing the Sun's energy from a few minutes ago!
7. The
Sun's Magnetic Field Generates the Solar Wind
The Sun has a powerful magnetic field that extends throughout the solar system. This magnetic field creates the solar wind, a continuous stream of charged particles that blows outward from the Sun and influences space weather.
The solar wind interacts with the magnetic fields of planets and can cause phenomena like auroras and magnetic storms.
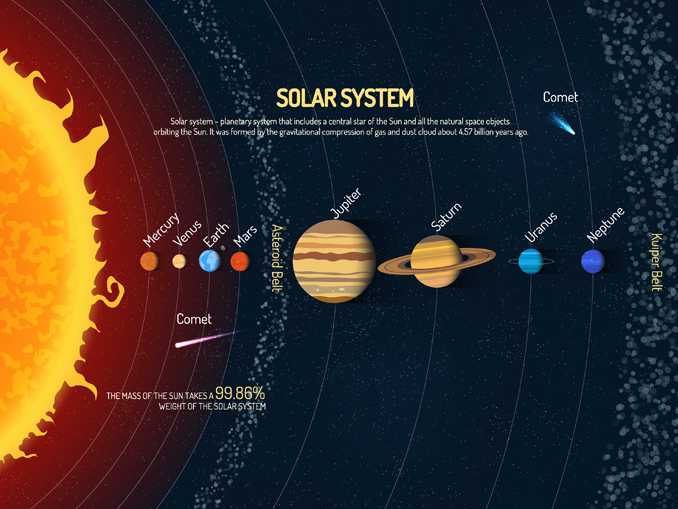
8. The
Sun's Mass Accounts for 99.86% of the Solar System
The Sun is incredibly massive. In fact, its mass comprises a staggering 99.86% of the entire Solar System! Its gravitational pull keeps all the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets in orbit around it, ensuring the stability of our cosmic neighborhood.
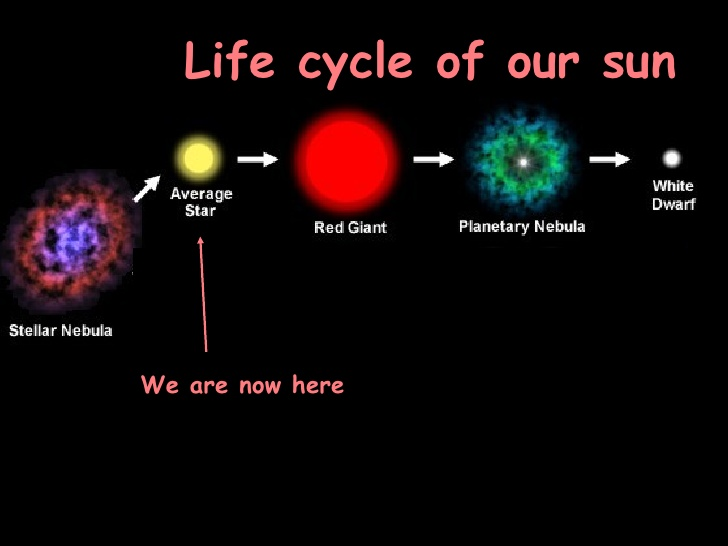
9. The Sun
Will Eventually Run Out of Fuel
As awe-inspiring as the Sun is, it won't shine forever. Eventually, it will deplete its hydrogen fuel, causing it to expand into a red giant. This event, expected to occur in about 5 billion years, will mark the end of the Sun's main sequence phase.
During this phase, the Sun will become hundreds of times larger than its current size, engulfing Mercury, Venus, and possibly even Earth. After its expansion, the Sun will shed its outer layers, leaving behind a dense, hot core known as a white dwarf.
10. Solar
Eclipses: A Spectacular Alignment
One of the most captivating celestial events involving the Sun is a solar eclipse.
This occurs when the Moon aligns perfectly between the Sun and Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon covers the Sun completely, revealing the Sun's beautiful corona, the outermost layer of its atmosphere. These rare events inspire awe and wonder, reminding us of the Sun's extraordinary presence in our lives.
11. The Sun's Magnetic Field Flips Every 11 Years
Every 11 years, the Sun's magnetic field goes through a complete flip, a phenomenon known as solar magnetic reversal. This means that the North and South poles of the Sun's magnetic field swap places. The magnetic activity during this time reaches its peak, resulting in an increased number of sunspots, solar flares, and other solar phenomena.
12. The
Sun's Rotation Varies
Surprisingly, the Sun does not rotate at a uniform speed. Its equatorial regions rotate faster than the polar regions. This differential rotation causes the Sun's magnetic field to become twisted and tangled, leading to the formation of sunspots, solar flares, and other magnetic disturbances.
Conclusion
The Sun,
our radiant celestial neighbor, continues to captivate us with its astounding
facts and hidden wonders. From its composition of hydrogen and helium to the
dynamic phenomena occurring on its surface, the Sun reminds us of the intricate
mechanisms that power our solar system. As we explore the Sun's mysteries, we
gain a deeper appreciation for the immense forces and delicate balance that
shape our existence.
So, the next time you feel the Sun's warmth on your skin or witness a spectacular solar eclipse, take a moment to reflect on the incredible marvel that is our Sun—a shining beacon of light, energy, and inspiration in the vast cosmic tapestry.









Comments
Post a Comment