10 Fascinating Mysteries of the Universe That Leave Scientists Baffled
Imagine a vast cosmic stage, adorned with celestial wonders and enigmatic phenomena that have baffled humanity for centuries. The universe, with its infinite expanse and boundless possibilities, holds within it secrets that continue to elude our understanding. From the smallest particles to the grandest galaxies, it beckons us to explore, question, and ponder the mysteries that lie beyond the known.
Welcome to the realm of the 10 greatest mysteries of
the universe!
1. Dark
Matter: The Invisible Cosmic Puzzle
2. Dark
Energy: The Enigmatic Force Driving Cosmic Expansion
Dark energy is an enigmatic force that permeates space and causes the universe to expand at an accelerating rate. It is believed to account for approximately 70% of the total energy density in the universe. The presence of dark energy was discovered through observations of distant supernovae, which revealed that the universe's expansion was accelerating instead of slowing down.
The nature of dark energy remains one of the greatest mysteries in physics. Various theories propose explanations, such as a cosmological constant or a dynamic field known as quintessence. Scientists are using astronomical surveys, gravitational lensing, and cosmic microwave background radiation studies to better understand the properties of dark energy and its influence on the universe's fate.
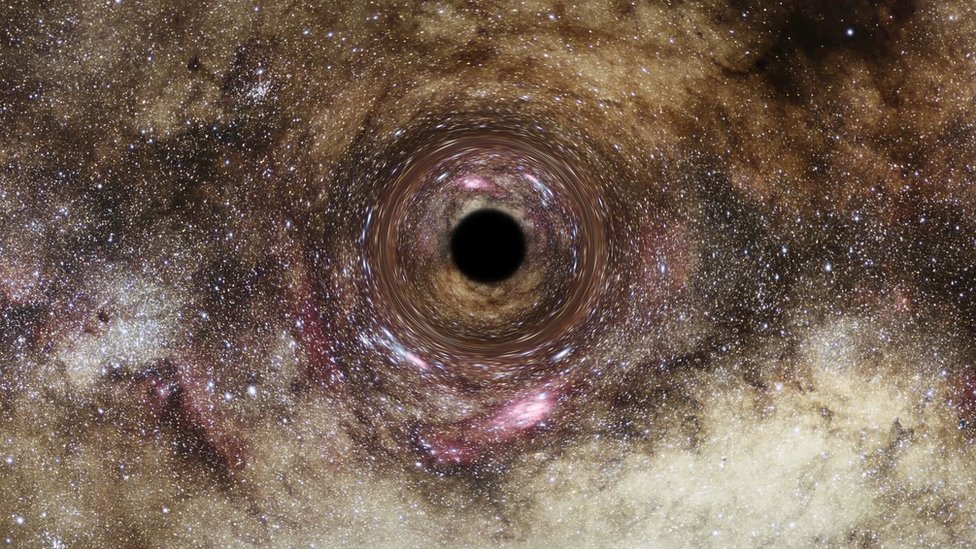
3. Black Holes: Mysterious Cosmic Vacuums
Black holes are fascinating yet mysterious cosmic objects formed from the remnants of massive stars that have undergone gravitational collapse. They possess an incredibly strong gravitational pull that not even light can escape, thanks to their intense density. Black holes are formed from the remnants of massive stars that have exhausted their nuclear fuel and undergone gravitational collapse. When such a star reaches the end of its life, it may explode in a supernova, leaving behind a dense core. If this core has a mass several times that of our Sun, it can collapse further under its own gravity, becoming a black hole.
The region from which nothing can escape, called the event horizon, marks the boundary of a black hole. Inside this boundary lies a singularity, a point of infinite density where the laws of physics, as we understand them, break down. The singularity represents a profound mystery, and physicists are actively seeking a theory of quantum gravity that can better describe the physics within a black hole.
Black holes play a crucial role in shaping galaxies and are believed to be at the centers of most, if not all, galaxies. Scientists study black holes using observations of their effects on surrounding matter, as well as through the detection of gravitational waves. They are also investigating the relationship between black holes and other phenomena, such as galactic evolution and the formation of massive structures in the universe.
4. The Big Bang: The Start of Everything
The Big Bang theory describes the origin and evolution of the universe. According to this theory, the universe began as an extremely hot and dense state about 13.8 billion years ago and has been expanding ever since. The concept of the Big Bang emerged from the work of astronomers and physicists who observed that galaxies were moving away from one another in all directions. This led to the realization that the universe was not static but instead undergoing expansion. Extrapolating this backward in time, scientists hypothesized that if the universe is currently expanding, then in the distant past it must have been much smaller and denser.
The evidence supporting the Big Bang includes the observed cosmic microwave background radiation, which is the afterglow of the early universe. It was discovered in 1965 and is considered a relic of the hot, dense state that prevailed shortly after the initial expansion.
Over billions of years, the universe continued to evolve, with matter and energy forming galaxies, stars, and ultimately the intricate structures we observe today. The expansion of the universe continues to this day, driven by a mysterious force called dark energy, which is responsible for the accelerating expansion.
However,
many questions remain about what triggered the Big Bang and what occurred in
the initial moments of cosmic inflation. For instance, what caused the initial
singularity to expand? What was the nature of the universe before the Big Bang?
These are areas of active research and speculation in cosmology, and scientists
continue to explore various hypotheses and theories to further our
understanding of the universe's origins.
5.
Multiverse: A Tapestry of Parallel Universes?
The concept of a multiverse suggests the existence of multiple universes beyond our own. Different theories propose the idea that our universe is just one of many universes within a grander cosmic ensemble.
Another concept within the multiverse theory is the idea of a "bubble" or "pocket" multiverse. According to this idea, each universe exists as a separate bubble or pocket within a greater multiverse. These bubbles may have formed through processes such as cosmic inflation or through the collisions of higher-dimensional objects known as branes. Each bubble universe could have its own unique set of properties, effectively creating a diverse array of parallel worlds.
The
multiverse concept also encompasses the notion of parallel timelines and
alternate histories. It suggests that every decision, every event, could branch
off into different timelines, resulting in a multitude of parallel realities
where different choices were made and different outcomes unfolded. This idea
resonates with popular culture references to parallel universes and alternate
versions of ourselves.
While the
multiverse theory is still highly speculative, it has gained traction within
the scientific community. It offers a potential explanation for the fine-tuning
of our universe and opens up new avenues for exploration and understanding.
However, it also poses challenges, as the existence of parallel universes is
inherently difficult to test or observe directly.
6. The Fate
of the Universe: Expansion or Contraction?
The fate of
the universe is a topic of great scientific interest. Several possible
scenarios exist for its ultimate destiny. One possibility is the Big Crunch,
where the gravitational pull of matter in the universe eventually halts the
expansion and causes it to contract. Another possibility is the Big Freeze,
also known as the Heat Death of the Universe, where the universe continues to
expand indefinitely, becoming increasingly cold and devoid of usable energy.
The outcome depends on the amount of matter and energy present in the universe,
as well as the behavior of dark energy. Scientists are studying the expansion
rate of the universe using various techniques, such as measuring the distances
to distant galaxies and observing the cosmic microwave background, to determine
the amount of matter and energy it contains. Understanding the fate of the
universe provides valuable insights into its past, present, and potential
future.
7. Extraterrestrial Life: Are We Alone in the Universe?
The
question of whether life exists beyond Earth has captivated human curiosity for
centuries. Scientists are actively searching for signs of extraterrestrial life
in our own solar system and beyond. The discovery of potentially habitable
exoplanets, planets orbiting stars outside our solar system, has increased the
possibility of finding life elsewhere. Let's explore some of the Earth-like
planets that have been discovered and are considered potential candidates for
hosting life:
Kepler-452b:
Located about 1,400 light-years away, Kepler-452b is Earth's
"cousin." It is slightly larger than Earth and orbits within its
star's habitable zone, making it a tantalizing prospect for finding conditions
suitable for life.
Kepler-186f: Discovered by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope, Kepler-186f is the first Earth-sized exoplanet found within the habitable zone of its star. It is located approximately 500 light-years away and receives a similar amount of sunlight as Earth, making it an intriguing candidate for hosting life.
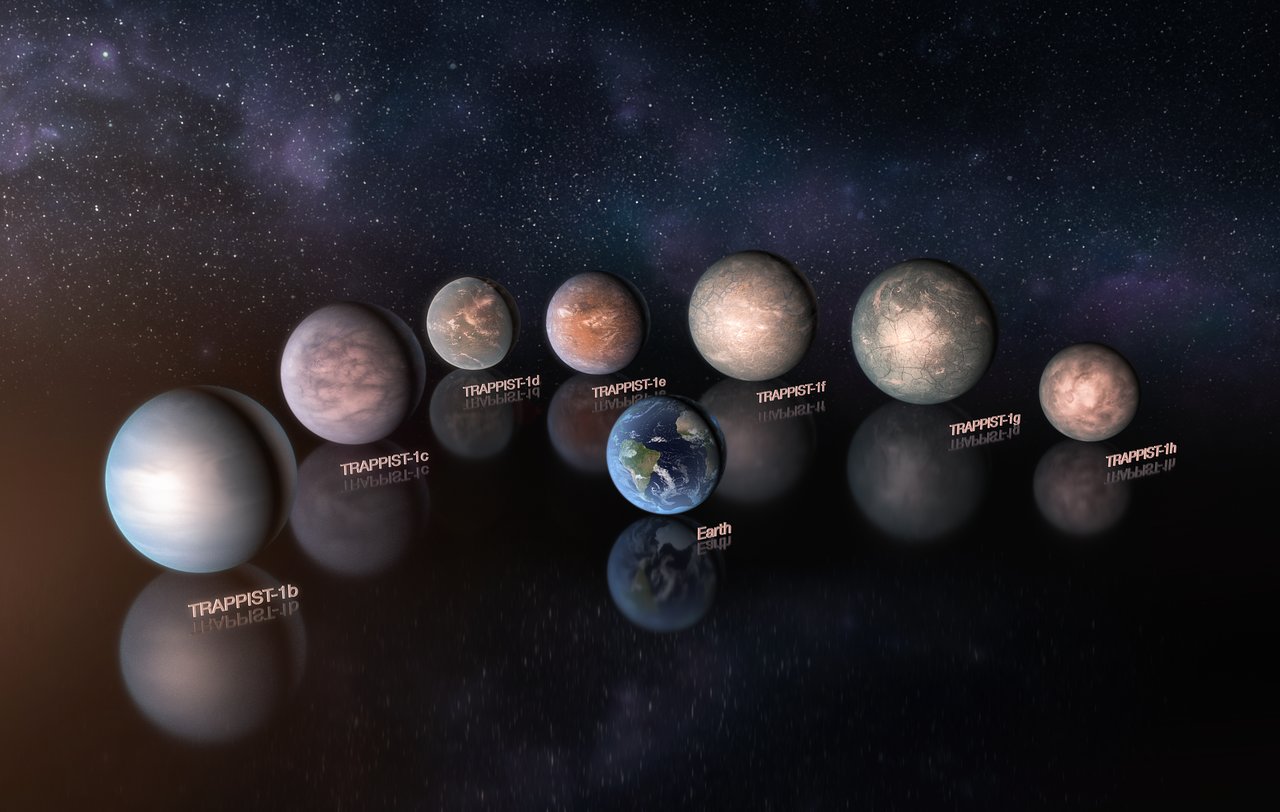
TRAPPIST-1 System: This system consists of seven Earth-sized planets orbiting the cool star TRAPPIST-1. Three of these planets, namely TRAPPIST-1e, f, and g, lie within the habitable zone. Scientists speculate that these planets may possess the right conditions for liquid water to exist on their surfaces, a crucial ingredient for life as we know it.
While no definitive evidence of extraterrestrial life has been found to date, the search continues, and each new discovery brings us closer to answering the age-old question of whether we are alone in the universe.
8. The
Mystery of Time: From its Direction to its Origin
But this explanation
only scratches the surface of the mystery. It doesn't unveil the underlying
cause or explain why time behaves this way. Scientists continue to delve
deeper, exploring the fundamental laws of physics and searching for a more
profound understanding of the nature of time.
Another
puzzling aspect of time is its origin. How did time come into existence? Did it
exist before the Big Bang, or did it emerge as a consequence of that cosmic
event? The answers to these questions lie in the realm of cosmology, where
theories and hypotheses intertwine. According to the Big Bang theory, the
universe originated from a singularity, a point of infinite density and
temperature. As the universe expanded, it brought forth the concept of time,
marking the beginning of our cosmic journey.
However,
understanding the precise origin of time remains elusive. It is an ongoing
quest for cosmologists and theoretical physicists to unravel the enigma of
time's birth and its connection to the early moments of the universe.
9. Quantum
Reality: The Bizarre World of the Subatomic
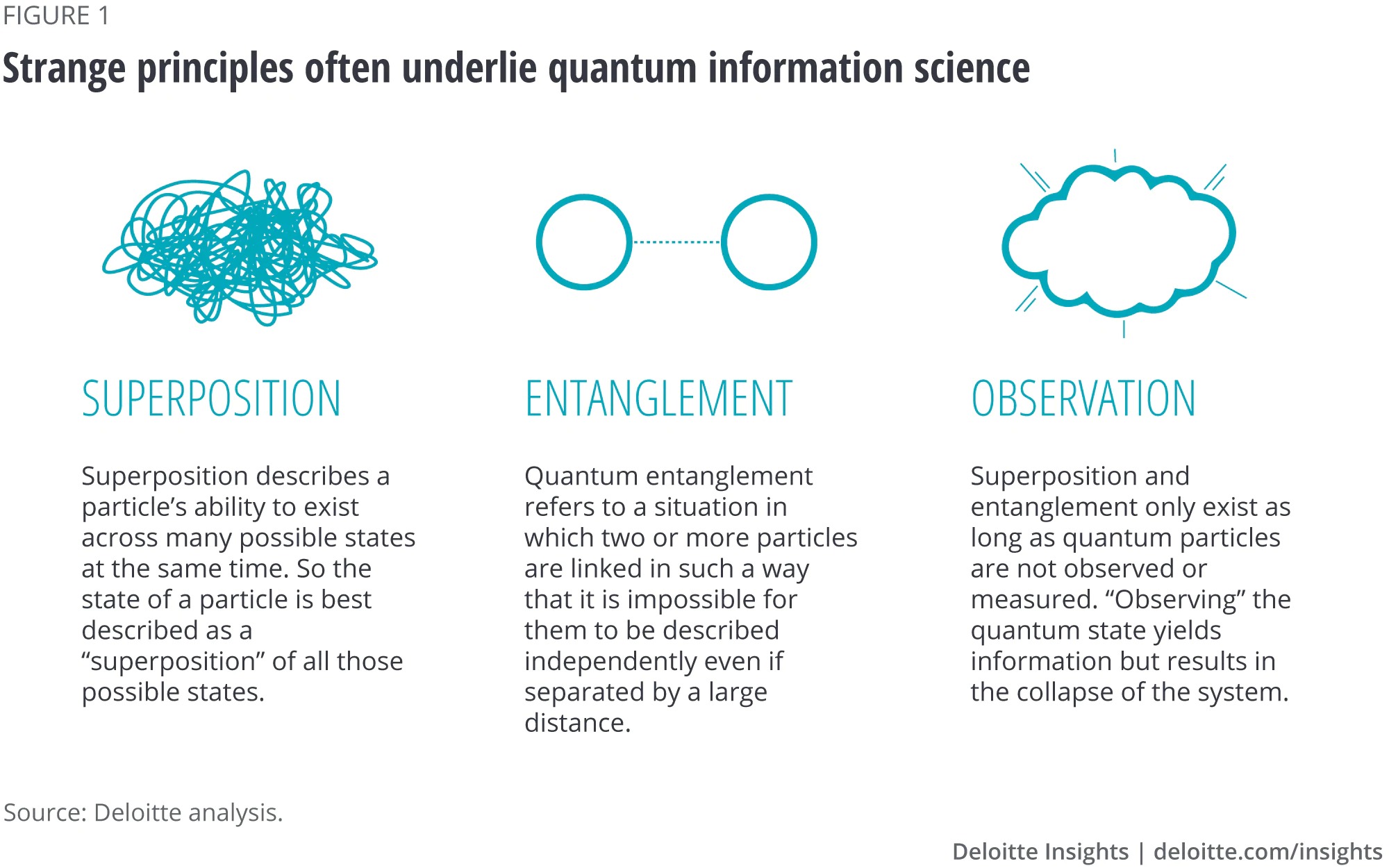
Quantum mechanics, the branch of physics that describes the behavior of particles at the subatomic level, introduces a world of profound strangeness and uncertainty. At the microscopic scale, where particles such as electrons and photons reign, the laws of classical physics no longer hold sway. Instead, the principles of quantum mechanics govern this bizarre domain, leading to a reality that defies our everyday intuitions. Quantum phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, challenge our intuitions and defy classical physics.
Superposition allows particles to exist in multiple states simultaneously, whereas entanglement creates correlations between particles that are maintained regardless of distance. Scientists are studying the quantum world to unravel its mysteries, understand the fundamental nature of reality, and develop technologies like quantum computing and quantum communication. The mysteries of quantum reality have led to various interpretations and theories, such as the Copenhagen interpretation, the many-worlds interpretation, and the pilot-wave theory, each offering different perspectives on how to understand and explain the peculiarities of quantum mechanics. However, the interpretation of quantum mechanics and its implications for our understanding of the universe's deepest workings remain subjects of ongoing debate and investigation.
10. Consciousness: The Enigma of Self-Awareness
Consciousness is the subjective experience of being aware and having a sense of self. It is one of the most profound yet mysterious aspects of human existence. At its core, consciousness refers to the subjective awareness of oneself and the external world. It encompasses our sensations, thoughts, emotions, and the intricate workings of our minds. But how does the physical matter of our brains give rise to this rich inner world? This is known as the hard problem of consciousness.
One prominent idea is that consciousness emerges from the complex interactions of neurons in our brains. According to this view, known as the neural correlates of consciousness, specific patterns of neural activity give rise to conscious experiences.
While consciousness
remains a profound mystery, advancements in neuroscience, cognitive science,
and philosophy have shed light on certain aspects of its workings. Research
exploring brain activity, neural networks, and cognitive processes has provided
valuable insights into the mechanisms that underlie our conscious experiences. For
example, research has shown that certain areas of the brain are active during
lucid dreaming, a state where a person is aware that they are dreaming and can
even control the content of their dreams. Additionally, studies have shown that
people with certain types of brain damage can lose their ability to be
self-aware, further emphasizing the important role of the brain in generating
consciousness.
However, a comprehensive and unified theory of consciousness still eludes us.
Each of these mysteries highlights the frontiers of scientific exploration and our desire to unravel the secrets of the universe. Scientists and researchers worldwide are dedicated to pushing the boundaries of knowledge, hoping to shed light on these enigmas and deepen our understanding of the cosmos we inhabit.








.jpg)











Comments
Post a Comment