Understanding and Managing Arthritis
Arthritis is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It refers to inflammation and pain in the joints, leading to reduced mobility and a significant impact on daily life. In this blog post, we will delve into the various aspects of arthritis, including its types, symptoms, treatment options, lifestyle modifications and coping mechanisms.
Understanding Arthritis
Arthritis
is a global health concern, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. Its
prevalence varies across countries and populations. According to the World
Health Organization (WHO), it is estimated that over 350 million people
worldwide suffer from arthritis, making it one of the leading causes of
disability.
In
Singapore, arthritis is also a significant health issue. According to a study
conducted by the Singapore Ministry of Health, it is estimated that
approximately 20% of the population in Singapore aged 18 years and above have
arthritis. This means that around 1 in 5 individuals in Singapore are affected
by this condition. The study further revealed that osteoarthritis is the most
common type of arthritis in Singapore, followed by rheumatoid arthritis and
gout.
The
prevalence of arthritis tends to increase with age, with a higher occurrence
among older adults. As Singapore's population ages, the burden of arthritis is
expected to grow. It is crucial to address this public health issue by promoting
awareness, early detection, and appropriate management strategies.
Arthritis is a complex condition influenced by various factors. It can result from joint wear and tear, autoimmune responses, or underlying medical conditions. The hallmark symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. Diagnosing arthritis often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory investigation.
Types of Arthritis
Arthritis
encompasses a range of conditions, each with its own characteristics, causes,
and treatment approaches. Understanding the different types of arthritis is
essential for effective management and targeted interventions. Let's explore
some of the most common types:
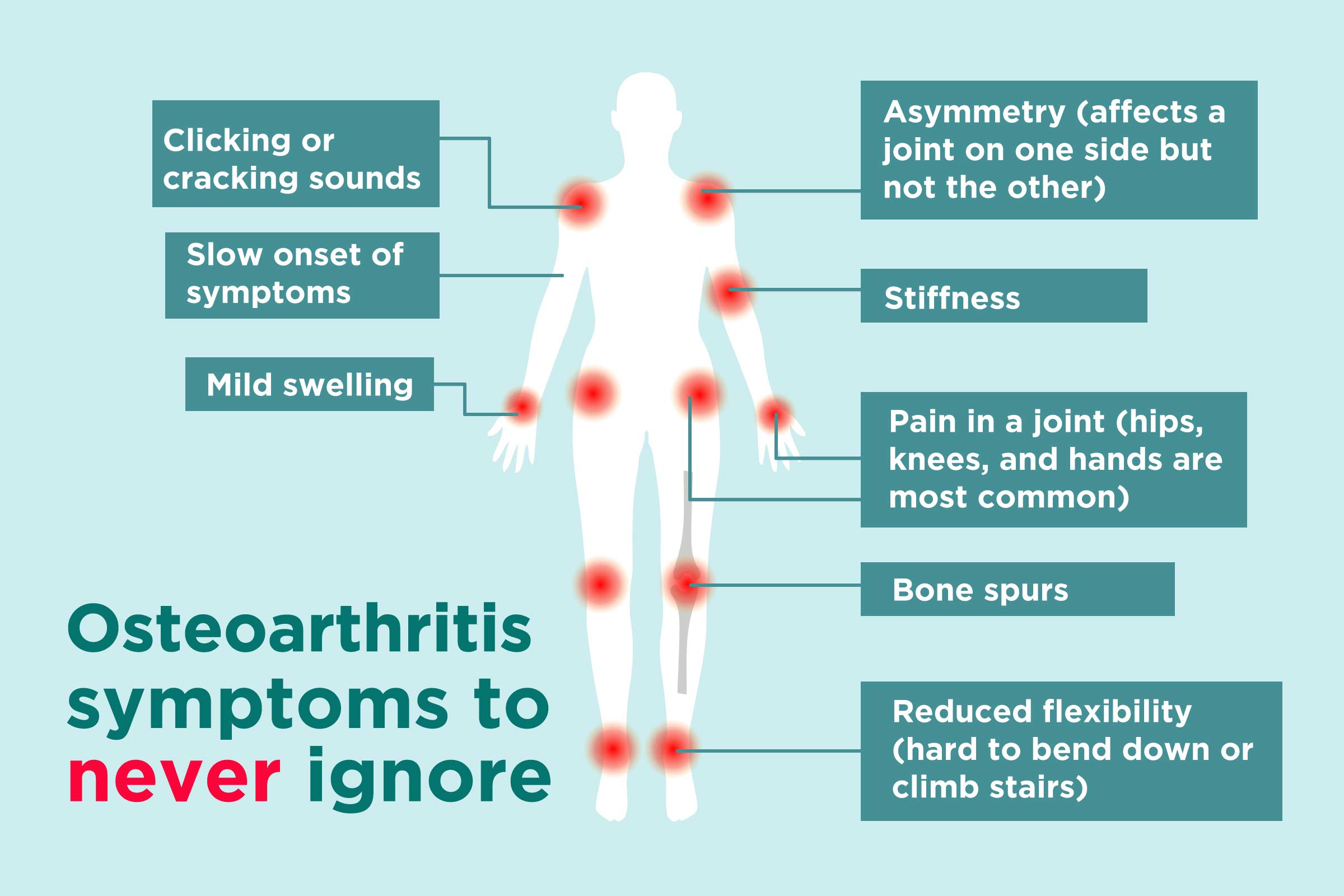
Osteoarthritis
(OA)
Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent form of arthritis, typically affecting older adults. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the joints wears down over time. This leads to joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Risk factors for OA include aging, obesity, joint injuries, and genetic factors. According to the Arthritis Foundation, more than 32.5 million adults in the United States have osteoarthritis[^1].
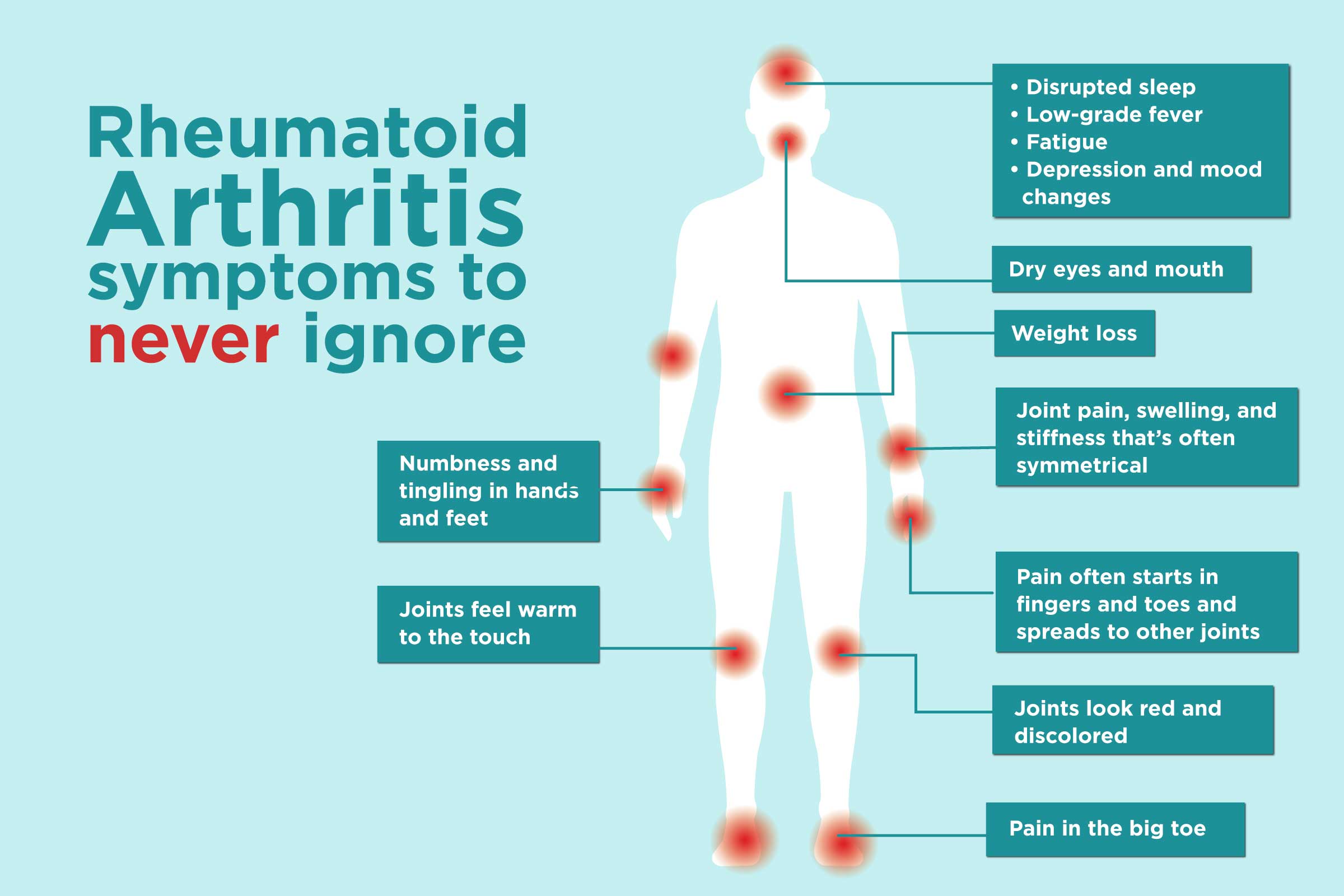
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic joint inflammation. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and joint deformity. RA can affect people of all ages, and it has a significant impact on daily life and overall well-being. Current estimates suggest that approximately 1.3 million people in the United States have rheumatoid arthritis[^2].
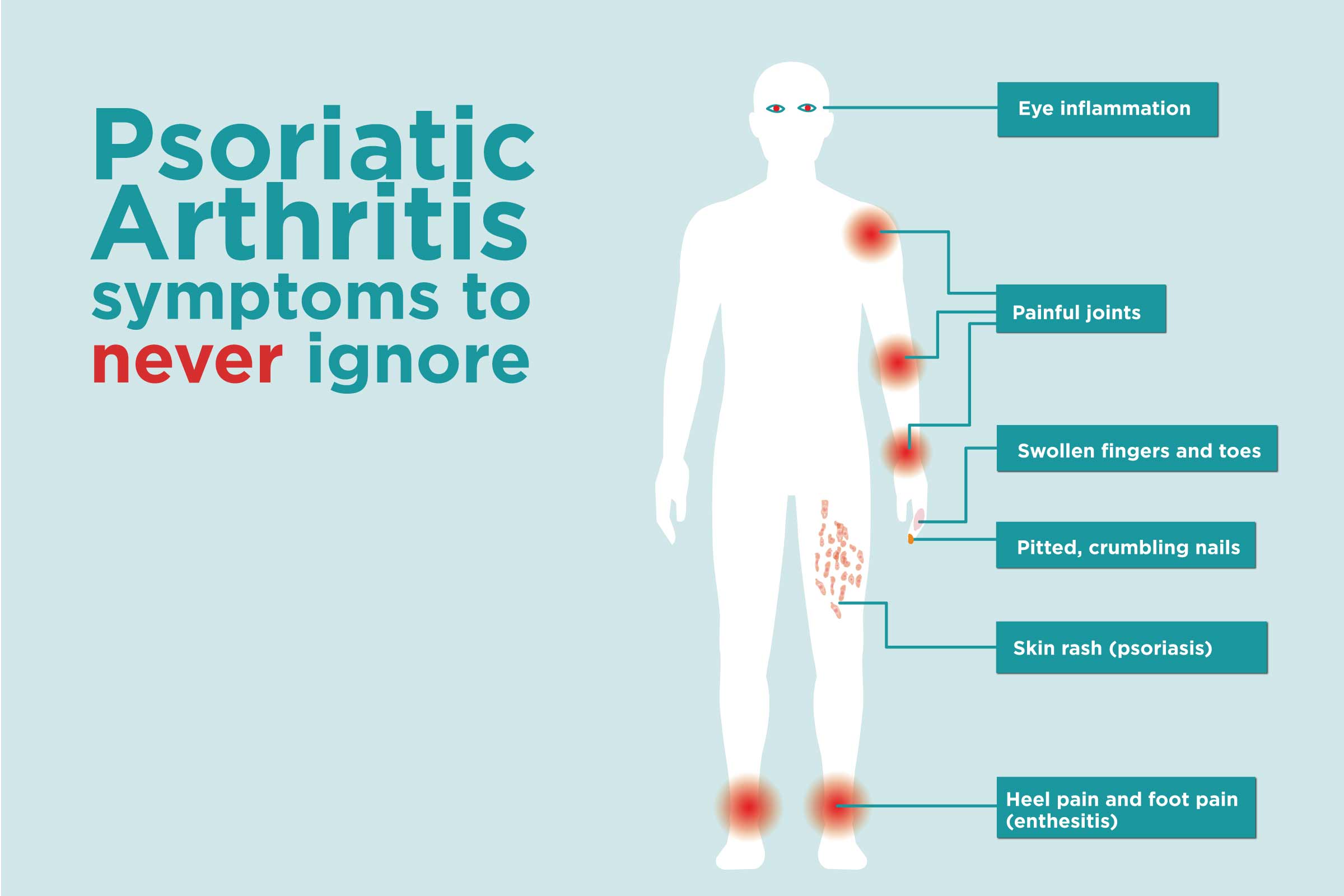
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
Psoriatic
arthritis is a type of arthritis that occurs in individuals with psoriasis, a
chronic skin condition. It causes joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, along
with skin manifestations such as red, scaly patches. PsA is an autoimmune
condition, and its exact cause is not fully understood. It affects
approximately 30% of individuals with psoriasis, according to the National
Psoriasis Foundation[^3].
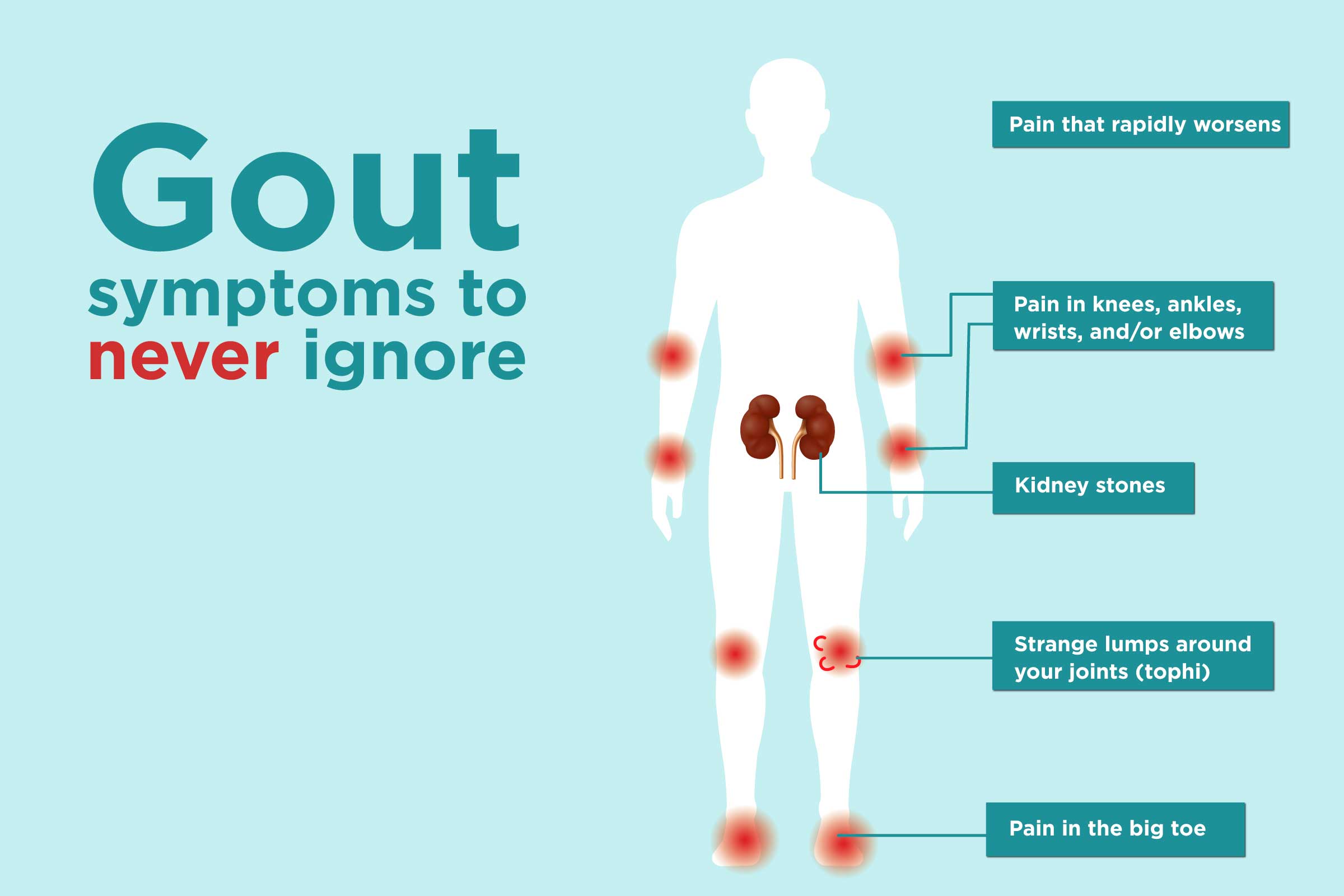
Gout
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that occurs due to the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It causes sudden and severe joint pain, typically affecting the big toe, although other joints can also be involved. Gout is associated with dietary factors, genetic predisposition, and certain medical conditions. It affects an estimated 9.2 million adults in the United States[^4].
Understanding the specific type of arthritis is crucial for tailored treatment and management strategies. Medical professionals, such as rheumatologists, play a vital role in diagnosing and providing appropriate care for individuals with arthritis. By seeking early intervention and adopting a multidisciplinary approach, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Treatment Options
Managing arthritis involves a multidimensional approach. Medications, including analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Physical therapy and targeted exercises can improve joint
function and strengthen surrounding muscles. Assistive devices like braces and
splints provide additional support. In some cases, surgical interventions may
be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints.
Lifestyle Modifications for Arthritis Management
In addition
to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing
arthritis symptoms and improving overall well-being. Making certain changes in
daily habits and adopting a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on
arthritis management. Consider incorporating the following lifestyle
modifications:
Weight
Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for individuals with arthritis, particularly for those with weight-bearing joint involvement such as knees and hips.
Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, leading to increased pain and reduced mobility. Losing weight, if necessary, can help alleviate joint pressure and improve symptoms. A balanced diet consisting of nutrient-rich foods and portion control, along with regular exercise, can support weight management efforts.
Exercise
and Physical Activity
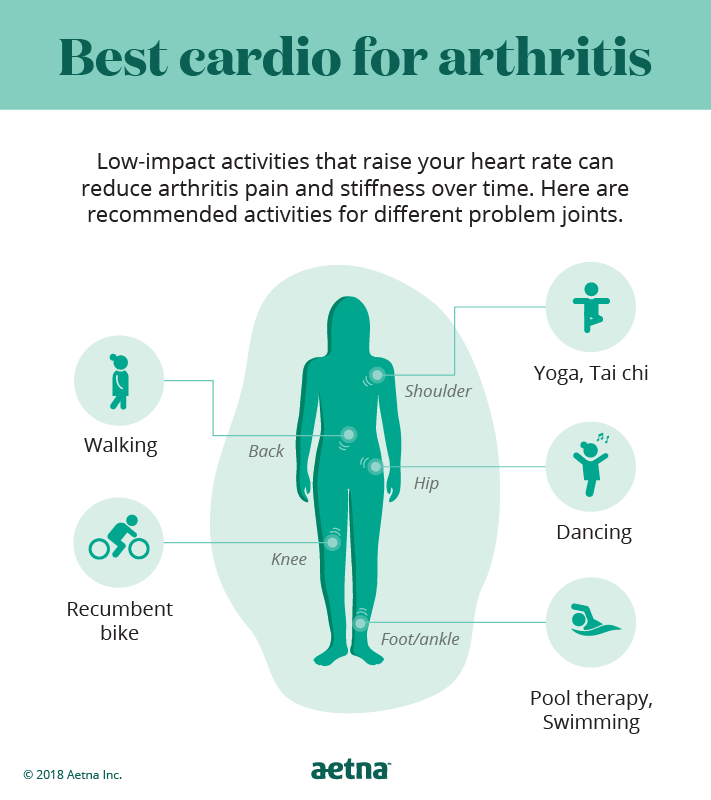
Regular physical activity is vital for managing arthritis symptoms and maintaining joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall physical function. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, cycling, and tai chi are generally well-tolerated by individuals with arthritis. These activities help improve joint range of motion, reduce stiffness, and strengthen supporting muscles. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional or a physical therapist to develop an exercise program tailored to your specific needs and capabilities.
Joint Protection
Protecting the joints from excessive strain and injury is essential for arthritis management. Simple modifications in daily activities can make a significant difference. Using ergonomic tools and aids with larger handles or grips can reduce stress on the joints and make tasks easier. For instance, using assistive devices like jar openers, long-handled reachers, or zipper pulls can minimize strain on the fingers and hands. It's also important to practice good posture and body mechanics during activities to avoid unnecessary joint stress.
Balanced Diet
Adopting a
balanced and nutritious diet can support overall health and help manage
arthritis symptoms. Include a variety of foods from different food groups,
focusing on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Certain foods, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fatty fish, walnuts,
chia seeds), may have anti-inflammatory properties and can be beneficial for
individuals with arthritis. Limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and
foods high in saturated and trans fats is recommended.
Stress Management
Stress can
exacerbate arthritis symptoms and contribute to increased pain and
inflammation. Finding effective stress management techniques, such as deep
breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies and activities
that bring joy and relaxation, can help reduce stress levels. It's important to
prioritize self-care and create a supportive environment that promotes
emotional well-being.
Fatigue is
common among individuals with arthritis, and quality sleep is crucial for
overall health and pain management. Establishing a regular sleep routine,
creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene can
contribute to better sleep quality. If arthritis-related pain interferes with
sleep, it may be helpful to explore strategies such as using pillows for joint
support or applying heat or cold therapy before bedtime.
Remember,
lifestyle modifications are an integral part of arthritis management.
Implementing these changes gradually and consistently can lead to improved
symptoms, enhanced joint function, and a better quality of life. It's essential
to work closely with healthcare professionals, such as rheumatologists and
occupational therapists, to develop a personalized approach to lifestyle
modifications that best suits your specific needs.
Coping with Arthritis
Living with arthritis can be physically and emotionally challenging. The condition often affects individuals' quality of life, leading to frustration, anxiety, and depression. Engaging in support groups or seeking professional counseling can provide a sense of community and emotional support. Developing coping strategies, such as maintaining a positive mindset, setting realistic goals, and pacing oneself, is crucial in managing the emotional impact of arthritis.
Conclusion
Arthritis
is a complex condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. By
understanding the different types of arthritis, recognizing the symptoms, and
seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively manage the condition
and improve their quality of life. Additionally, making lifestyle
modifications, practicing self-care, and seeking support can further enhance
well-being and empower individuals living with arthritis. Remember, early
diagnosis, professional guidance, and a proactive approach are key to
effectively managing arthritis and enjoying a fulfilling life.
Disclaimer: The information provided here is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Please consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stress-relief-strategies-5191480-RegFinal-2bb33f27b9e4402b88c4088177472460.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment