Fats: Friend or Foe? Unlocking the Truth about Dietary Fats
Are fats your worst enemy when it comes to maintaining a healthy diet? The answer might surprise you. For years, fats have been demonized and labeled as the primary culprits behind weight gain, heart disease, and a host of other health problems. But what if the truth about fats is more nuanced than we've been led to believe?
Understanding the impact of dietary fats on our health is crucial for making informed choices about our diets. Fats play a vital role in our bodies, contributing to energy production, nutrient absorption, cell function, and even brain health. Yet, navigating the world of dietary fats can be overwhelming, with countless myths and misconceptions clouding our judgment.In this blog post, we will debunk common fat myths, delve into the important functions of fats in our bodies, and guide you toward making wise choices about fat consumption. By unlocking the truth about dietary fats, you'll gain the knowledge necessary to embrace fats as valuable allies in your pursuit of a balanced and nourishing diet.
Debunking Fat Myths and Misconceptions
Myth #1: "All Fats Are Unhealthy"

For far too long, fats have been unfairly labeled as dietary villains. This misconception has had a profound impact on our dietary choices, leading many to adopt low-fat or fat-free diets in an attempt to improve their health. However, the truth is that not all fats are created equal, and demonizing fats as a whole is an oversimplification.
It's important to understand that there are different types of fats, each with its own effects on the body. Saturated and trans fats, commonly found in processed foods and fried snacks, have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other health issues. These are the fats we should be cautious about.
On the other hand, healthy fats can actually promote optimal health. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon, are associated with numerous health benefits. These fats can contribute to heart health, improve brain function, and support overall well-being.
Including healthy fats in your diet is not only delicious but also beneficial for your health. Avocado, known for its creamy texture, is packed with heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. Nuts, such as almonds, walnuts, and pistachios, offer a satisfying crunch while providing a good dose of healthy fats. Seeds like chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds are versatile additions to meals and snacks, offering a rich source of polyunsaturated fats. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are not only delicious but also deliver omega-3 fatty acids, which are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Myth #2: "Eating Fat Makes You Fat"

One of the most prevalent fat-related myths is the belief that consuming dietary fat automatically leads to weight gain. This misconception likely stems from a misunderstanding of the role of fat in our bodies and how weight management works.
While it's true that dietary fat is more calorie-dense compared to protein or carbohydrates, the key to weight management lies in the overall balance of calories consumed and expended. Regardless of the macronutrient, consuming an excess of calories can lead to weight gain.
Portion control plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy weight. Overconsumption of any macronutrient, including fat, can contribute to an energy surplus and potential weight gain. Choosing healthy fats and being mindful of portion sizes can support a balanced diet.

When incorporating fats into your meals, opt for healthier sources such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and nut butter. These foods provide essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and beneficial fatty acids, while adding flavor and satiety to your meals.
Practicing portion control and being mindful of your overall calorie intake can help you enjoy the benefits of dietary fats without overindulging.
Myth #3: "Low-Fat Diets Are Always Healthier"
The belief that cutting out fat would automatically lead to better health and weight management became ingrained in popular culture over the years.
The belief that cutting out fat would automatically lead to better health and weight management became ingrained in popular culture over the years.
However, it is important to note that fats play essential roles in our bodies, including providing a concentrated source of energy, supporting hormone production, insulating organs, and aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K).
Essential fatty acids, such as omega-3 and omega-6, cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from the diet. These fatty acids are crucial for brain function, heart health, and reducing inflammation. Restricting fat intake too severely can lead to a deficiency in these essential fatty acids, which may negatively impact overall health. Consuming a variety of healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish, can provide the body with essential nutrients while promoting overall well-being. Including moderate amounts of healthy fats in your diet can also enhance the taste and satisfaction of meals, making it easier to sustain a nutritious eating pattern.
The Role of Fats in the Body
Having dispel the myths of fats, let's look at the role of fats in the body.
Energy production and storage: One important role of fats in the body is to provide a concentrated source of energy. Fats are a highly efficient fuel source, offering more than twice the amount of energy compared to carbohydrates or proteins. They serve as a long-lasting and readily available source of fuel, especially during periods of prolonged physical activity or when carbohydrate stores are depleted. Excess dietary fat can also be stored in adipose tissue for future energy needs.
Nutrient absorption: Certain vitamins, known as fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), require the presence of dietary fats for optimal absorption. Fats act as carriers for these vitamins, allowing them to be absorbed and utilized by the body. Without sufficient fat intake, the absorption of these important vitamins may be compromised, leading to potential deficiencies.
Cell structure and function: Fats play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and function of cell membranes. The cell membrane, composed of a lipid bilayer, relies on fats for stability and flexibility. Additionally, fats provide insulation and protection to vital organs, cushioning them against physical impact.
Hormone production and regulation: Fats are essential for the production and regulation of hormones in the body. Hormones, such as estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, rely on cholesterol and other fats as building blocks. These hormones are involved in various physiological processes, including growth, reproduction, metabolism, and stress response. Research supports the role of fats in hormone production and regulation. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that dietary fat intake influenced the production of sex hormones, with low-fat diets resulting in lower testosterone levels in men (Muller et al., 2003). It's important to note that the quality and balance of fats in the diet are essential for optimal hormone production and regulation. Including healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish can support hormone synthesis and activity.
Brain health and cognitive function: The brain is composed of nearly 60% fat, making fats vital for brain health and cognitive function. Essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, play a critical role in brain development, functioning, and overall mental well-being. These fatty acids support neuron communication, enhance memory and learning, and help regulate mood and emotions.

By appreciating the diverse functions of fats, we can move beyond the myths and misconceptions surrounding dietary fats.
Understanding Healthy Fats and Making Informed Choices
Nutrient absorption: Certain vitamins, known as fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), require the presence of dietary fats for optimal absorption. Fats act as carriers for these vitamins, allowing them to be absorbed and utilized by the body. Without sufficient fat intake, the absorption of these important vitamins may be compromised, leading to potential deficiencies.
Cell structure and function: Fats play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and function of cell membranes. The cell membrane, composed of a lipid bilayer, relies on fats for stability and flexibility. Additionally, fats provide insulation and protection to vital organs, cushioning them against physical impact.
Hormone production and regulation: Fats are essential for the production and regulation of hormones in the body. Hormones, such as estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, rely on cholesterol and other fats as building blocks. These hormones are involved in various physiological processes, including growth, reproduction, metabolism, and stress response. Research supports the role of fats in hormone production and regulation. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that dietary fat intake influenced the production of sex hormones, with low-fat diets resulting in lower testosterone levels in men (Muller et al., 2003). It's important to note that the quality and balance of fats in the diet are essential for optimal hormone production and regulation. Including healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish can support hormone synthesis and activity.
Brain health and cognitive function: The brain is composed of nearly 60% fat, making fats vital for brain health and cognitive function. Essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, play a critical role in brain development, functioning, and overall mental well-being. These fatty acids support neuron communication, enhance memory and learning, and help regulate mood and emotions.

By appreciating the diverse functions of fats, we can move beyond the myths and misconceptions surrounding dietary fats.
Understanding Healthy Fats and Making Informed Choices
Understanding the different types of fats and making informed choices can significantly impact our health. Let's explore the saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Saturated fats are a type of fat that is typically solid at room temperature. They are commonly found in animal-based foods such as meat, poultry, butter, and full-fat dairy products. Some plant-based sources of saturated fats include coconut oil, palm oil, and cocoa butter. Consuming excessive amounts of saturated fats has been associated with an increased risk of heart disease and high cholesterol levels.
Monounsaturated fats are considered as a healthier type of fat compared to saturated fats. Monounsaturated fats are abundant in foods like olive oil, canola oil, avocados, and various nuts, including almonds, cashews, and peanuts. Incorporating monounsaturated fats into the diet has been associated with improved heart health, as they can help lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL cholesterol) and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Polyunsaturated fats include two essential fatty acids, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These fats play vital roles in the body and must be obtained from the diet as the body cannot produce them on its own. Polyunsaturated fats are found in fatty fish (such as salmon, trout, and mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and various plant-based oils like soybean oil, sunflower oil, and corn oil. Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and have been linked to heart health and brain function.
Saturated fats are a type of fat that is typically solid at room temperature. They are commonly found in animal-based foods such as meat, poultry, butter, and full-fat dairy products. Some plant-based sources of saturated fats include coconut oil, palm oil, and cocoa butter. Consuming excessive amounts of saturated fats has been associated with an increased risk of heart disease and high cholesterol levels.
Monounsaturated fats are considered as a healthier type of fat compared to saturated fats. Monounsaturated fats are abundant in foods like olive oil, canola oil, avocados, and various nuts, including almonds, cashews, and peanuts. Incorporating monounsaturated fats into the diet has been associated with improved heart health, as they can help lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL cholesterol) and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Polyunsaturated fats include two essential fatty acids, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These fats play vital roles in the body and must be obtained from the diet as the body cannot produce them on its own. Polyunsaturated fats are found in fatty fish (such as salmon, trout, and mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and various plant-based oils like soybean oil, sunflower oil, and corn oil. Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and have been linked to heart health and brain function.
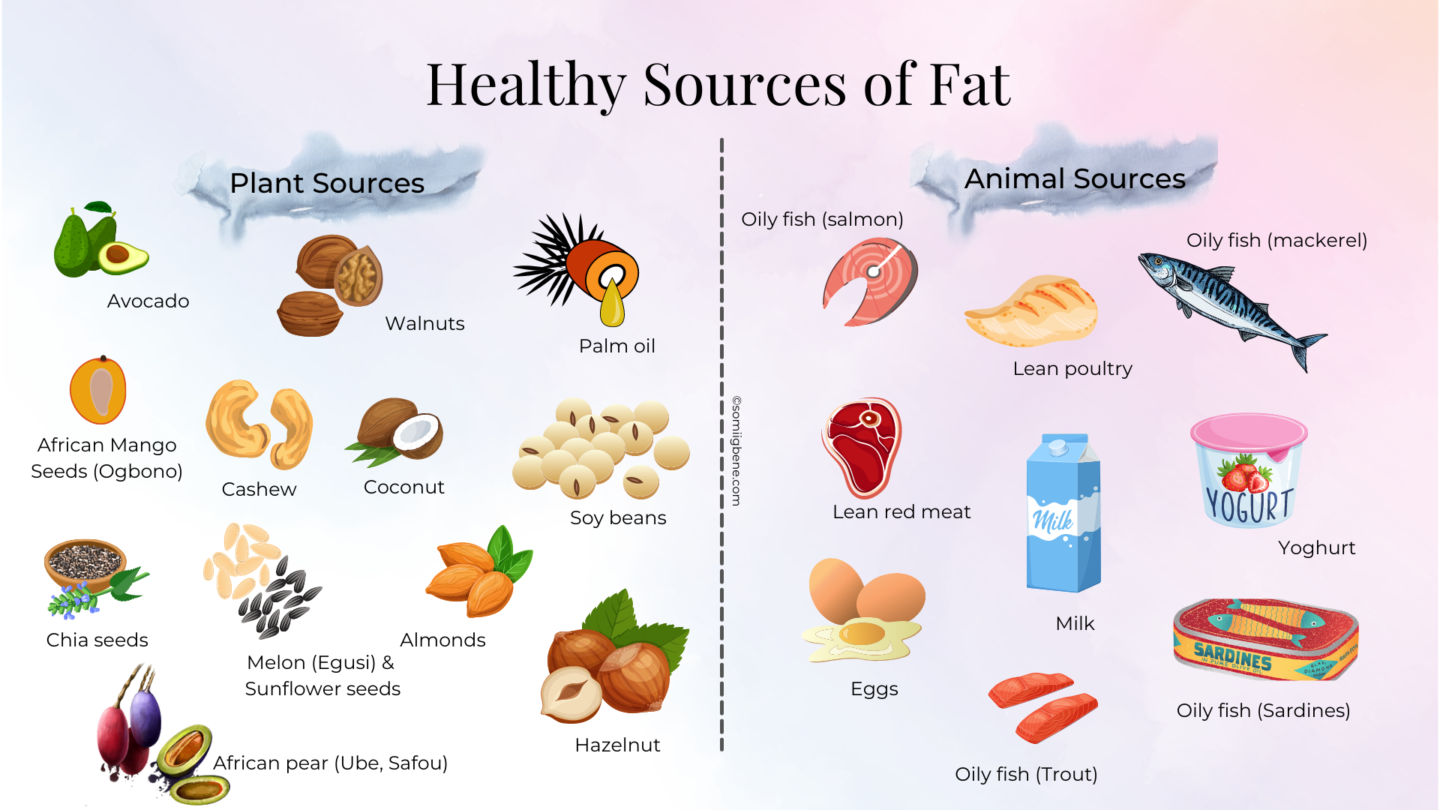
Sources of healthy fats from animal and plant-based foods
Healthy fats can be obtained from a variety of sources. Animal-based foods such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), lean meats, and eggs are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids and other beneficial fats. Plant-based sources include avocados, nuts (almonds, walnuts), seeds (chia seeds, flaxseeds), and oils like olive oil and coconut oil. Incorporating a mix of these foods into your diet can provide a range of healthy fats.
Recommendations for incorporating healthy fats into meals and snacks
To optimize your fat intake, aim for a balanced approach. Include a variety of healthy fats in your meals and snacks. For instance, drizzle olive oil over salads, use avocado as a spread or topping, snack on a handful of nuts, or add ground flaxseeds to smoothies or oatmeal. It's important to remember that while healthy fats offer numerous benefits, moderation is key, as fats are calorie-dense.
By understanding the different types of fats and their sources, you can make informed choices to incorporate healthy fats into your daily diet. Remember, a balanced approach that includes a mix of animal and plant-based sources will provide a wide array of nutrients and promote overall health.
Guidance for incorporating fats into a well-rounded, nutritious diet
When it comes to incorporating fats into a healthy diet, it's important to focus on choosing the right types of fats and practicing moderation. Here are some strategies and tips to help you make informed choices:
Limit unhealthy fats: Reduce your intake of unhealthy fats, such as saturated and trans fats. These fats can increase the risk of heart disease and other health problems. Minimize your consumption of fried foods, processed snacks, and high-fat baked goods, as they often contain these unhealthy fats. Read food labels and choose products with lower amounts of saturated and trans fats.
To optimize your fat intake, aim for a balanced approach. Include a variety of healthy fats in your meals and snacks. For instance, drizzle olive oil over salads, use avocado as a spread or topping, snack on a handful of nuts, or add ground flaxseeds to smoothies or oatmeal. It's important to remember that while healthy fats offer numerous benefits, moderation is key, as fats are calorie-dense.
By understanding the different types of fats and their sources, you can make informed choices to incorporate healthy fats into your daily diet. Remember, a balanced approach that includes a mix of animal and plant-based sources will provide a wide array of nutrients and promote overall health.
Guidance for incorporating fats into a well-rounded, nutritious diet
When it comes to incorporating fats into a healthy diet, it's important to focus on choosing the right types of fats and practicing moderation. Here are some strategies and tips to help you make informed choices:
Limit unhealthy fats: Reduce your intake of unhealthy fats, such as saturated and trans fats. These fats can increase the risk of heart disease and other health problems. Minimize your consumption of fried foods, processed snacks, and high-fat baked goods, as they often contain these unhealthy fats. Read food labels and choose products with lower amounts of saturated and trans fats.
Cook with healthier oils: Opt for healthier cooking oils like olive oil, canola oil, and avocado oil, which are rich in monounsaturated fats. These oils provide a delicious flavor to your dishes while offering potential health benefits. Use them for sautéing, roasting, or making salad dressings.
Embrace natural sources of fats: Include whole food sources of healthy fats in your diet. Avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon and trout are excellent choices. Avocados can be sliced and added to salads or used as a spread on toast. Nuts and seeds can be enjoyed as a snack or sprinkled on top of yogurt or salads. Fatty fish can be baked, grilled, or added to stir-fries for a boost of omega-3 fatty acids.
Practice portion control: While healthy fats provide important nutrients, they are still calorie-dense. Be mindful of portion sizes to maintain a balanced diet. A serving of healthy fats, such as nuts or seeds, is typically around a handful. Use measuring spoons or cups when cooking with oils to ensure you're using the recommended amount.
Be mindful of added fats: Minimize the use of added fats in cooking and meal preparation. Instead of frying, try baking, grilling, or steaming foods. When using oils for cooking, use them sparingly and consider using non-stick cookware to reduce the need for excessive added fats.
Experiment with herbs and spices: Enhance the flavor of your meals with herbs, spices, and citrus juices. This can help reduce the reliance on added fats for taste. Fresh herbs like basil, cilantro, and rosemary, along with spices such as turmeric, cumin, and paprika, can add depth and complexity to your dishes.
Read labels and make informed choices: When purchasing packaged foods, read the nutrition labels and ingredient lists. Look for products with healthier fat profiles, lower amounts of saturated and trans fats, and minimal or no added sugars. Opt for whole foods whenever possible, as they are naturally low in unhealthy fats.
By incorporating these strategies and tips into your daily routine, you can enjoy the benefits of healthy fats while maintaining a well-rounded, nutritious diet.
Remember, balance and moderation are key. Aim for a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, to support overall health and well-being.
Remember, balance and moderation are key. Aim for a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, to support overall health and well-being.
It's important to shift our perspective and view fats as friends when consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced diet. Fats are not something to be feared or avoided; they play essential roles in our overall health and well-being. By understanding the different types of fats and making informed choices, we can enjoy their benefits while maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
By making conscious choices and viewing fats as friends, we can enjoy the benefits they offer while nourishing our bodies and supporting our overall health. Remember, it's all about balance, moderation, and making informed choices that align with your unique dietary needs and preferences.
By making conscious choices and viewing fats as friends, we can enjoy the benefits they offer while nourishing our bodies and supporting our overall health. Remember, it's all about balance, moderation, and making informed choices that align with your unique dietary needs and preferences.














Comments
Post a Comment