Vitamin A: Illuminating the Path to Optimal Health and Vitality
They say that the eyes are the windows to the soul, but what if I told you that behind those windows lies a superhero nutrient known as Vitamin A? Yes, you heard it right! In the realm of essential vitamins, Vitamin A shines bright with its remarkable powers and profound impact on our overall health and vitality.
Join me as we explore the wonders of Vitamin A, from its pivotal role in vision health to its influence on immune function, cell growth, and so much more. Get ready to be amazed by the benefits this little powerhouse brings to the table, as we navigate through the vast landscapes of health and well-being.
What is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is vital for various bodily functions. It exists in two primary forms: retinol, found in animal-based foods, and beta-carotene, a plant-based precursor that converts to vitamin A in the body.
According to research published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, vitamin A plays a crucial role in supporting vision, promoting a healthy immune system, and aiding in cell growth and differentiation.
Functions and Benefits of Vitamin A
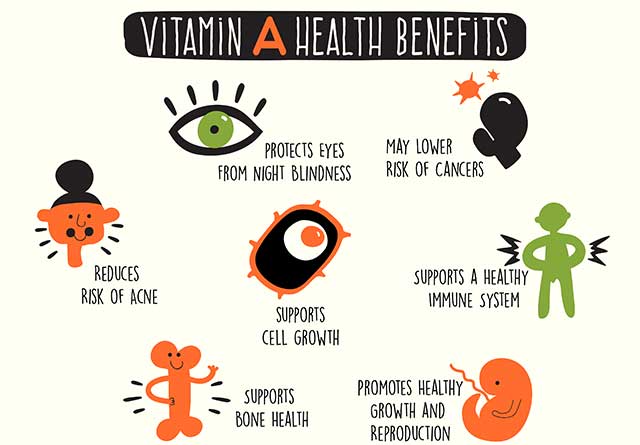
Vitamin A is well-known for its role in maintaining good vision. It is essential for the proper functioning of the retina and the adaptation of the eyes to changes in light. Research has shown that vitamin A deficiency can lead to night blindness and other eye-related issues (West et al., 2014).
Additionally, vitamin A is critical for a healthy immune system. It helps regulate the immune response and supports the integrity of mucosal surfaces, such as the lining of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that vitamin A plays a vital role in enhancing immune function and protecting against infections3. It helps maintain the integrity of the skin and mucosal barriers, which act as the first line of defense against pathogens (Stephensen, 2001).
Moreover, vitamin A contributes to the growth and development of cells and tissues throughout the body. It is involved in the formation and maintenance of healthy skin, as well as the growth and repair of bones and teeth. Research suggests that vitamin A promotes proper cell development and helps regulate gene expression (Duester, 2008). Research conducted by the Journal of Clinical Medicine highlights the importance of vitamin A in promoting healthy skin and preventing skin conditions like acne.
Vitamin A is also a potent antioxidant. It helps protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. This protective effect may contribute to reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as certain types of cancer (Higdon & Frei, 2003).
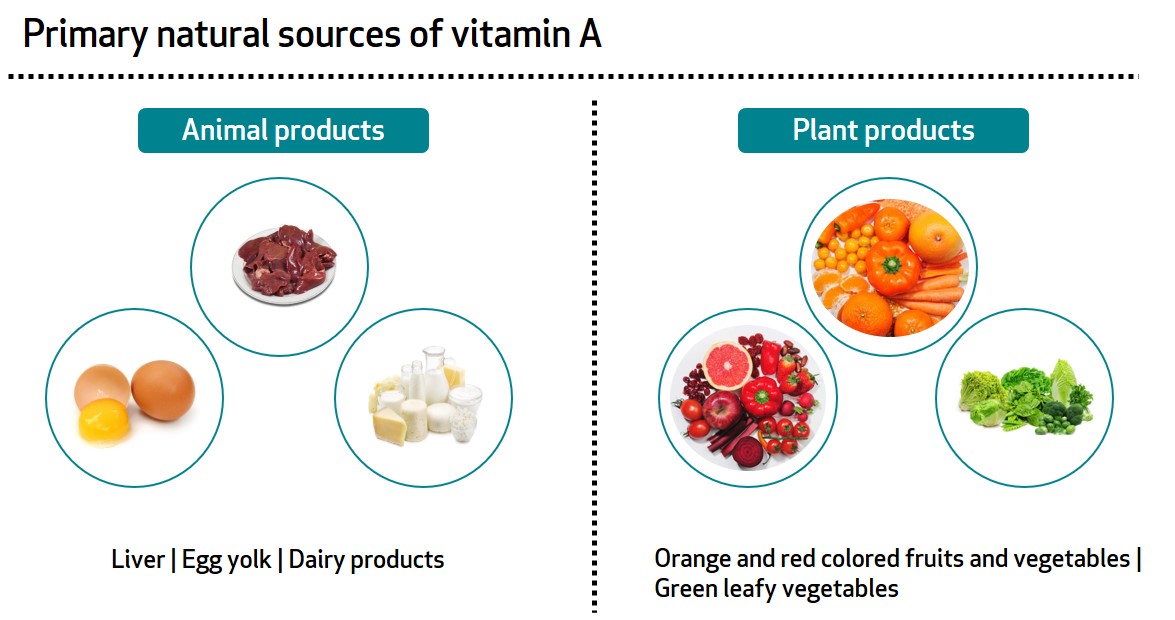
Best Sources of Vitamin A
To ensure an adequate intake of vitamin A, it is important to include a variety of foods in your diet that are rich in this essential nutrient. Animal-based sources of vitamin A include liver, fish oil, and dairy products, while plant-based sources include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and mangoes. According to a study published in the Journal of Food Science and Technology, consuming a diverse range of fruits and vegetables can significantly contribute to meeting your vitamin A needs5.
The recommended daily intake of vitamin A varies depending on age, gender, and life stage. The National Institutes of Health suggests that adult males should aim for 900 micrograms (mcg) of vitamin A per day, while adult females should aim for 700 mcg6. However, it's important to note that excessive intake of vitamin A can be harmful. High doses of vitamin A from supplements or medications should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid toxicity.
Vitamin A deficiency can have significant consequences for overall health and well-being. Here are some key areas where a deficiency in vitamin A can impact the body:
Vision Impairment: As mentioned earlier, vitamin A plays a critical role in maintaining healthy vision. A deficiency in vitamin A can lead to night blindness, where it becomes difficult to see in low light or at night. In severe cases, it can even cause permanent blindness. Research conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights that vitamin A deficiency is a leading cause of preventable blindness in children and increases the risk of eye infections1.
Weakened Immune System: Vitamin A is essential for proper immune function. A deficiency in vitamin A compromises the immune system's ability to fight off infections and increases the susceptibility to various illnesses. It can impair the body's response to pathogens and hinder the production of immune cells that help combat infections. This can lead to increased vulnerability to respiratory infections, diarrhea, and other infectious diseases2.
Delayed Growth and Development: Vitamin A is crucial for normal growth and development, especially in children. Insufficient intake of vitamin A can result in stunted growth, delayed bone development, and reduced overall physical development. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that vitamin A deficiency contributes to growth faltering in children and can have long-lasting effects on their health and well-being3.
Impaired Reproductive Health: Vitamin A plays a role in reproductive health for both men and women. In women, vitamin A deficiency can lead to complications during pregnancy, such as an increased risk of maternal mortality and adverse birth outcomes. In men, it can affect sperm production and quality, potentially leading to fertility issues. Research conducted by the WHO emphasizes the importance of adequate vitamin A intake for optimal reproductive health4. A deficiency during pregnancy can increase the risk of maternal complications and birth defects (Ramakrishnan et al., 2012).
By understanding the consequences of vitamin A deficiency, we can emphasize the importance of including vitamin A-rich foods in our diets and taking proactive measures to prevent deficiencies and their associated health risks.
Vitamin A is a vital nutrient that offers numerous benefits for your health and well-being. From supporting vision and immune function to promoting healthy skin and cell growth, it plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal bodily functions. By incorporating a diverse range of vitamin A-rich foods into your diet, you can ensure an adequate intake of this essential nutrient and reap its enlightening benefits.
Remember, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice on your dietary needs and vitamin A intake.
Conclusion
Vitamin A is a vital nutrient that offers numerous benefits for your health and well-being. From supporting vision and immune function to promoting healthy skin and cell growth, it plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal bodily functions. By incorporating a diverse range of vitamin A-rich foods into your diet, you can ensure an adequate intake of this essential nutrient and reap its enlightening benefits.
Remember, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice on your dietary needs and vitamin A intake.




Comments
Post a Comment