Bite by Bite: Building Resilience Against Cancer with Everyday Foods
Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While genetics and environmental factors play a significant role in its development, emerging research suggests that certain dietary choices can contribute to reducing the risk of cancer. A well-balanced and nutrient-rich diet is a cornerstone of good health, and specific foods have been studied for their potential to counteract cancer cells and support overall wellness. By incorporating these foods into your daily meals, you can take proactive steps towards safeguarding your health and well-being.
Understanding Cancer and Nutrition
Cancer, characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread
of abnormal cells, remains a leading cause of mortality across the globe.
However, scientific advancements have shed light on the potential impact of
nutrition on cancer prevention. The link between diet and cancer prevention
stems from the understanding that certain nutrients and bioactive compounds
found in foods can influence cellular processes and pathways associated with
tumor growth. While a healthy diet cannot guarantee complete immunity from cancer,
it can play a pivotal role in reducing the risk of its onset.
Foods with Potential Cancer-Fighting Properties
Numerous foods have been identified for their potential to counteract cancer cells due to their rich content of bioactive compounds. Here are some foods that have been studied for their potential cancer-fighting properties:
Cruciferous Vegetables
This is a family of nutrient-dense plants that includes broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, kale and cabbage, that have gained significant attention for their potential role in cancer prevention. These vegetables contain a unique class of bioactive compounds known as glucosinolates, which are broken down into biologically active compounds when chewed or digested. These compounds, such as sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol, have been extensively studied for their potential anti-cancer properties.
Sulforaphane has also been observed to stimulate the body's detoxification enzymes, helping to neutralize potentially harmful substances and carcinogens that can contribute to the initiation of cancer. Research suggests that sulforaphane may have protective effects against various types of cancer, including breast, prostate, lung, and colon cancers.
Indole-3-carbinol
can help regulate estrogen levels, which may be linked to a reduced risk of
hormone-related cancers, such as breast and ovarian cancers. Indole-3-carbinol
also exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which contribute to
its potential cancer-fighting effects. The unique combination of glucosinolates,
sulforaphane, and indole-3-carbinol, along with various vitamins, minerals, and
antioxidants found in cruciferous vegetables, creates a powerful synergy that
supports overall health and may help counteract cancer cells. These compounds
work together to enhance the body's defense mechanisms, target cancer cell
pathways, and promote a balanced immune response.
It's important to note that while cruciferous vegetables hold significant potential in cancer prevention, they are most effective when consumed as part of a diverse and balanced diet. Optimal preparation methods, such as lightly steaming or sautéing, can help preserve the beneficial compounds while making the vegetables more palatable.
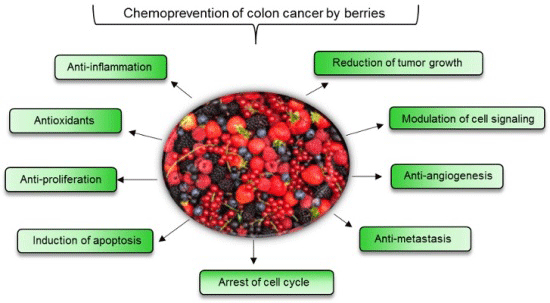
Berries
Berries, including blueberries, strawberries, raspberries,
and blackberries, are not only delicious additions to your diet but also potent
sources of antioxidants and phytochemicals that have been linked to potential
cancer-fighting properties. These vibrant fruits are rich in compounds like
anthocyanins, quercetin, resveratrol, and ellagic acid, which contribute to
their diverse health benefits.
Anthocyanins have the potential to neutralize harmful free
radicals that contribute to oxidative stress and damage to DNA, a hallmark of
cancer development.
Present in various berries, quercetin is a flavonoid with
anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It has shown promised in
inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and suppressing the formation of blood
vessels that nourish tumors. Quercetin also has the potential to enhance the
body's immune response and support DNA repair mechanisms.
Resveratrol is also found in berries like blueberries and
cranberries. This polyphenol has been studied for its potential anti-cancer
effects, including its ability to interfere with the progression of cancer
cells and induce apoptosis. Resveratrol may also play a role in reducing
inflammation and inhibiting the growth of blood vessels that supply tumors.
Ellagic acid has garnered attention for its potential to inhibit
the growth of cancer cells and promote apoptosis. It may also act as a
chemo-preventive agent by blocking the activation of carcinogens and enhancing
the detoxification of harmful substances.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes contain lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that has
been studied for its potential to reduce the risk of certain cancers,
especially prostate cancer. Lycopene is a carotenoid pigment that gives
tomatoes their characteristic red hue. This compound is a potent antioxidant,
meaning it can neutralize harmful free radicals in the body that contribute to
oxidative stress and damage to cells and DNA. Multiple studies have suggested
that lycopene may play a significant role in protecting cells from mutations
that can lead to cancer development. Research suggests that higher intake of
lycopene-rich foods, such as tomatoes, may be associated with a lower risk of
developing prostate cancer. Lycopene's mechanisms include inhibiting cell
proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and interfering with the signaling pathways
that promote cancer growth.
Interestingly, the cooking process can actually enhance the availability of lycopene in tomatoes. Heat breaks down the cell walls, making the lycopene more accessible. This means that products like tomato sauce and cooked tomato dishes may offer even greater concentrations of this valuable compound.
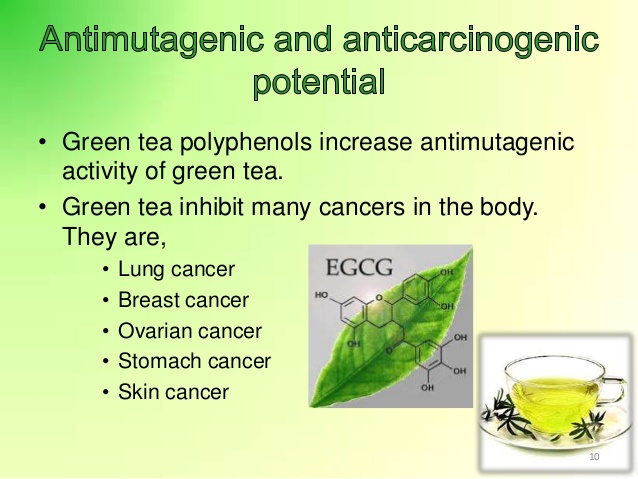
Green Tea
Green tea contains compounds called catechins that have shown anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects in some studies. The star player in green tea's cancer-fighting potential is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a catechin that accounts for a significant portion of the tea's antioxidant content.
EGCG has demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer effects in various studies. EGCG has the ability to interfere with cell signaling pathways that regulate cell growth and proliferation. This includes pathways that are crucial for cancer cell survival and division. By disrupting these pathways, EGCG may help prevent uncontrolled cell growth characteristic of cancer. Green tea catechins, particularly EGCG, have been found to induce apoptosis, which is a natural process of programmed cell death. In cancer cells, apoptosis is often disrupted, leading to uncontrolled cell growth. EGCG's ability to trigger apoptosis in cancer cells while sparing healthy cells is of particular interest in cancer research.
Another intriguing aspect of green tea's potential is its ability to inhibit angiogenesis, the process by which tumors create new blood vessels to support their growth. By preventing the formation of these blood vessels, green tea catechins can limit the tumor's access to nutrients and oxygen, slowing its progression.
Green tea's potential cancer-fighting properties are
believed to be enhanced when consumed with other health-promoting compounds.
For example, combining green tea with citrus fruits may improve the absorption
of catechins due to the presence of vitamin C.
Garlic
Garlic, revered for its distinctive flavor and aroma, has a
history dating back thousands of years for its medicinal properties. Beyond its
culinary uses, garlic contains sulfur-containing compounds, such as allicin,
that are believed to contribute to its potential health benefits, including its
potential to counteract cancer cells.
Allicin is a bioactive compound that is released when garlic is crushed or chopped. It's responsible for garlic's pungent smell and is also credited with many of its health-promoting effects. Sulfur compounds found in garlic are thought to contribute to its potential cancer-fighting properties.
Further, garlic's sulfur compounds act as antioxidants,
helping to neutralize free radicals that can damage cells and DNA.
Additionally, these compounds exhibit anti-inflammatory effects, reducing
chronic inflammation that can contribute to cancer development. Similar to green tea, garlic contains
compounds that may inhibit angiogenesis. By limiting the development of new
blood vessels around tumors, garlic's components could impede the tumor's
growth and metastasis.
Turmeric
Turmeric, a vibrant yellow spice commonly used in Indian and
Asian cuisines, contains a bioactive compound called curcumin that gives it
both its color and its potential health benefits. Curcumin has gained significant
attention in recent years due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and
potentially anticancer properties.
Curcumin's powerful anti-inflammatory properties help modulate the body's inflammatory response, potentially reducing the conditions that contribute to cancer development. Curcumin acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing harmful free radicals that can damage cells and DNA. This protection is essential in preventing DNA mutations that can lead to the formation of cancer cells. Curcumin is also able to promote apoptosis, which helps eliminate damaged and potentially cancerous cells.
While curcumin shows promise, its bioavailability can be a challenge. Consuming curcumin with black pepper, which contains piperine, may enhance its absorption. Additionally, curcumin supplements are available, but their effectiveness varies.
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens, such as spinach, kale, collard greens, and
Swiss chard, are well-known for their exceptional nutrient content and
potential health benefits.
Leafy greens are abundant in antioxidants, which are essential for combating oxidative stress and preventing DNA damage that can lead to cancer cell formation. Antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene work together to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
Some compounds found in leafy greens, like sulfur-containing
glucosinolates, have been shown to support the body's detoxification processes.
By assisting in the elimination of harmful substances, leafy greens can
potentially reduce the risk of cancer. Leafy greens are also rich in
phytochemicals, such as flavonoids and carotenoids, which have been linked to a
lower risk of various types of cancer. These compounds exert protective effects
by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells, promoting apoptosis, and reducing
inflammation.
High fiber content in leafy greens benefits gut health by promoting regular bowel movements and fostering a healthy gut microbiome. A well-functioning gut contributes to overall health, including a reduced risk of certain cancers. Leafy greens are exceptional sources of vitamin K, which plays a crucial role in bone health and blood clotting. Emerging research suggests that vitamin K might also contribute to reducing the risk of certain cancers, including prostate and liver cancers.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are nutrient-dense powerhouses that offer a wide array of health benefits, including potential cancer-fighting properties. Nuts and seeds like almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds provide healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants that are beneficial for health.
Nuts and seeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These fats are heart-protective and can contribute to overall well-being. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, are particularly noteworthy for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Nuts and seeds contain a variety of antioxidants, such as
vitamin E and selenium, that help combat oxidative stress and protect cells from
damage.
Phytochemicals present in nuts and seeds have been linked to
anticancer effects. For instance, lignans found in flaxseeds have shown
potential in inhibiting the growth of hormone-related cancers. Additionally,
phytosterols in nuts can interfere with cholesterol absorption and have been
associated with lower cancer risk.
Nuts and seeds are also rich in essential minerals like
magnesium, zinc, and selenium. These minerals play roles in immune function,
DNA repair, and other cellular processes that contribute to cancer prevention.
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout, are nutritional powerhouses that offer a wealth of health benefits, including their potential role in reducing the risk of cancer. These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to overall well-being and may have protective effects against certain types of cancer.
Fatty fish are renowned for their high content of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and have been linked to reduced inflammation, which is a factor in cancer development.
Omega-3 fatty acids may inhibit the growth of cancer cells by affecting various cellular pathways. They can influence cell proliferation, apoptosis (programmed cell death), and angiogenesis (formation of blood vessels that supply tumors). They also play a role in enhancing the body's immune response. A robust immune system is essential for recognizing and eliminating abnormal cells, including potentially cancerous ones.
Fatty fish are also excellent sources of vitamin D, a nutrient that plays a crucial role in immune function, bone health, and regulation of cell growth. Adequate vitamin D levels have been associated with a reduced risk of certain cancers.
Incorporating Cancer-Fighting Foods into Your Daily Meals
Integrating cancer-fighting foods into your daily meals is a powerful way to promote overall health and reduce the risk of cancer. While each food group offers unique benefits, creating a well-rounded and diverse diet that includes a variety of these foods can optimize their potential effects. Here are some practical tips to help you incorporate these foods seamlessly into your meals:
1. Start Your Day Right
Breakfast Boost: Begin your day with a bowl of whole-grain
oatmeal topped with a mix of berries, nuts, and seeds. This combination
provides fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats to fuel your morning.
2. Vibrant Lunch Options
Leafy Greens Salad: Create a colorful salad with a base of
leafy greens like spinach, kale, or arugula. Add an assortment of colorful
vegetables, such as bell peppers, tomatoes, and broccoli. Incorporate lean
protein sources like grilled chicken, chickpeas, or tofu.
Fatty Fish Delight: Enjoy a salmon or mackerel wrap with
whole-grain tortillas. Load it up with mixed greens, avocado slices, and a
drizzle of olive oil-based dressing for a satisfying and nutrient-rich lunch.
3. Wholesome Dinners
Rainbow Stir-Fry: Prepare a vegetable stir-fry with a medley
of cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts. Add
lean protein sources like tofu or lean chicken, and serve it over brown rice or
quinoa.
Nut and Fruit Mix: Keep a variety of nuts and seeds on hand for a quick and nutritious snack. Pair them with a small serving of fresh fruits like berries or apple slices.
Greek Yogurt Parfait: Enjoy a parfait with Greek yogurt, topped with a mix of berries, a drizzle of honey, and a sprinkle of chopped nuts for added texture and flavor.
Green Tea Elixir: Substitute sugary beverages with green
tea, which contains beneficial compounds that may support your health goals.
Opt for unsweetened varieties to maximize the benefits.
6. Mindful Cooking Techniques
Grill and Roast: Utilize grilling and roasting methods to
bring out the flavors of vegetables, lean proteins, and fatty fish while
preserving their nutritional content.
Steaming and Stir-Frying: These techniques help retain the vibrant colors and nutrients of vegetables without excessive cooking.
7. Plan Ahead
Meal Prep: Prepare batches of cancer-fighting foods in
advance. Wash and chop vegetables, portion out nuts and seeds, and marinate
lean proteins for easy access during busy days.
8. Experiment and Explore
Culinary Adventures: Embrace new recipes and ingredients to
keep your meals exciting and varied. Experiment with different combinations of
cancer-fighting foods to discover your favorite flavors.
Remember that no single food or meal plan can guarantee the
prevention of cancer. However, adopting a diet rich in cancer-fighting foods
can contribute to overall health and well-being. Combine these dietary choices
with other healthy habits, such as staying physically active and avoiding tobacco,
to create a comprehensive approach to reducing your risk of cancer and
promoting optimal health.
Cultivating a Cancer-Fighting Diet: Nourishing Your Health from Within
In the journey to promote wellness and reduce the risk of
cancer, the power of nutrition cannot be overstated. The foods we choose to
include in our daily meals can have a profound impact on our health, bolstering
our body's natural defenses and aiding in the fight against cancer cells. By
incorporating a variety of cancer-fighting foods, we can harness the potential
benefits of antioxidants, phytochemicals, vitamins, and minerals that work
synergistically to support our well-being.
As you embark on your journey to nourish your body and protect your health, take pleasure in the process of exploring new flavors, experimenting with recipes, and making mindful food choices.
Celebrate the vibrant colors, textures, and tastes that nature provides in the form of cancer-fighting foods. Your plate becomes a canvas upon which you paint a masterpiece of wellness, with every bite contributing to the masterpiece of your life's journey toward vibrant health and vitality.


































Comments
Post a Comment