Erectile Dysfunction: Breaking the Silence and Seeking Solutions
Erectile
dysfunction, often abbreviated as ED, is a common condition that affects men of
all ages. While it can be a sensitive and challenging topic to discuss, it's essential
to address it openly and seek help when needed. In this comprehensive guide,
we'll explore what ED is, its causes, and effective strategies for managing it.
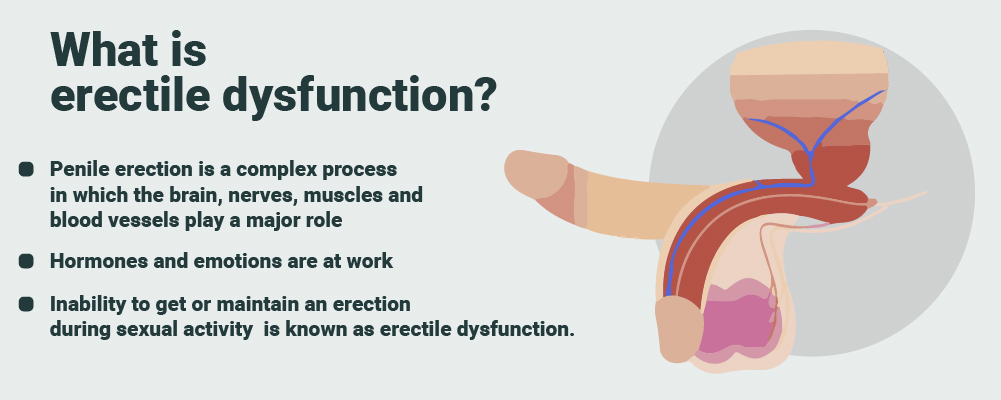
What Is Erectile
Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction, also known as impotence, refers to the consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. It's important to understand the physiology of an erection to grasp how ED functions. The following is an explanation on how an erection occurs.
How an Erection
Occurs
Desire and Stimulation: It all begins with sexual desire or arousal, often triggered by physical, emotional, or visual stimuli.
Brain Signals: When
the brain perceives sexual stimuli or fantasies, it sends signals to the nerves
in the pelvic region, specifically the sacral nerves.
Relaxation of Blood
Vessels: These signals lead to the release of a neurotransmitter called nitric
oxide (NO) in the erectile tissues of the penis. NO relaxes the smooth muscle
cells lining the blood vessels in the penis, allowing them to dilate or expand.
Increased Blood
Flow: As the smooth muscle cells relax, blood flow to the penis increases
significantly. This surge of blood fills the two cylindrical chambers in the
penis, known as the corpora cavernosa.
Compression of
Veins: Simultaneously, the veins that usually carry blood away from the penis
become compressed. This compression traps blood within the corpora cavernosa,
maintaining the erection.
Rigidity and
Elevation: The increased blood flow and trapped blood cause the penis to become
rigid and erect. This is essential for sexual penetration and intercourse.
Sustaining the
Erection: The erection is maintained as long as sexual arousal and stimulation
continue. Once sexual activity is complete or arousal diminishes, the brain
signals a return to the flaccid state.
An erection occurs
when blood flow to the penis increases, filling the erectile tissues. Nerves,
blood vessels, hormones, and psychological factors all play a role in this
complex process. ED can occur when any of these components are disrupted.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile
dysfunction (ED) can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms may differ from
one individual to another. Understanding these symptoms is essential for
recognizing when to seek help. Here are some common signs and symptoms of ED:
Difficulty
Achieving an Erection: One of the primary indicators of ED is the consistent
difficulty in achieving an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse.
Difficulty
Maintaining an Erection: Some individuals with ED can achieve an initial
erection but struggle to maintain it long enough for satisfactory sexual
activity.
Reduced Sexual
Desire: While ED primarily pertains to the physical ability to attain and
sustain an erection, it can also impact sexual desire or libido. Individuals
with ED may experience a decrease in their interest in sexual activity.
Softer Erections:
Erections may not be as firm as they once were, which can affect sexual
performance and satisfaction.
Premature
Ejaculation: In some cases, ED may coexist with premature ejaculation, where
ejaculation occurs too quickly, often before or shortly after achieving an
erection.
Delayed
Ejaculation: Conversely, ED may also be associated with difficulty ejaculating
or experiencing a delay in achieving orgasm.
Psychological
Distress: ED can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or low self-esteem.
Individuals may worry about their ability to satisfy their partner or may avoid
sexual encounters altogether.
It's essential to note that occasional difficulties with erections are common and may not necessarily indicate ED. However, when these issues become persistent and affect one's overall well-being or relationships, it's advisable to consult a healthcare provider.
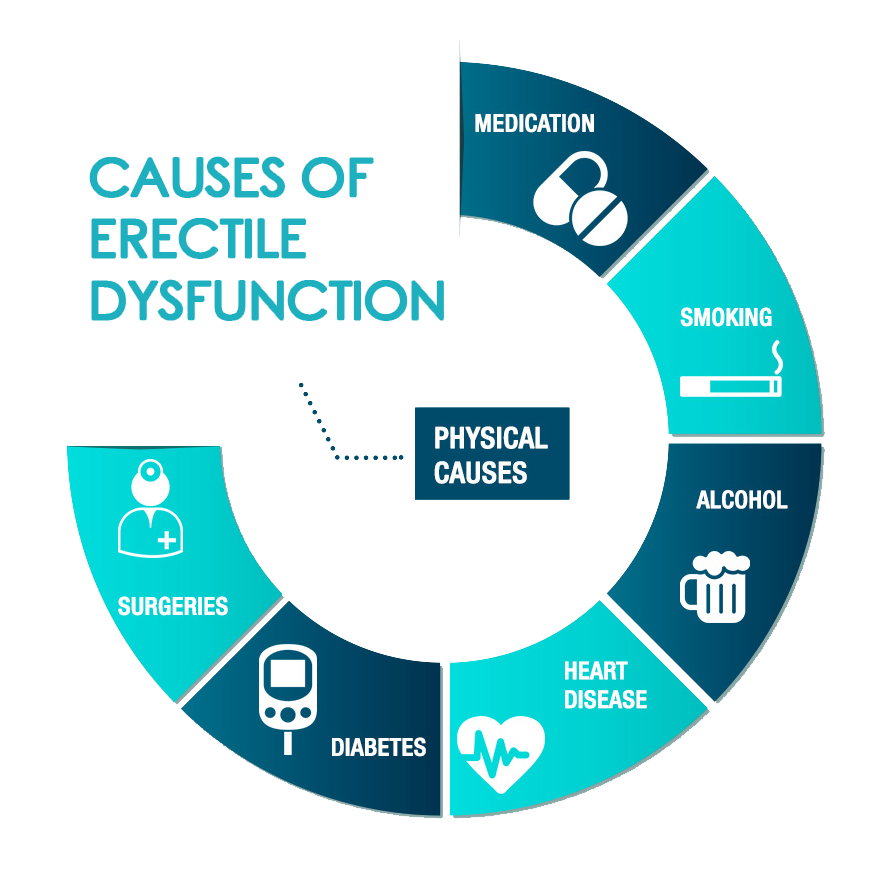
Causes of
Erectile Dysfunction
Understanding the
causes of ED is crucial for effective management. It can stem from various
factors, including:
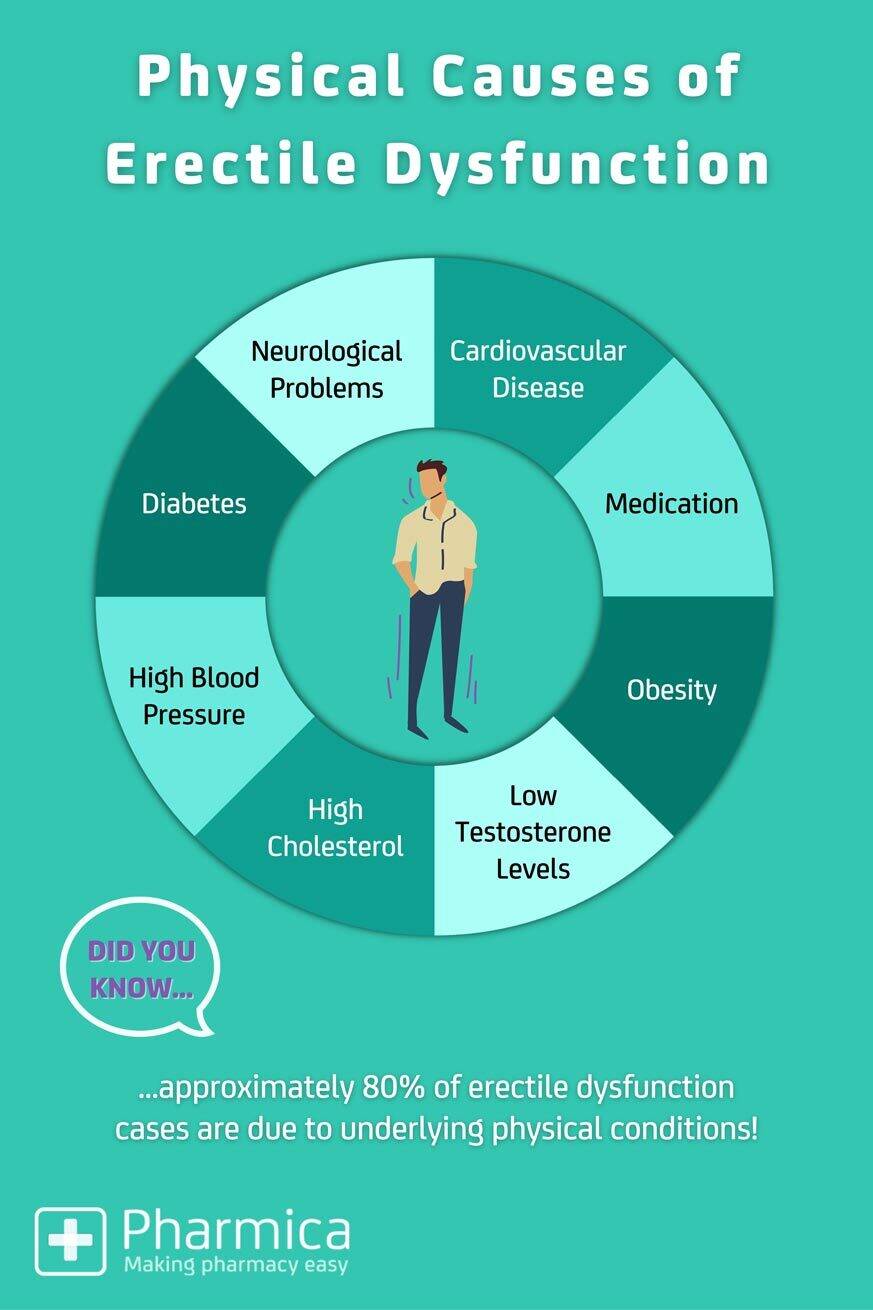
Physical Causes.
These include
conditions like diabetes, heart disease, obesity, high blood pressure, and
hormonal imbalances. Physical causes are
normally health-related like vascular Issues whereby blood flow plays a crucial
role in achieving and maintaining an erection.
Various vascular problems can disrupt this process, including:
Atherosclerosis:
This condition involves the buildup of plaque in the arteries that reduce blood
flow. It can affect the penile arteries
and hinder the ability to achieve a firm erection.
Hypertension (High
Blood Pressure): Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage blood vessels and
reduce blood flow to the penis. Medications used to manage hypertension can
also contribute to ED in some cases.
Peripheral Artery
Disease (PAD): PAD narrows the arteries, limiting blood flow to the
extremities, including the penis.
Neurological
Disorders whereby the nervous system that play a crucial role in transmitting
signals that trigger erections are impaired. Conditions affecting nerves can
lead to ED:
Diabetes: High
blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels responsible for
erectile function, making ED more likely in individuals with diabetes.
Multiple Sclerosis
(MS): MS can disrupt the communication between the brain and the genital area,
leading to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection.
Spinal Cord Injury:
Damage to the spinal cord can interrupt the transmission of nerve signals
needed for erections.
Hormonal Imbalances,
particularly testosterone play a role in sexual function and an imbalance can
cause ED:
Low Testosterone: A
decrease in testosterone levels, often associated with aging, can contribute to
ED. Testosterone is essential for libido and the maintenance of erectile
function.
Certain medications
and substance abuse can also lead to ED:
Medications: Some
drugs, including certain antidepressants, antihypertensives, and sedatives, can
have side effects that impact sexual function.
Substance Abuse:
Excessive alcohol consumption, recreational drug use, and smoking can
contribute to ED by affecting blood flow, nerves, and overall health.
Finally, anatomical or structural issues in the penis can lead to ED. For example, Peyronie's Disease involves the development of scar tissue in the penis, causing curvature and potential difficulties with erections.
Psychological Factors
While physical causes often take the spotlight in discussions about ED, it's essential not to underestimate the significant role that psychological factors can play in this condition. Psychological factors can either contribute to ED or exacerbate its effects. Let's delve deeper into this aspect, backed by research evidence.
1. Stress and
Anxiety
Stress and anxiety
are among the most common psychological factors associated with ED. Research
studies have shown that chronic stress and anxiety can lead to the release of
stress hormones like cortisol, which, over time, can impact sexual function and
lead to ED. High-stress levels can also affect sexual desire and performance.
2. Depression
Depression is a complex
psychological condition that can intersect with ED in various ways. A study
published in the "Journal of Sexual Medicine" found that men with
depression were more likely to experience ED. Depression can lead to changes in
brain chemistry and neurotransmitter imbalances that affect sexual function.
3. Performance
Anxiety
The fear of not
being able to perform sexually, often referred to as performance anxiety, can
become a self-fulfilling prophecy. A study in the "Journal of Sex &
Marital Therapy" highlighted the negative impact of performance anxiety on
erectile function. Overthinking and worrying about sexual performance can lead
to tension, stress, and ED.
4. Relationship
Issues
Problems within a
relationship, such as communication difficulties, unresolved conflicts, or
emotional distance, can contribute to ED. A study published in "Sexual
Medicine Reviews" emphasized the intricate link between relationship
satisfaction and sexual function. Open communication and addressing relationship
issues can be essential for overcoming ED caused by these factors.
5. Body Image
Concerns
Body image issues,
often associated with low self-esteem, can also impact sexual confidence and
lead to ED. A study in the "Journal of Sexual Medicine" revealed that
body image concerns were linked to ED in young men. Promoting a positive body
image and self-esteem can be beneficial for those affected.
Lifestyle Factors
Making healthy
lifestyle choices is essential for managing ED. Quitting smoking, moderating
alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical
activity can all improve sexual function.
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in the development and management of erectile dysfunction (ED). By understanding how these factors can influence sexual health, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk or improve their condition. Let's explore these lifestyle factors in more detail, supported by research evidence.
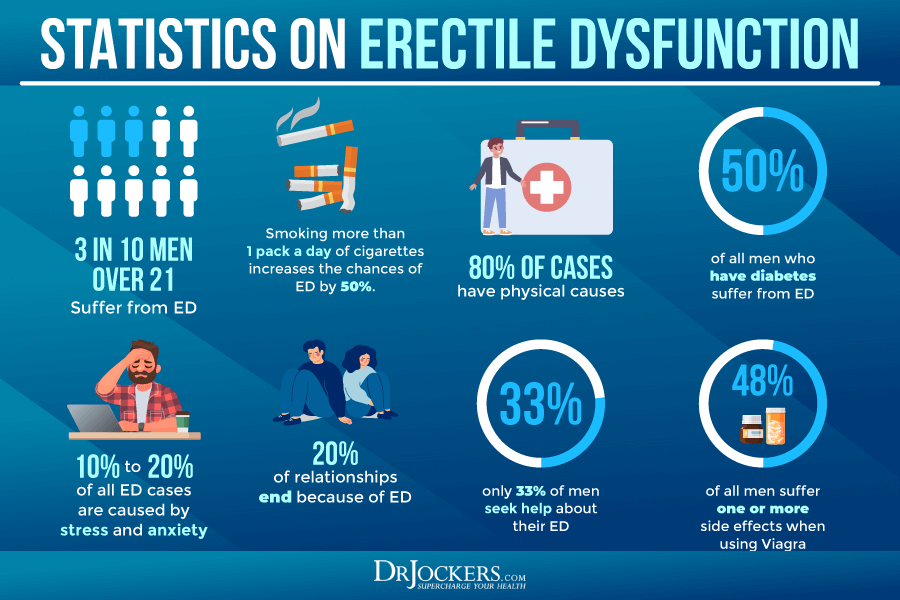
1. Smoking and
Tobacco Use
Smoking and the use
of tobacco products are well-documented risk factors for ED. Research has shown
that nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the penis, and
impairs erectile function. A study published in the "Journal of Sexual
Medicine" found a strong association between smoking and ED. Quitting
smoking can lead to significant improvements in erectile function.
2. Excessive
Alcohol Consumption
While moderate
alcohol consumption may not have a significant impact on sexual function,
excessive drinking can lead to ED. Chronic alcohol abuse can disrupt the
hormonal balance and impair the nervous system, both of which are essential for
healthy sexual function. Limiting alcohol intake is advisable for those
concerned about ED.
3. Poor Diet and
Obesity
A diet high in
saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods can contribute to obesity,
diabetes, and cardiovascular issues—conditions strongly linked to ED.
Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet can reduce the risk of ED.
Additionally, research has shown that the Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits,
vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can have a positive impact on
sexual function.
4. Lack of Physical
Activity
A sedentary
lifestyle can lead to obesity and contribute to ED. Regular physical activity
improves blood circulation, helps maintain a healthy weight, and promotes
overall cardiovascular health, all of which are crucial for erectile function.
Engaging in regular exercise can be an effective strategy for preventing or
managing ED.
5. Sleep Disorders
Sleep plays a vital
role in sexual health. Conditions like sleep apnea and insomnia can disrupt
hormonal balance and impair sexual function. Research has shown that addressing
sleep disorders can lead to improvements in erectile function.
Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Diagnosing erectile dysfunction (ED) involves a systematic evaluation by a healthcare provider to identify its underlying causes and determine the most appropriate treatment options.
The diagnostic process typically includes the following components:
1. Medical History
The healthcare
provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history, including questions
about the onset and duration of ED, any underlying health conditions,
medications being taken, and lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol
consumption, and physical activity.
This information
helps the healthcare provider understand potential causes and contributing
factors.
2. Physical
Examination
A physical
examination may be conducted to assess general health and identify any physical
issues that could be contributing to ED. This may include checking blood
pressure, examining the genitals, and assessing overall cardiovascular health.
3. Psychological
Evaluation
Understanding the
psychological factors contributing to ED is essential. A healthcare provider
may ask about stress, anxiety, depression, or relationship issues that could be
affecting sexual function.
In some cases, a
referral to a mental health professional or sex therapist may be recommended.
4. Laboratory Tests
Blood tests may be
conducted to check for underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, hormonal
imbalances (e.g., testosterone levels), and lipid profiles.
A nocturnal penile
tumescence (NPT) test may be performed to assess whether spontaneous erections
occur during sleep, which can provide insights into the nature of the ED.
5. Psychological
Questionnaires
Healthcare
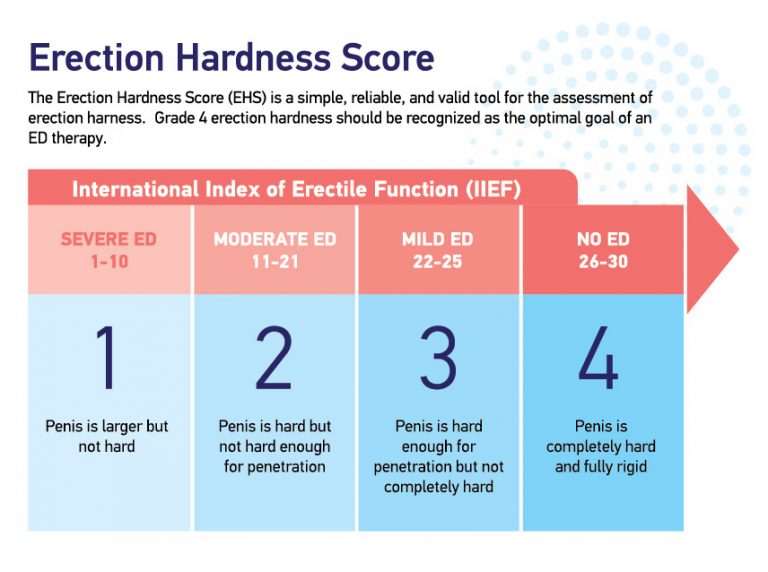
providers may use validated questionnaires such as the International Index of
Erectile Function (IIEF) to assess the severity of ED and its impact on sexual
function and quality of life.
6. Specialized
Tests
In some cases, specialized tests may be recommended to evaluate specific aspects of sexual function. These tests may include penile Doppler ultrasound, which assesses blood flow to the penis, or dynamic infusion cavernosometry and cavernosography (DICC), which examines penile blood vessels.
Once a thorough evaluation is completed, the healthcare provider will discuss the findings with the individual and develop a tailored treatment plan. Treatment options may include lifestyle modifications, medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of approaches based on the specific causes and needs of the individual.
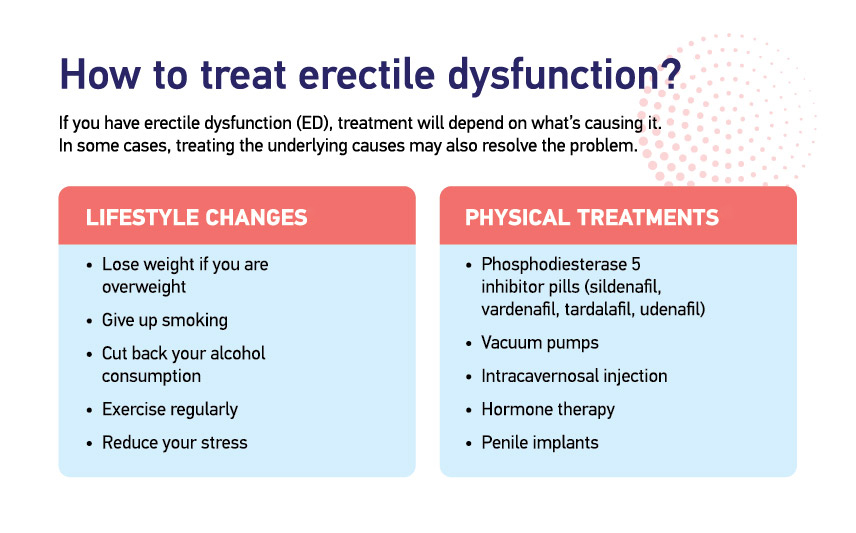
Medical Treatments
Several medical
treatments are available for ED, including medications like Viagra
(sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), and Levitra (vardenafil). These drugs enhance
blood flow to the penis, facilitating erections.
Medical treatments for erectile dysfunction (ED) have evolved significantly in recent years, providing effective options for individuals seeking to improve their sexual function. These treatments primarily focus on enhancing blood flow to the penis or addressing underlying health conditions contributing to ED. Here's a closer look at the available medical interventions, supported by research evidence:
1. Oral Medications
(PDE5 Inhibitors)
The most well-known and widely prescribed ED medications belong to a class
called phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. These include sildenafil
(Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra).
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of PDE5 inhibitors in treating ED. For instance, a meta-analysis published in "JAMA Internal Medicine" found that these medications significantly improved erectile function.
2. Intracavernosal
Injections
Injections of medications directly into the base of the penis can produce erections. Alprostadil (Caverject, Edex) is a common medication used for this purpose. These injections relax the blood vessels and smooth muscles in the penis, promoting blood flow. Research has shown that intracavernosal injections can be highly effective, even in cases where oral medications may not work.
3. Penile Implants
Penile implants are surgically implanted devices that provide on-demand erections. Two main types are inflatable implants and semi-rigid implants. Penile implants create an erection when the individual manually activates the device, allowing them to control the timing and duration of their erections. Studies have indicated that penile implants can be a highly effective and satisfying treatment option for ED, particularly in cases where other treatments have failed.
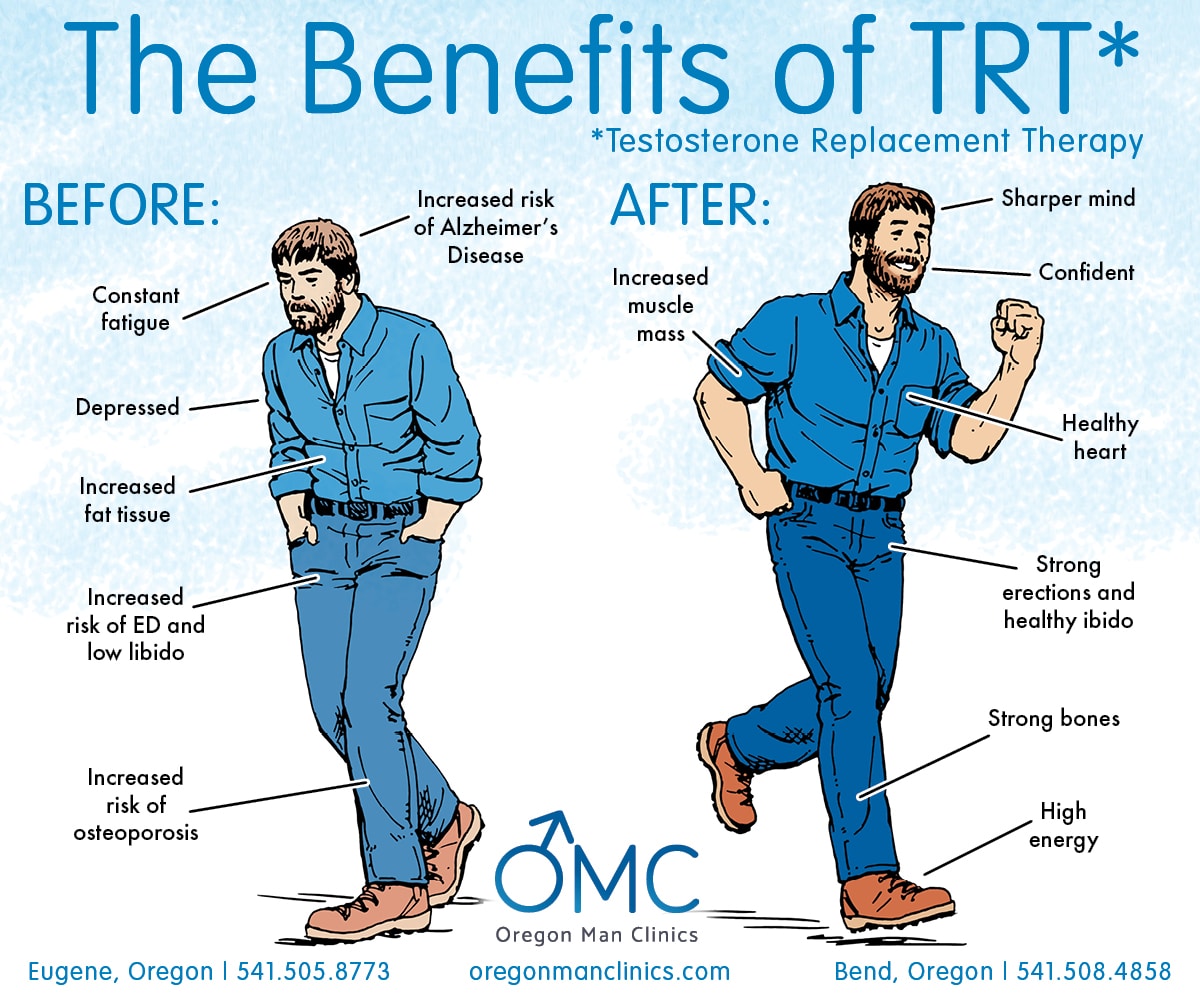
4. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
TRT may be considered for men with low testosterone levels contributing to ED. TRT restores testosterone levels in the body, which can improve sexual function in men with low testosterone. Research suggests that TRT may benefit individuals with ED and low testosterone levels. However, it is essential to identify testosterone deficiency through blood tests before initiating TRT.
It's crucial to note that the choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the underlying cause of ED, individual preferences, and overall health. Effective ED treatment often involves a collaborative approach between the individual and their healthcare provider.
Non-Medical
Treatments
Non-medical
treatments for erectile dysfunction (ED) are essential components of
comprehensive care plans. These approaches often focus on lifestyle
modifications, psychological support, and therapeutic techniques to enhance
sexual function. Let's delve into these non-medical treatment options,
considering research literature where applicable:
1. Lifestyle
Modification
Diet and Nutrition:
Research suggests that adopting a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits,
vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can benefit erectile
function. Foods high in antioxidants and flavonoids, such as berries, citrus
fruits, and dark chocolate, may have a positive impact on vascular health,
promoting better blood flow.
Exercise: Regular
physical activity, including aerobic and resistance training, can improve
overall cardiovascular health, reduce obesity, and enhance blood circulation,
all of which are crucial for erectile function. A study in "JAMA Network
Open" found that men who engaged in physical activity had a lower risk of
ED.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for ED prevention and management.
Obesity is associated with an increased risk of ED, and losing excess weight
can lead to improvements in sexual function.
2. Psychotherapy and Counseling
Sex Therapy: Sex
therapists specialize in addressing sexual issues, including ED.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychotherapy can help individuals
identify and address psychological factors contributing to ED, such as
performance anxiety, stress, or relationship problems.
Couples Counseling:
ED can affect both partners in a relationship. Couples counseling can foster
open communication, improve intimacy, and provide support for couples facing
ED-related challenges.
3. Vacuum Erection
Devices (VEDs)
A vacuum erection device is a non-invasive device that creates a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into the organ to induce an erection. Research has demonstrated that VEDs can be effective in producing erections in many men with ED, even when other treatments fail.
4. Pelvic Floor
Muscle Exercises (Kegels)
Kegel exercises involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles. These exercises can improve blood flow to the pelvic area and enhance erectile function. Studies have shown that regular pelvic floor exercises can lead to improvements in ED symptoms and sexual satisfaction.
Chronic stress can contribute to ED. Stress management techniques
such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga have been
shown to reduce stress and improve sexual function.
Non-medical
treatments can be particularly beneficial for individuals who prefer
non-pharmacological approaches or those seeking additional support alongside
medical treatments. A comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle
modifications, psychological support, and non-medical interventions can often
yield the best results in managing ED.
Coping Strategies
Coping with ED involves addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition. Couples can work together to maintain intimacy, strengthen their emotional bond, and explore alternative forms of sexual expression.
Here are some comprehensive strategies to help you cope effectively:
Open Dialogue:
Communication is key. Discuss your feelings and concerns with your partner
openly and honestly. Share your experiences, fears, and expectations to foster
understanding and emotional support
Seek Professional
Help: Consider couples therapy or individual counseling to address any
emotional or relationship challenges that ED may have brought to the surface.
Lifestyle
Modifications: Adopt a healthy lifestyle by maintaining a balanced diet,
engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco
and excessive alcohol use.
Knowledge is Power:
Educate yourself about ED, its causes, and treatment options. Understanding the
condition can alleviate anxiety and empower you to make informed decisions
about your health.
Self-Help
Techniques: Explore relaxation techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep
breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation to manage stress and
anxiety.
Joining a Support
Group: Connecting with others who have experienced ED can provide a sense of
community and emotional support. Sharing experiences and coping strategies can
be empowering.
Non-Sexual
Intimacy: Explore non-sexual forms of intimacy, such as cuddling, hugging, and
kissing. These expressions of affection can help maintain emotional connection
and reduce the pressure associated with sexual performance.
Conclusion
Erectile
dysfunction is a common and treatable condition. By understanding its causes,
seeking professional help when needed, and making positive lifestyle changes,
individuals can regain sexual function and enhance their overall well-being. Remember, you're not alone in dealing with
ED, and there are effective strategies and treatments available to help you on
your journey to better sexual health.
Do understand that
coping with ED is a journey that may require patience and perseverance. Seeking
both professional help and emotional support from loved ones can significantly
improve your overall well-being and enhance your ability to manage ED
effectively.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/erectile-dysfunction-diagnosis1-5ace3b103128340037d94fc5.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/yoga-for-erectile-dysfunction-poses-benefits-risks-5200227-FINAL-090c7ea41a9548eca9a88dcba274237d.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Tips-for-Managing-E-D_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-c7a184632f7a4e52918bae22b1d75199.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment