Navigating the Path: Understanding and Managing an Enlarged Prostate
The prostate, a small walnut-shaped gland nestled beneath the bladder, plays a crucial role in men's reproductive health. However, as men age, this seemingly unassuming gland can present challenges. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of an enlarged prostate – what it is, how it manifests, and strategies for effective management.
Understanding
Enlarged Prostate
While aging is a
primary factor, several contributing elements are worth exploring to comprehend
the intricacies of this prevalent condition.
1. Hormonal
Changes
Hormones,
especially the interplay between testosterone and estrogen, play a crucial role
in prostate health. With age, testosterone levels decrease, while estrogen
levels may remain relatively stable or even increase. This shift in hormonal
balance is believed to contribute to the growth of the prostate.
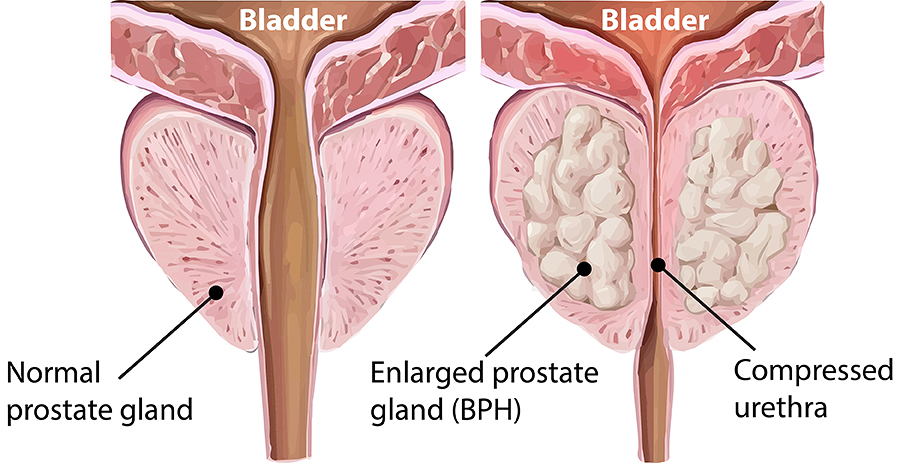
2. Age-Related
Growth
The prostate tends
to grow throughout a man's life. This growth is initially spurred by the surge
of testosterone during puberty. However, as men enter their forties and beyond,
the prostate can undergo a second growth phase. This natural progression, often
referred to as benign prostatic hyperplasia, is the most common cause of an
enlarged prostate.
3. Family History
Genetics may also
play a role in the development of an enlarged prostate. If close male
relatives, such as a father or brother, have experienced BPH, there may be an
increased likelihood of developing the condition. Genetic factors can influence
how the body responds to hormones and, consequently, impact prostate health.
4. Lifestyle
Factors
Certain lifestyle
elements may contribute to the risk of an enlarged prostate. Diets high in red
meat and low in fruits and vegetables have been associated with a higher
incidence of BPH. Sedentary lifestyles and obesity are additional factors that
may influence the development of prostate enlargement.
5. Inflammation
Chronic
inflammation within the prostate, often linked to prostatitis (inflammation of
the prostate), has been proposed as a potential contributor to the development
of an enlarged prostate. Inflammation can lead to cellular changes and alter
the normal growth patterns of the prostate tissue.
6. Erectile
Dysfunction
Research suggests a
potential link between erectile dysfunction (ED) and an increased risk of BPH.
While the exact nature of this association is complex and multifaceted, it
underscores the interconnectedness of various aspects of male reproductive
health.
7. Testosterone
Conversion
The conversion of
testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) within the prostate cells is a
critical process in prostate growth. DHT is a potent form of testosterone that
contributes to the growth of the prostate gland. Medications that inhibit this
conversion can be effective in managing the symptoms of an enlarged prostate.
Common Symptoms
While the severity
of symptoms varies from person to person, understanding these signs is crucial
for seeking timely medical attention and appropriate management.
Urinary Frequency and Urgency
One of the hallmark
symptoms of an enlarged prostate is an increased frequency of urination. Men
may find themselves making more trips to the bathroom, especially during the
night. Additionally, there might be a heightened sense of urgency, where the
need to urinate feels immediate and pressing.
Weak or
Intermittent Urine Stream
As the prostate
enlarges, it can constrict the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the
bladder. This constriction can lead to a weakened or intermittent urine stream.
Men may notice that it takes longer to empty the bladder, and the stream may
not be as forceful as before.
Difficulty
Initiating Urination
An enlarged
prostate can create resistance to the flow of urine, making it challenging to
initiate urination. This can result in hesitancy and a sense that the bladder
is not fully emptied after urination.
Incomplete Emptying
of the Bladder
Feeling as though
the bladder is not entirely emptied after urination is another common symptom.
This sensation can contribute to the need for frequent trips to the bathroom as
the bladder doesn't empty fully.
Straining During
Urination
Straining to
initiate or complete urination may occur due to the increased resistance caused
by an enlarged prostate. This can lead to discomfort and frustration during the
urination process.
Urinary Retention
In some cases, an
enlarged prostate can cause urinary retention, where the bladder doesn't empty
at all. This is a more severe symptom that requires immediate medical
attention.
Urinary Incontinence
An enlarged
prostate can contribute to urinary incontinence, characterized by the
unintentional leakage of urine. This can happen during activities such as
coughing, sneezing, or lifting, and may be linked to the pressure the enlarged
prostate puts on the bladder.
Pain or Discomfort
Some men may
experience pain or discomfort during urination or ejaculation. Pain in the
lower abdomen or pelvic area can also be associated with an enlarged prostate.
Blood in the Urine
While less common,
an enlarged prostate can cause blood to appear in the urine. This symptom
warrants prompt medical attention for further evaluation.
These symptoms can significantly impact a man's quality of life, affecting daily activities and even sleep patterns. Simple tasks like sitting through a movie or traveling can become daunting. Many individuals find themselves planning their activities around the proximity of bathrooms. However, understanding the condition and adopting coping strategies can make a significant difference.
Diagnosis
Medical History and
Symptom Assessment
The diagnostic
process often begins with a detailed medical history and a discussion of the
individual's symptoms. The healthcare provider will inquire about the nature
and duration of urinary symptoms, as well as any associated discomfort or pain.
Physical
Examination
A physical
examination, including a digital rectal examination (DRE), may be performed.
During a DRE, the healthcare provider assesses the size and condition of the
prostate by inserting a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum. This allows
for a palpation of the prostate to check for enlargement, irregularities, or
signs of other prostate conditions.
Prostate-Specific
Antigen (PSA) Test
A blood test
measuring prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels may be conducted. While an
elevated PSA level can be indicative of various prostate conditions, including
an enlarged prostate, it does not provide a definitive diagnosis. It helps
guide further assessments and evaluations.
Urinalysis
A urinalysis may be performed to rule out urinary tract infections or other conditions that could contribute to urinary symptoms. Examination of the urine can provide additional insights into the overall health of the urinary system.
Urodynamic Tests
For a more detailed
assessment of bladder function, urodynamic tests may be conducted. These tests
measure various aspects of bladder and urethral function, helping to identify
issues such as poor bladder emptying or abnormal contractions.
Transrectal
Ultrasound (TRUS)
A transrectal
ultrasound may be recommended to provide a visual image of the prostate. This
imaging technique uses sound waves to create a detailed image of the prostate
gland, helping to assess its size and structure.
Cystoscopy
In some cases, a
cystoscopy may be performed. During this procedure, a thin, flexible tube with
a camera (cystoscope) is inserted through the urethra to visually inspect the
bladder and urethra. This can help identify any structural issues or
abnormalities.
Prostate Biopsy
In certain
situations, a prostate biopsy may be recommended. This involves obtaining small
tissue samples from the prostate for laboratory analysis. While not typically
the first line of diagnostic testing for an enlarged prostate, a biopsy may be
considered if there are concerns about prostate cancer.
The combination of
these diagnostic tools allows healthcare professionals to form a comprehensive
understanding of the nature and severity of an enlarged prostate. It also helps
in differentiating an enlarged prostate from other conditions, such as prostate
cancer, which may have similar symptoms.
Medical Treatments
Addressing the symptoms of an enlarged prostate often involves various medical interventions tailored to the severity of the condition and the impact on an individual's quality of life. Here's an in-depth look at the medical treatments commonly employed:
Alpha-Blockers
Alpha-blockers are
medications that relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, easing
urinary symptoms. Commonly prescribed examples include tamsulosin, alfuzosin,
and doxazosin. These medications work by improving urine flow and reducing
symptoms like hesitation and urgency.
5-Alpha Reductase
Inhibitors
These medications,
such as finasteride and dutasteride, target the hormonal aspect of prostate
enlargement. They inhibit the production of a hormone called
dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which contributes to prostate growth. 5-alpha
reductase inhibitors can help shrink the prostate over time, relieving urinary
symptoms.
Combination Therapy
In some cases,
healthcare providers may prescribe a combination of alpha-blockers and 5-alpha
reductase inhibitors for a more comprehensive approach. This dual therapy aims
to address both the muscle and hormonal components contributing to prostate
enlargement.
Phosphodiesterase-5
Inhibitors
While commonly
associated with erectile dysfunction treatment, medications like tadalafil can
also be prescribed to manage urinary symptoms associated with an enlarged
prostate. These drugs help relax the smooth muscles in the bladder and
prostate, promoting improved urine flow.
Antibiotics
If symptoms are
exacerbated by a urinary tract infection (UTI), antibiotics may be prescribed
to address the infection and alleviate associated symptoms. It's essential to
differentiate between prostate-related symptoms and those caused by infection.
Minimally Invasive
Procedures
For individuals
with more severe symptoms or those not responding well to medications,
minimally invasive procedures may be considered. Transurethral microwave
thermotherapy (TUMT) and transurethral needle ablation (TUNA) are examples of
procedures that use heat to reduce excess prostate tissue.
Transurethral
Resection of the Prostate (TURP)
TURP is a surgical
procedure where excess prostate tissue is removed to improve urine flow. It
involves the insertion of a scope through the urethra to access and remove
portions of the prostate obstructing the urinary pathway.
Laser Therapy
Laser procedures,
such as photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP) and holmium laser
enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP), use laser energy to remove or vaporize
excess prostate tissue, reducing symptoms.
Prostatic Urethral
Lift (UroLift)
UroLift is a
relatively newer, minimally invasive procedure that involves placing small
implants in the prostate to lift and hold the enlarged tissue away from the
urethra, improving urine flow.
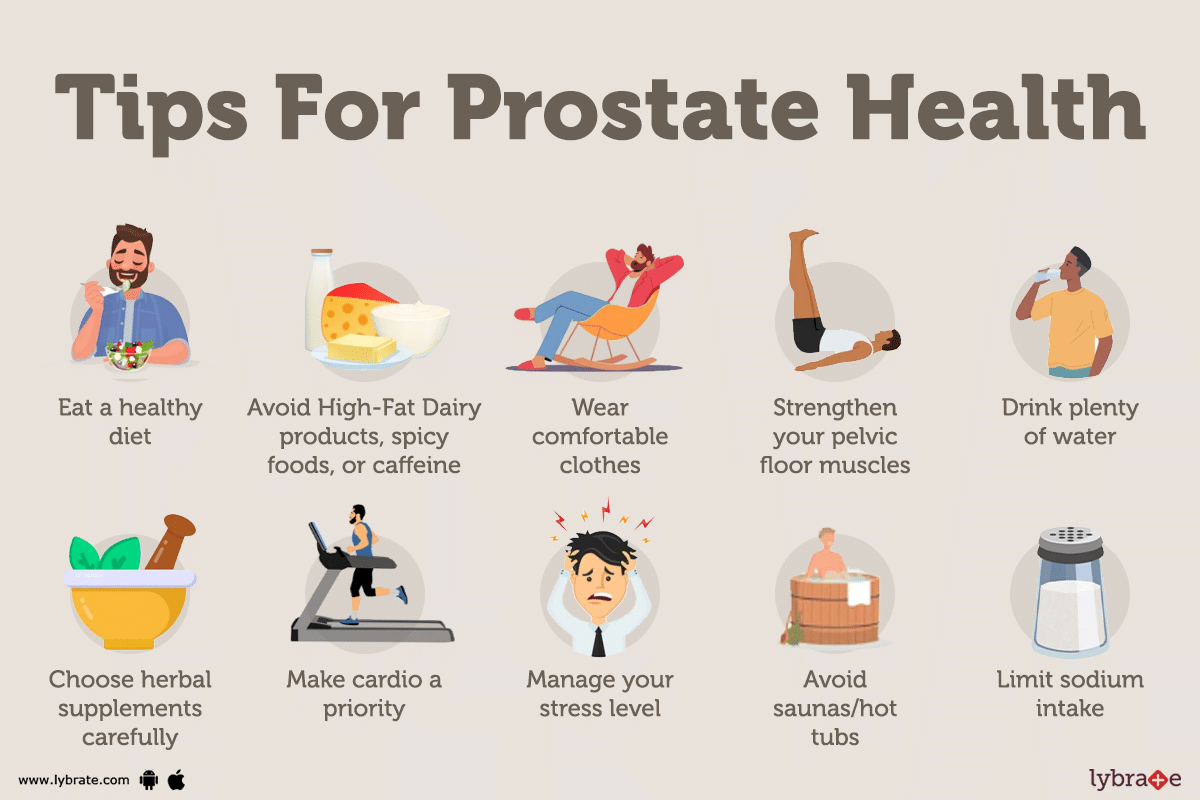
Prevention: Lifestyle
Strategies for Proactive Health
While some risk factors for an enlarged prostate are beyond our control, adopting a proactive approach to certain lifestyle factors may contribute to overall prostate health and potentially reduce the risk of developing prostate enlargement.
Consider the following strategies:
Maintain a Healthy
Diet
A diet rich in
fruits and vegetables provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants
that support overall health, including prostate health. Also, opt for sources
of healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and
walnuts.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking an
adequate amount of water helps maintain overall health, including urinary
health. Staying hydrated can contribute to regular and healthy urine flow.
Regular Physical
Activity
Engage in regular
exercise, as it is associated with various health benefits. Physical activity
may help maintain a healthy weight and contribute to overall well-being.
Limit Red Meat and
Dairy Consumption
Some studies
suggest a potential link between a diet high in red meat and dairy products and
an increased risk of prostate issues. Consider moderating the intake of these
foods.
Maintain a Healthy
Weight
Obesity is
associated with an increased risk of developing an enlarged prostate. Adopting
a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet can
contribute to maintaining a healthy weight.
Monitor
Testosterone Levels
While testosterone
is essential for various bodily functions, imbalances may contribute to
prostate issues. Regular health checkups can help monitor hormone levels and
address any imbalances.
Practice Stress
Management
Chronic stress can
negatively impact overall health, including prostate health. Incorporate stress
management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga into your
routine.
Limit Alcohol and
Caffeine Intake
Excessive
consumption of alcohol and caffeinated beverages may irritate the bladder and
contribute to urinary symptoms. Moderation is key.
Regular Health
Checkups
Schedule regular
checkups with a healthcare provider. Proactive healthcare allows for early
detection and management of potential health issues.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking is linked
to various health issues, and some studies suggest it may be associated with an
increased risk of developing prostate problems. Quitting smoking is beneficial
for overall health.
Consider
Prostate-Healthy Supplements
Some supplements,
such as saw palmetto and beta-sitosterol, are thought to support prostate
health. Before taking any supplements, it's crucial to consult with a
healthcare professional.
It's important to note that while these lifestyle strategies may contribute to overall health and well-being, individual responses can vary. Additionally, maintaining open communication with a healthcare provider is essential for personalized guidance and early detection of any potential health concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an
enlarged prostate is a common aspect of aging for many men. Understanding the
symptoms, seeking timely medical attention, and adopting a holistic approach to
prostate health can empower individuals to manage this condition effectively. By
prioritizing prostate health, men can continue to lead fulfilling lives without
being hindered by the challenges an enlarged prostate may pose.






Comments
Post a Comment