Exploring the Power of Music: How Music Influences Mood and Emotions
Welcome to the fascinating world of music and emotions. In this blog post, we'll embark on a journey to explore the profound influence that music has on our mood and emotions. From the exhilarating rush of a catchy tune to the poignant melancholy of a soulful ballad, music has the remarkable ability to evoke a kaleidoscope of feelings within us.
But why is it important to delve into the intricacies of how music affects our emotional landscape? The answer lies in the profound impact that music has on our overall well-being. In today's fast-paced world, where stress and anxiety often loom large, understanding how music can serve as a powerful tool for emotional regulation and self-care is more crucial than ever.
By unraveling the science behind music and emotions, we can unlock new insights into how music influences our mental and emotional states. Armed with this knowledge, we can harness the therapeutic potential of music to cultivate greater resilience, reduce stress, and enhance our overall quality of life.
So, join me as we embark on a journey to discover the transformative power of music. From the soothing melodies that calm our nerves to the uplifting anthems that ignite our spirits, let's explore how music has the power to touch our hearts and souls in ways that words alone cannot express.
The Science Behind Music and Emotions
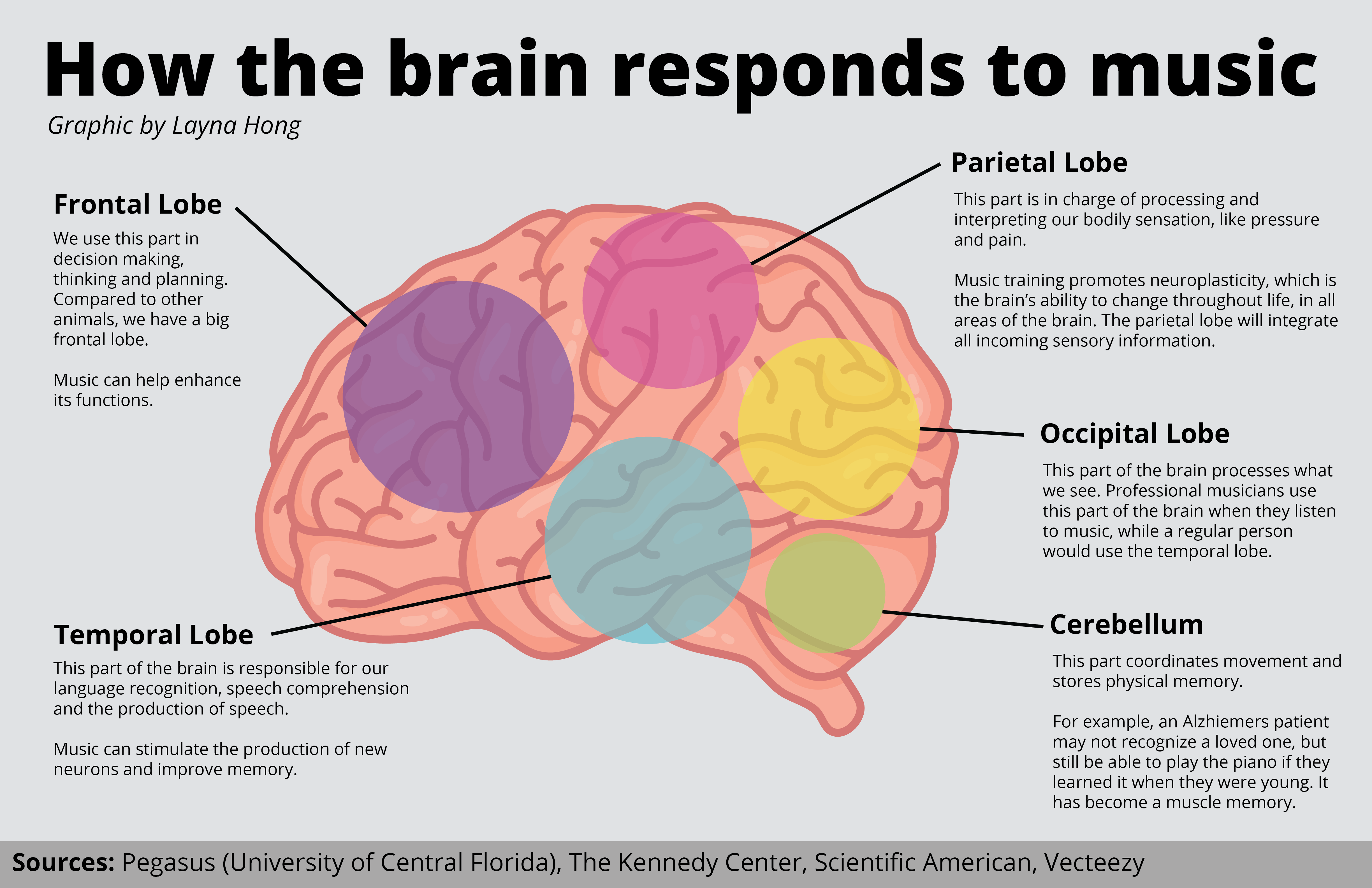
Music has a profound impact on our emotions, and this effect is rooted in both psychological and physiological mechanisms. Researchers have long sought to understand how music can evoke such powerful emotional responses, uncovering fascinating insights into the inner workings of the brain.
Psychological Mechanisms
At a psychological level, music engages with our emotions through a complex interplay of auditory processing, memory, and cognitive appraisal. When we listen to music, our brains decode the auditory signals and extract meaning from the sound patterns, rhythms, and melodies. These musical elements can trigger memories, associations, and emotional responses based on our past experiences and cultural background.
Moreover, music often acts as a form of communication, conveying emotional messages and evoking empathetic responses in listeners. Whether it's the melancholic strains of a violin or the exuberant beats of a drum, music has the power to elicit a wide range of emotional states, from joy and nostalgia to sadness and awe.
Physiological Mechanisms
On a physiological level, music directly affects the brain's neural activity and biochemical processes. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have revealed that listening to music activates multiple brain regions associated with emotion processing, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex.
On a physiological level, music directly affects the brain's neural activity and biochemical processes. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have revealed that listening to music activates multiple brain regions associated with emotion processing, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex.
The amygdala, often referred to as the brain's emotional center, plays a crucial role in processing and modulating emotional responses to stimuli, including music. Meanwhile, the hippocampus, involved in memory formation and retrieval, contributes to the emotional significance of music by linking auditory stimuli to past experiences and emotions.
Furthermore, music has been shown to influence the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin, which are known to regulate mood and emotions. Dopamine, often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, is released in response to pleasurable experiences, including listening to music. Serotonin, a neurotransmitter linked to mood regulation, is also released during music listening, contributing to feelings of relaxation and contentment. Additionally, oxytocin, sometimes called the "love hormone," is released during social bonding experiences, such as singing in a choir or attending a concert, fostering feelings of connection and well-being.
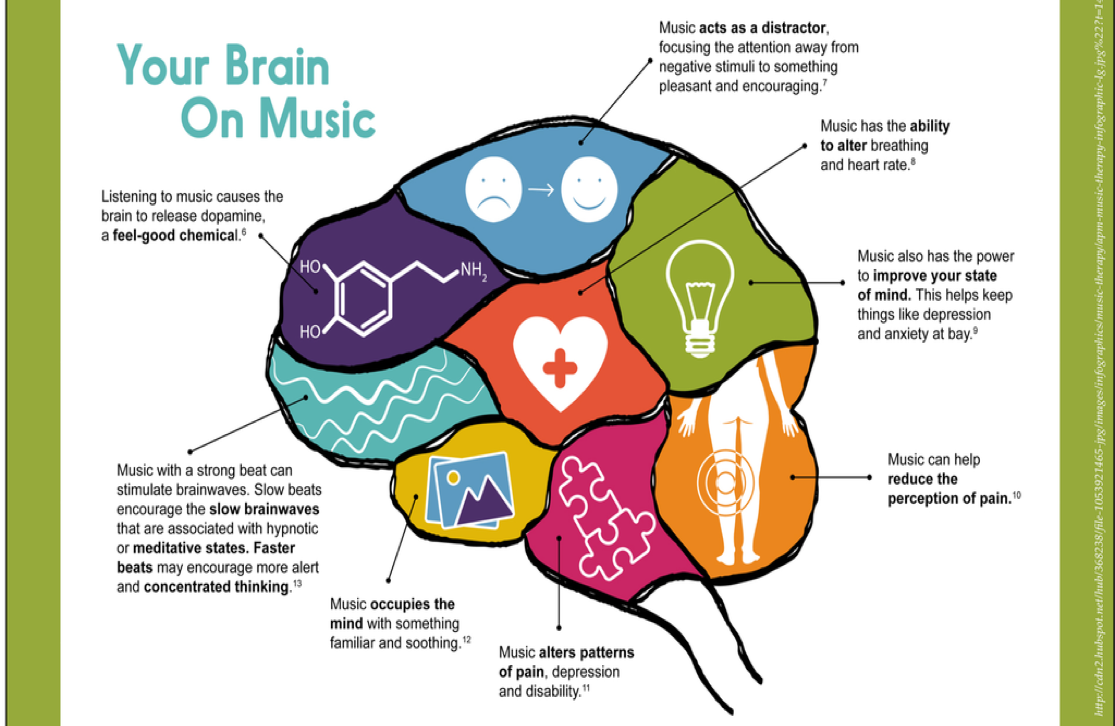
There are some research into the relationship between different types of music and the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin. While findings can vary depending on the study and the specific context, here are some general trends:
Dopamine Release: Research suggests that music with a fast tempo, strong rhythm, and a positive, upbeat melody tends to be more effective in eliciting dopamine release. This includes genres such as pop, rock, dance, and electronic music. Additionally, music that is personally enjoyable or emotionally arousing is more likely to trigger dopamine release. For example, Dancing Queen by Abba and even the electrifying J.Lo can make one happy.
Oxytocin Release: Oxytocin release is linked to social bonding and feelings of connection with others. Music that involves social interaction, such as singing in a choir, playing in a band, or attending a live concert, can promote oxytocin release. Additionally, music with lyrics that convey themes of love, empathy, and togetherness may enhance oxytocin release.
While these generalizations provide insights into the relationship between music and neurotransmitter release, it's essential to recognize that individual responses to music can vary widely. Factors such as personal preferences, cultural background, and past experiences all play a role in shaping how different people respond to music stimuli. Additionally, more research is needed to further explore the nuances of this relationship and its implications for emotional well-being.
Music has a remarkable ability to influence our mood, and different genres can evoke a wide range of emotional states. From the soul-stirring melodies of classical music to the infectious beats of pop and the introspective lyrics of folk, each genre has its unique emotional signature. Let's explore how various music genres can shape our emotional landscape:
2.1 Classical Music:
Classical music is renowned for its ability to evoke a wide range of emotions, from serenity and awe to melancholy and introspection. Research has shown that listening to classical music can reduce stress, lower blood pressure, and promote relaxation.
In one study published in the journal PLOS ONE, participants who listened to classical music reported higher levels of positive emotions and lower levels of negative emotions compared to those who listened to other genres.
2.2 Pop Music:
Pop music is characterized by catchy melodies, upbeat rhythms, and relatable lyrics that often celebrate love, friendship, and self-expression. Research suggests that listening to pop music can enhance mood, increase feelings of happiness, and boost energy levels.
Studies have found that certain pop songs with uplifting lyrics and catchy hooks can trigger the release of dopamine, the neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward.
2.3 Rock Music:
Rock music is known for its raw energy, powerful instrumentation, and emotive vocals, which can evoke feelings of rebellion, passion, and intensity. Research has shown that listening to rock music can be cathartic, providing an outlet for pent-up emotions and helping individuals cope with stress and anger.

In a study published in the Journal of Music Therapy, participants who listened to rock music reported feeling more empowered and in control of their emotions compared to those who listened to other genres.
2.4 Jazz Music:
Jazz music is characterized by its improvisational nature, complex harmonies, and rhythmic complexity, which can evoke feelings of spontaneity, freedom, and creativity. Research suggests that listening to jazz music can enhance mood, reduce anxiety, and promote relaxation.
Studies have found that jazz music stimulates brain regions associated with creativity and emotional expression, leading to increased feelings of inspiration and well-being.
2.5 Folk Music:
Folk music is rooted in tradition and storytelling, often conveying themes of resilience, community, and social justice. Research suggests that listening to folk music can evoke feelings of nostalgia, connection to one's cultural heritage, and a sense of belonging.
In one study published in the Journal of Happiness Studies, participants who listened to folk music reported higher levels of life satisfaction and overall well-being compared to those who listened to other genres.
In recent years, music therapy has emerged as a powerful tool for promoting emotional well-being and enhancing quality of life. Rooted in the belief that music has the ability to heal and transform, music therapy utilizes the therapeutic properties of music to address a wide range of physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs.
Dancing and Movement
Use music as a catalyst for movement and expression by incorporating dancing or physical activity into your routine. Put on your favorite dance playlist and let loose in the comfort of your own home, or join a dance class or group to connect with others and experience the joy of movement together. Let's enjoy Dua Lipa, "Don't Start Now".
Furthermore, music has been shown to influence the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin, which are known to regulate mood and emotions. Dopamine, often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, is released in response to pleasurable experiences, including listening to music. Serotonin, a neurotransmitter linked to mood regulation, is also released during music listening, contributing to feelings of relaxation and contentment. Additionally, oxytocin, sometimes called the "love hormone," is released during social bonding experiences, such as singing in a choir or attending a concert, fostering feelings of connection and well-being.

There are some research into the relationship between different types of music and the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin. While findings can vary depending on the study and the specific context, here are some general trends:
Dopamine Release: Research suggests that music with a fast tempo, strong rhythm, and a positive, upbeat melody tends to be more effective in eliciting dopamine release. This includes genres such as pop, rock, dance, and electronic music. Additionally, music that is personally enjoyable or emotionally arousing is more likely to trigger dopamine release. For example, Dancing Queen by Abba and even the electrifying J.Lo can make one happy.
Serotonin Release: Serotonin release is associated with feelings of relaxation, contentment, and well-being. Music that is slow-paced, calming, and harmonious may be more effective in promoting serotonin release. This includes genres such as classical music, ambient music, and certain types of instrumental music like the Winding Path from Kevin Kern. However, individual preferences and associations with specific songs or genres can also influence serotonin release.
Oxytocin Release: Oxytocin release is linked to social bonding and feelings of connection with others. Music that involves social interaction, such as singing in a choir, playing in a band, or attending a live concert, can promote oxytocin release. Additionally, music with lyrics that convey themes of love, empathy, and togetherness may enhance oxytocin release.
While these generalizations provide insights into the relationship between music and neurotransmitter release, it's essential to recognize that individual responses to music can vary widely. Factors such as personal preferences, cultural background, and past experiences all play a role in shaping how different people respond to music stimuli. Additionally, more research is needed to further explore the nuances of this relationship and its implications for emotional well-being.
Music's Impact on Mood
2.1 Classical Music:
Classical music is renowned for its ability to evoke a wide range of emotions, from serenity and awe to melancholy and introspection. Research has shown that listening to classical music can reduce stress, lower blood pressure, and promote relaxation.
In one study published in the journal PLOS ONE, participants who listened to classical music reported higher levels of positive emotions and lower levels of negative emotions compared to those who listened to other genres.
2.2 Pop Music:
Pop music is characterized by catchy melodies, upbeat rhythms, and relatable lyrics that often celebrate love, friendship, and self-expression. Research suggests that listening to pop music can enhance mood, increase feelings of happiness, and boost energy levels.
Studies have found that certain pop songs with uplifting lyrics and catchy hooks can trigger the release of dopamine, the neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward.
2.3 Rock Music:
Rock music is known for its raw energy, powerful instrumentation, and emotive vocals, which can evoke feelings of rebellion, passion, and intensity. Research has shown that listening to rock music can be cathartic, providing an outlet for pent-up emotions and helping individuals cope with stress and anger.

In a study published in the Journal of Music Therapy, participants who listened to rock music reported feeling more empowered and in control of their emotions compared to those who listened to other genres.
2.4 Jazz Music:
Jazz music is characterized by its improvisational nature, complex harmonies, and rhythmic complexity, which can evoke feelings of spontaneity, freedom, and creativity. Research suggests that listening to jazz music can enhance mood, reduce anxiety, and promote relaxation.
Studies have found that jazz music stimulates brain regions associated with creativity and emotional expression, leading to increased feelings of inspiration and well-being.
2.5 Folk Music:
Folk music is rooted in tradition and storytelling, often conveying themes of resilience, community, and social justice. Research suggests that listening to folk music can evoke feelings of nostalgia, connection to one's cultural heritage, and a sense of belonging.
In one study published in the Journal of Happiness Studies, participants who listened to folk music reported higher levels of life satisfaction and overall well-being compared to those who listened to other genres.
Music as Therapy
In recent years, music therapy has emerged as a powerful tool for promoting emotional well-being and enhancing quality of life. Rooted in the belief that music has the ability to heal and transform, music therapy utilizes the therapeutic properties of music to address a wide range of physical, emotional, cognitive, and social needs.
Let's explore the benefits of music therapy, some techniques used by professionals, and its effectiveness:
Benefits of Music Therapy
Emotional Regulation: Music therapy can help individuals regulate their emotions, reduce stress, and manage anxiety and depression. Through music, individuals can express and process complex feelings in a safe and supportive environment.
Enhanced Mood: Listening to or engaging in music-making activities can elevate mood, increase feelings of happiness, and promote a sense of well-being. Music has the power to uplift spirits, provide comfort, and foster a positive outlook on life.
Improved Cognitive Function: Music therapy can stimulate cognitive processes such as memory, attention, and executive function. For individuals with cognitive impairments or neurological conditions, music therapy may enhance cognitive skills and promote brain plasticity.
Social Connection: Participating in group music-making activities can foster social connections, promote teamwork, and enhance communication skills. Music therapy sessions provide opportunities for individuals to connect with others, build relationships, and cultivate a sense of community.
Active Music-Making: In active music-making interventions, individuals engage in creating music through singing, playing instruments, or improvisation. This hands-on approach allows for self-expression, creativity, and exploration of emotions.
Guided Relaxation: Guided relaxation techniques involve listening to soothing music or guided imagery while focusing on deep breathing and relaxation exercises. This technique can help reduce stress, induce relaxation, and promote mindfulness.
Lyric Analysis: Lyric analysis involves exploring the meaning and symbolism of song lyrics as a way of processing emotions and gaining insight into personal experiences. This technique encourages reflection, self-awareness, and emotional exploration.
Songwriting: Songwriting interventions involve composing original songs or lyrics as a means of self-expression and emotional communication. Songwriting can provide individuals with a creative outlet for expressing thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
Music-Assisted Relaxation: Music-assisted relaxation techniques combine music listening with progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery to promote relaxation and stress reduction. This approach utilizes the calming effects of music to facilitate relaxation and mental clarity.
A meta-analysis published in the Journal of Music Therapy found that music therapy interventions were associated with significant reductions in anxiety and depression symptoms in individuals with mental health disorders.
Another study published in Frontiers in Psychology found that group music therapy was effective in reducing stress and improving mood in adults undergoing cancer treatment.
Additionally, research has shown that music therapy can be beneficial for individuals with autism spectrum disorder, dementia, chronic pain, and other health conditions.
Overall, music therapy offers a holistic approach to healing that addresses the emotional, psychological, and social aspects of well-being. By harnessing the therapeutic power of music, individuals can experience profound transformations and improve their overall quality of life.
Curated Playlists for Different Emotional States
Create curated playlists tailored to specific emotional states to set the mood for different activities or moments throughout the day. For relaxation, consider instrumental music or ambient soundscape that promotes tranquility and calmness. For motivation, opt for upbeat songs with catchy rhythms and empowering lyrics to energize and inspire you. For joy and happiness, choose feel-good anthems and upbeat pop songs that bring a smile to your face and uplift your spirits.
Music for Mindful Activities
Incorporate music into mindful activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to enhance relaxation and focus. Choose soft, soothing music with slow tempos and gentle melodies to create a serene atmosphere conducive to mindfulness practice. Let's listen to "Weightless" by Marconi Union.
Benefits of Music Therapy
Emotional Regulation: Music therapy can help individuals regulate their emotions, reduce stress, and manage anxiety and depression. Through music, individuals can express and process complex feelings in a safe and supportive environment.
Enhanced Mood: Listening to or engaging in music-making activities can elevate mood, increase feelings of happiness, and promote a sense of well-being. Music has the power to uplift spirits, provide comfort, and foster a positive outlook on life.
Improved Cognitive Function: Music therapy can stimulate cognitive processes such as memory, attention, and executive function. For individuals with cognitive impairments or neurological conditions, music therapy may enhance cognitive skills and promote brain plasticity.
Social Connection: Participating in group music-making activities can foster social connections, promote teamwork, and enhance communication skills. Music therapy sessions provide opportunities for individuals to connect with others, build relationships, and cultivate a sense of community.
Techniques Used in Music Therapy
Active Music-Making: In active music-making interventions, individuals engage in creating music through singing, playing instruments, or improvisation. This hands-on approach allows for self-expression, creativity, and exploration of emotions.
Guided Relaxation: Guided relaxation techniques involve listening to soothing music or guided imagery while focusing on deep breathing and relaxation exercises. This technique can help reduce stress, induce relaxation, and promote mindfulness.
Lyric Analysis: Lyric analysis involves exploring the meaning and symbolism of song lyrics as a way of processing emotions and gaining insight into personal experiences. This technique encourages reflection, self-awareness, and emotional exploration.
Songwriting: Songwriting interventions involve composing original songs or lyrics as a means of self-expression and emotional communication. Songwriting can provide individuals with a creative outlet for expressing thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
Music-Assisted Relaxation: Music-assisted relaxation techniques combine music listening with progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery to promote relaxation and stress reduction. This approach utilizes the calming effects of music to facilitate relaxation and mental clarity.
A meta-analysis published in the Journal of Music Therapy found that music therapy interventions were associated with significant reductions in anxiety and depression symptoms in individuals with mental health disorders.
Another study published in Frontiers in Psychology found that group music therapy was effective in reducing stress and improving mood in adults undergoing cancer treatment.
Additionally, research has shown that music therapy can be beneficial for individuals with autism spectrum disorder, dementia, chronic pain, and other health conditions.
Overall, music therapy offers a holistic approach to healing that addresses the emotional, psychological, and social aspects of well-being. By harnessing the therapeutic power of music, individuals can experience profound transformations and improve their overall quality of life.
Practical Applications and Tips
Music has the power to uplift, soothe, and inspire, making it a valuable tool for enhancing mood and well-being in daily life. Whether you're looking to relax after a long day, boost your energy levels, or simply lift your spirits, here are some practical tips for incorporating music into your daily routine:Curated Playlists for Different Emotional States
Create curated playlists tailored to specific emotional states to set the mood for different activities or moments throughout the day. For relaxation, consider instrumental music or ambient soundscape that promotes tranquility and calmness. For motivation, opt for upbeat songs with catchy rhythms and empowering lyrics to energize and inspire you. For joy and happiness, choose feel-good anthems and upbeat pop songs that bring a smile to your face and uplift your spirits.
Music for Mindful Activities
Incorporate music into mindful activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to enhance relaxation and focus. Choose soft, soothing music with slow tempos and gentle melodies to create a serene atmosphere conducive to mindfulness practice. Let's listen to "Weightless" by Marconi Union.
Dancing and Movement
Use music as a catalyst for movement and expression by incorporating dancing or physical activity into your routine. Put on your favorite dance playlist and let loose in the comfort of your own home, or join a dance class or group to connect with others and experience the joy of movement together. Let's enjoy Dua Lipa, "Don't Start Now".
Singing and Vocal Expression
Singing is a powerful form of self-expression that can release tension, boost mood, and increase feelings of happiness and well-being. Whether you're singing along to your favorite songs in the shower or participating in a choir or karaoke night, let your voice be heard and revel in the joy of vocal expression.
Playing Musical Instruments
Playing a musical instrument offers a unique opportunity for creative expression and emotional release. Whether you're strumming a guitar, tickling the ivories of a piano, or pounding the drums, playing music can provide a sense of accomplishment, fulfillment, and stress relief.
Mindful Listening
Practice mindful listening by immersing yourself fully in the experience of music without distractions. Set aside dedicated time to listen to your favorite albums or discover new music, allowing yourself to be fully present and engaged in the auditory experience.

As you embark on your journey to harness the power of music for emotional well-being, remember that the beauty of music lies in its diversity and personal significance. Take the time to explore different genres, artists, and musical styles to discover what resonates most deeply with you. Whether it's the soothing strains of classical music, the infectious rhythms of pop, or the soulful melodies of jazz, trust your intuition and embrace the music that speaks to your heart. Experiment with creating your own playlists, attending live concerts, or engaging in musical activities that bring you joy and fulfillment. By embracing music as a tool for emotional regulation and self-care, you can cultivate greater resilience, enhance your mood, and enrich your overall quality of life. So, let the music guide you on a journey of self-discovery and emotional empowerment, and may the melodies of your soul be a source of comfort, inspiration, and healing.
Singing is a powerful form of self-expression that can release tension, boost mood, and increase feelings of happiness and well-being. Whether you're singing along to your favorite songs in the shower or participating in a choir or karaoke night, let your voice be heard and revel in the joy of vocal expression.
Playing Musical Instruments
Playing a musical instrument offers a unique opportunity for creative expression and emotional release. Whether you're strumming a guitar, tickling the ivories of a piano, or pounding the drums, playing music can provide a sense of accomplishment, fulfillment, and stress relief.
Mindful Listening
Practice mindful listening by immersing yourself fully in the experience of music without distractions. Set aside dedicated time to listen to your favorite albums or discover new music, allowing yourself to be fully present and engaged in the auditory experience.

As you embark on your journey to harness the power of music for emotional well-being, remember that the beauty of music lies in its diversity and personal significance. Take the time to explore different genres, artists, and musical styles to discover what resonates most deeply with you. Whether it's the soothing strains of classical music, the infectious rhythms of pop, or the soulful melodies of jazz, trust your intuition and embrace the music that speaks to your heart. Experiment with creating your own playlists, attending live concerts, or engaging in musical activities that bring you joy and fulfillment. By embracing music as a tool for emotional regulation and self-care, you can cultivate greater resilience, enhance your mood, and enrich your overall quality of life. So, let the music guide you on a journey of self-discovery and emotional empowerment, and may the melodies of your soul be a source of comfort, inspiration, and healing.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/surprising-psychological-benefits-of-music-4126866-Final-44c12600b86a4c71883710685fe13a7f.png)



Comments
Post a Comment