Reporting on Climate Change and Carbon Footprint: A Beginner's Guide
In recent years, climate change has moved to the forefront of global conversations. Global temperatures are rising, extreme weather events are becoming more frequent, and the impact on our planet is becoming increasingly evident. Businesses, as major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, have a crucial role to play in mitigating climate change. With increasing awareness of the environmental impacts of carbon emissions, businesses and individuals alike are now expected to play their part in reducing their carbon footprint. And reporting on climate change and carbon footprint is a critical step in demonstrating their commitment to environmental responsibility and transparency.
But how do you get started, especially if you're new to
sustainability reporting?
This guide is here to help. We'll break down the basics of
climate change, what a carbon footprint is, and most importantly, how you can
begin tracking and reporting your own carbon emissions. Whether you're an
individual trying to make a difference or a business leader looking to comply
with sustainability regulations, this beginner's guide will provide you with
the knowledge and tools to take action.
Understanding the Basics
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in
temperature, weather patterns, and environmental conditions on Earth, primarily
caused by human activities. Over the past century, the planet has experienced
unprecedented warming due to the increased concentration of greenhouse gases
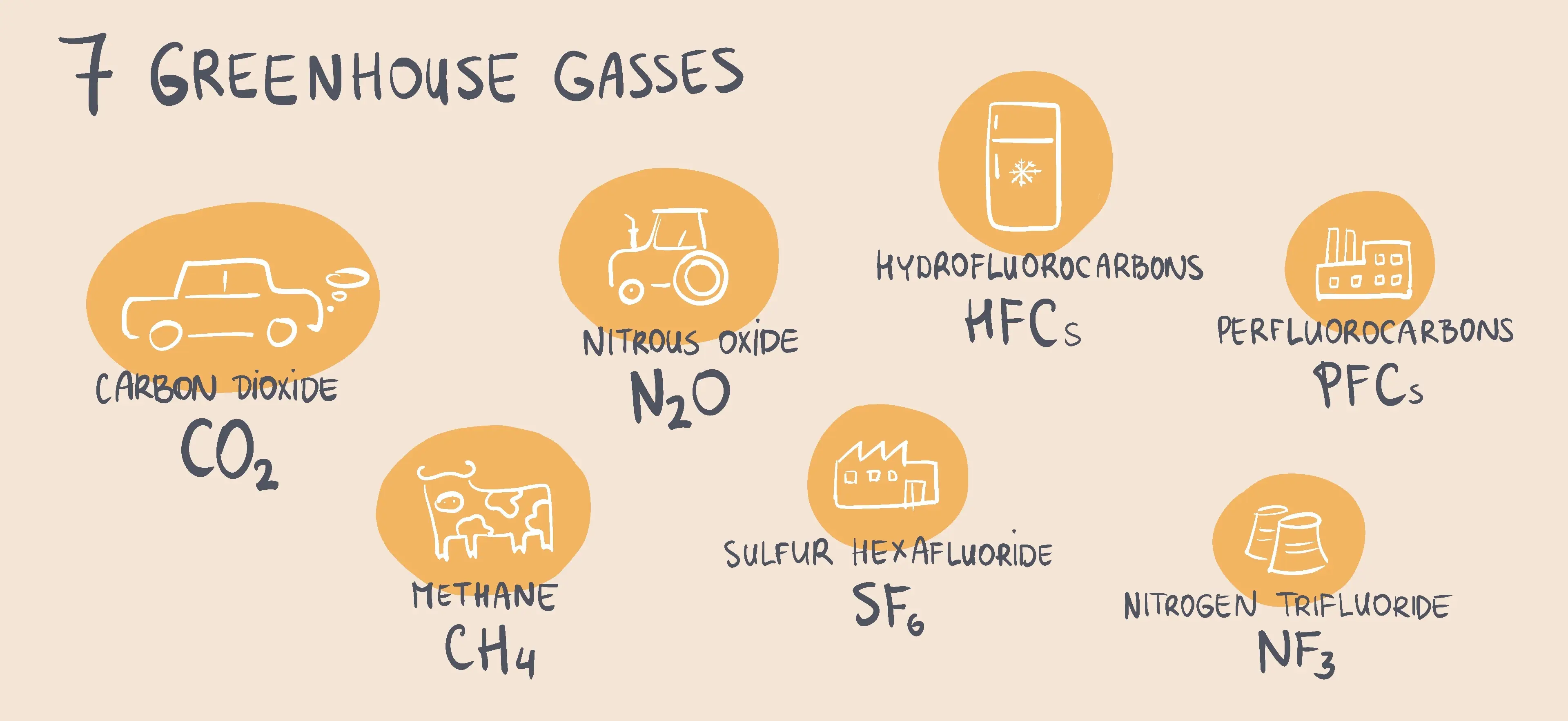
(GHGs) in the atmosphere. These gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane
(CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O), trap heat from the sun, leading to what is
commonly known as the "greenhouse effect."
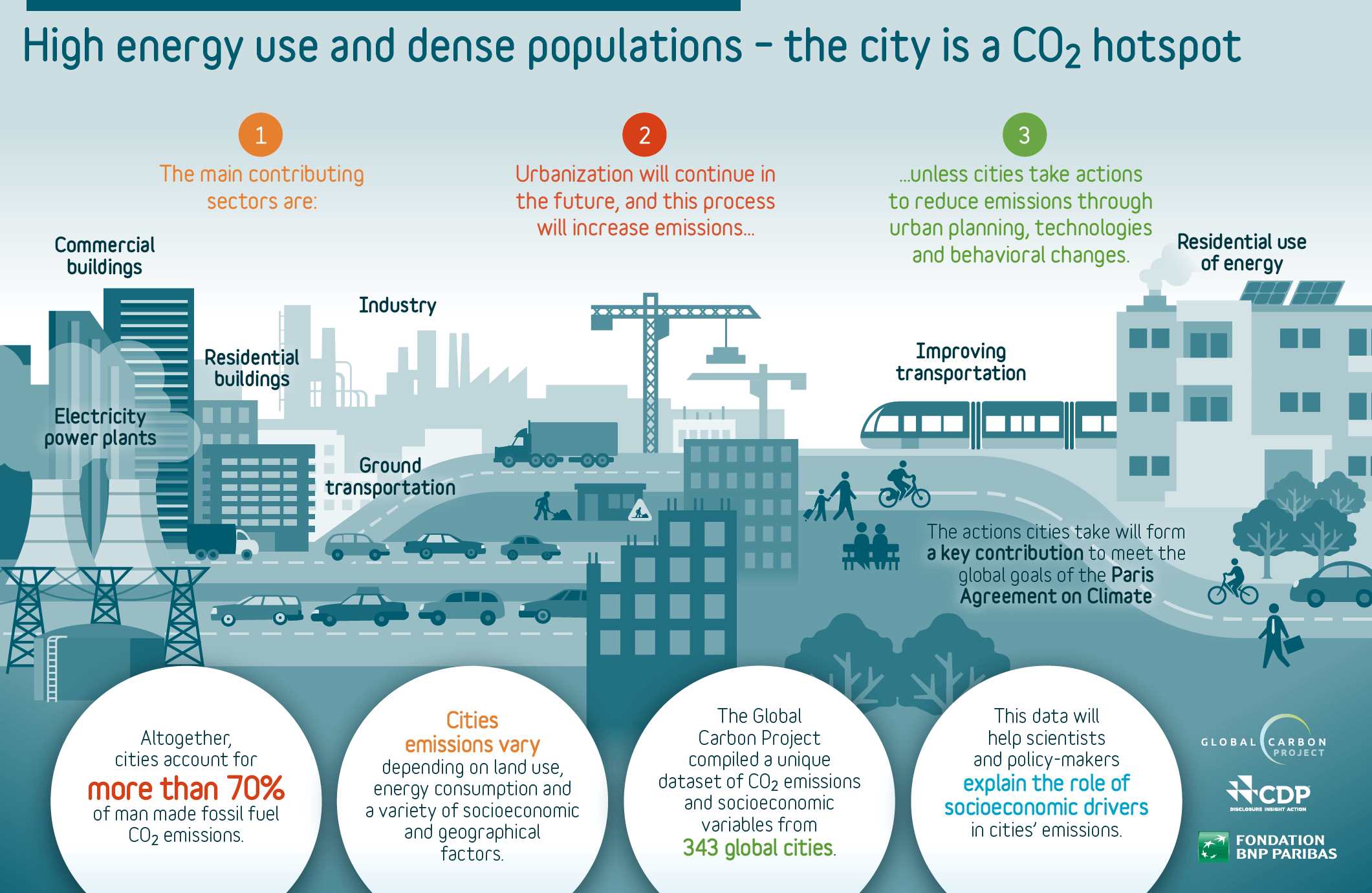
While the Earth’s climate has naturally fluctuated over millions of years, the current rate of change is far more rapid due to activities like burning fossil fuels (e.g., coal, oil, and gas), deforestation, and industrial production. This rapid climate change leads to extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems, ultimately affecting human societies, agriculture, and economies globally.
As the world faces the impacts of climate change, reducing GHG emissions has become critical to mitigating further harm. Your business, like many others, contributes to these emissions through various activities, from energy consumption to transportation and waste management. This collective impact is known as your carbon footprint.
What is a Carbon Footprint?
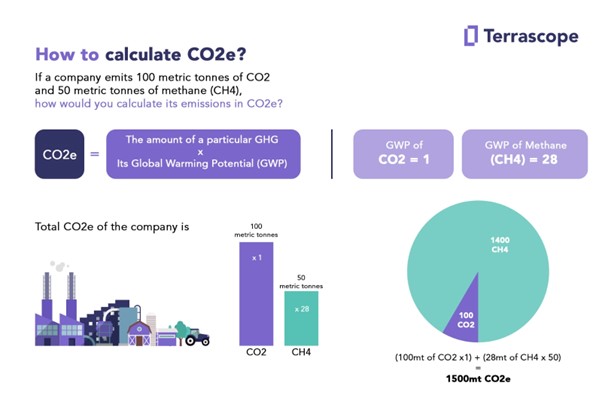
The term "carbon footprint" is used to describe
the total amount of greenhouse gases generated by an individual, organization,
event, or product. It’s measured in units of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO₂e),
which means that all GHG emissions are converted into the equivalent amount of
CO₂ to provide a unified metric. This makes it easier to compare different
types of emissions.
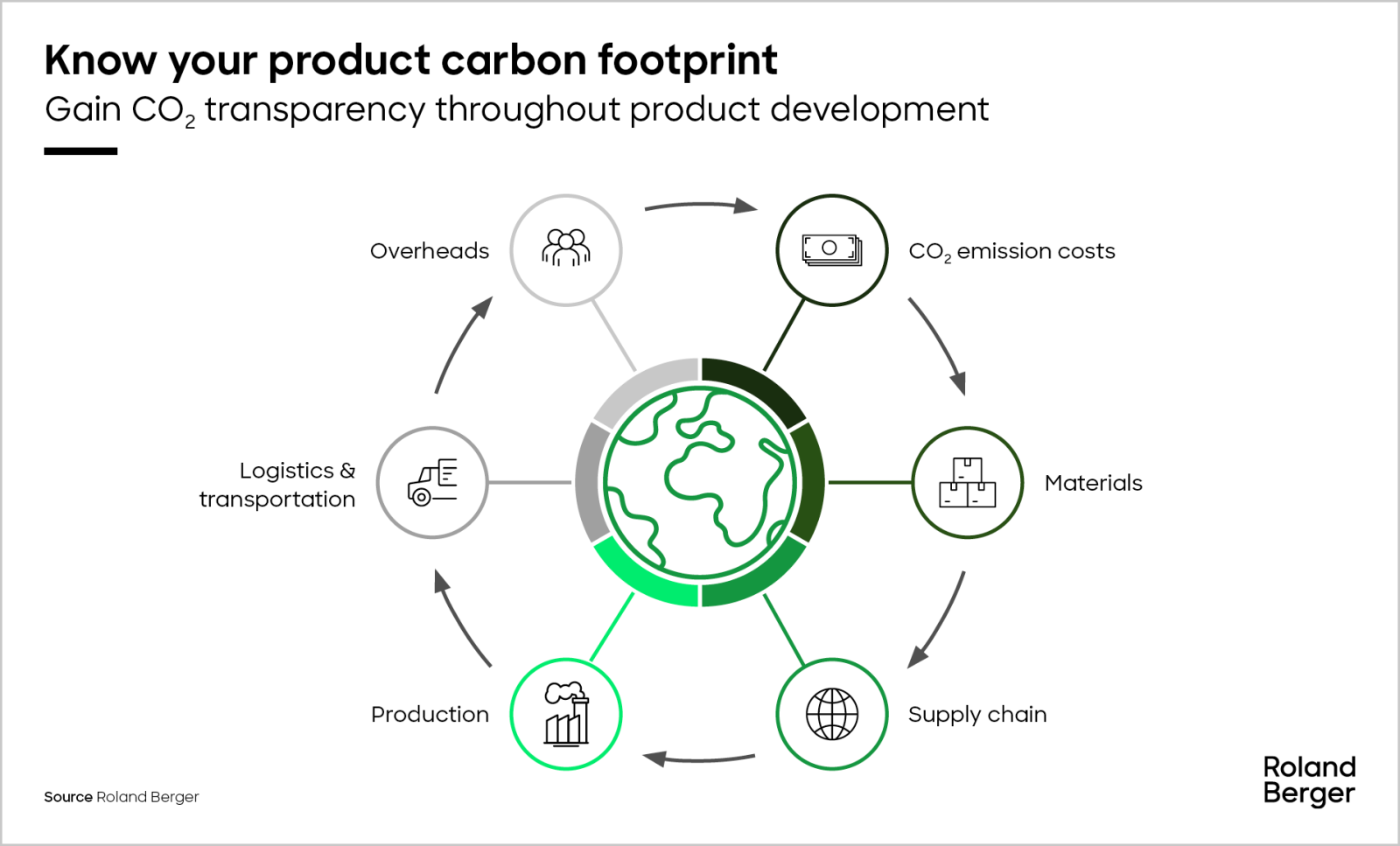
To break it down further, your carbon footprint is the sum of all emissions resulting from daily activities such as:
- Electricity
Use: Energy generated from fossil fuels like coal or natural gas is a
major source of emissions.
- Transportation:
Cars, airplanes, and other modes of transportation that burn fossil fuels
contribute significantly to your footprint.
- Food
Production: Agriculture, especially livestock farming, produces large
amounts of methane and other gases.
- Manufacturing:
The production and consumption of goods, including clothes, electronics,
and packaging, release emissions.
Example: Imagine a typical day where you drive to
work, use electricity at home, and purchase a product shipped from another
country. All of these activities contribute to your carbon footprint. Over
time, these emissions accumulate, affecting the planet’s climate.
Understanding your carbon footprint is essential because once you can measure your impact, you can take steps to reduce it. For businesses, this is even more important as they are responsible for a large share of global emissions and are under growing pressure to disclose their carbon output.
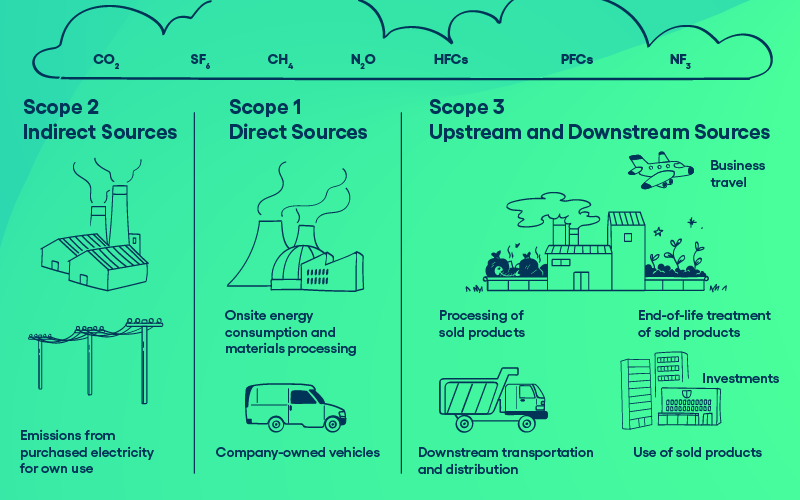
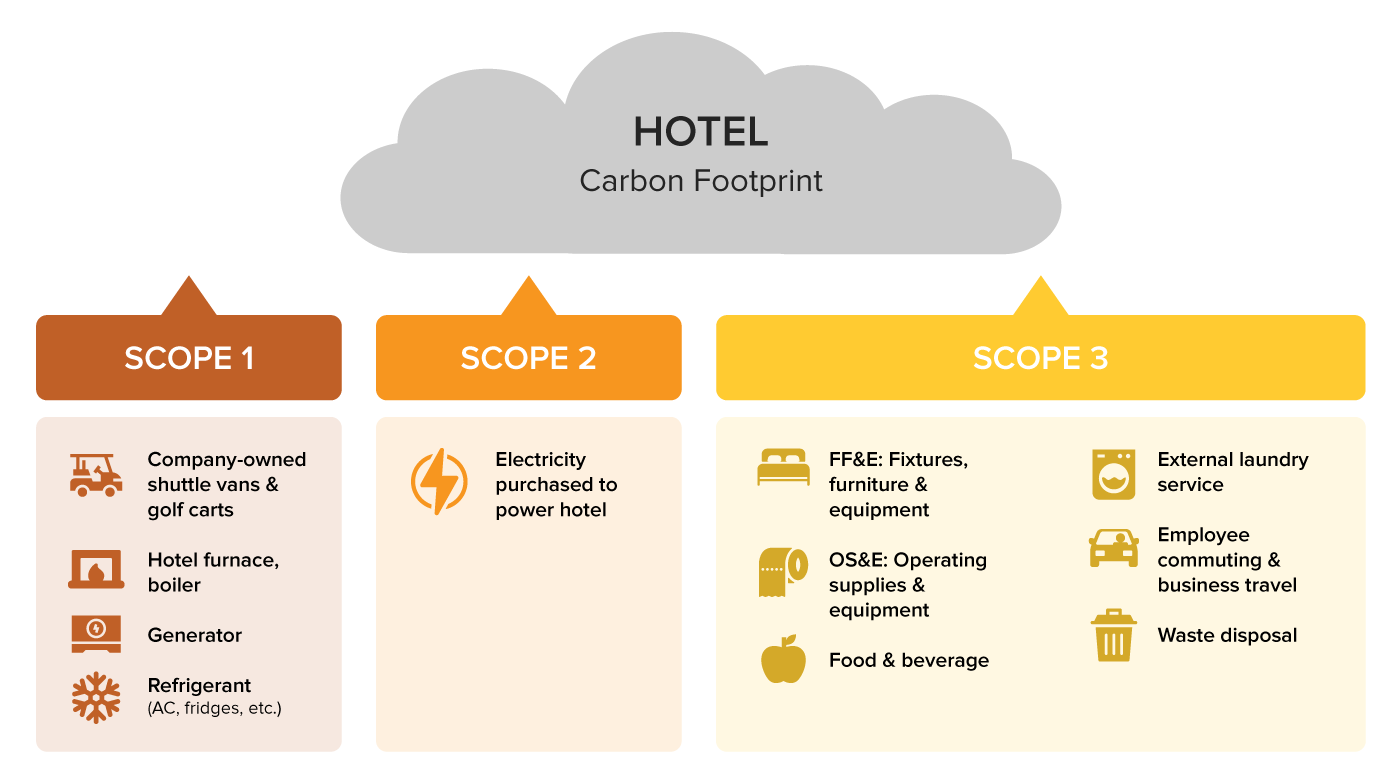
All of the above elements are classified into three main categories
of emissions:
- Scope
1 emissions: Direct emissions from sources owned or controlled by
your company, such as emissions from your company vehicles, industrial
processes, or on-site energy generation.
- Scope
2 emissions: Indirect emissions from the generation of purchased
electricity, heat, or steam used by your company.
- Scope
3 emissions: Indirect emissions from activities in your value
chain that are not owned or controlled by your company, such as emissions
from your suppliers, transportation, and the use of your products by
customers.
The Link Between Climate Change and Carbon Footprints
Carbon footprints are a measurable way to understand the impact of human activities on climate change. By calculating emissions from activities like energy use, transportation, and consumption, we can pinpoint which actions are most responsible for increasing the concentration of GHGs in the atmosphere.
Individuals and businesses alike contribute to this carbon accumulation, meaning everyone has a role to play in reducing their carbon footprint. By understanding your carbon footprint, you can make informed choices, such as switching to renewable energy, optimizing resource use, and minimizing waste, which can ultimately help mitigate the effects of climate change.
Whether you're an individual or an organization, measuring
your carbon footprint is the first step toward accountability and taking
climate action. Here’s why:
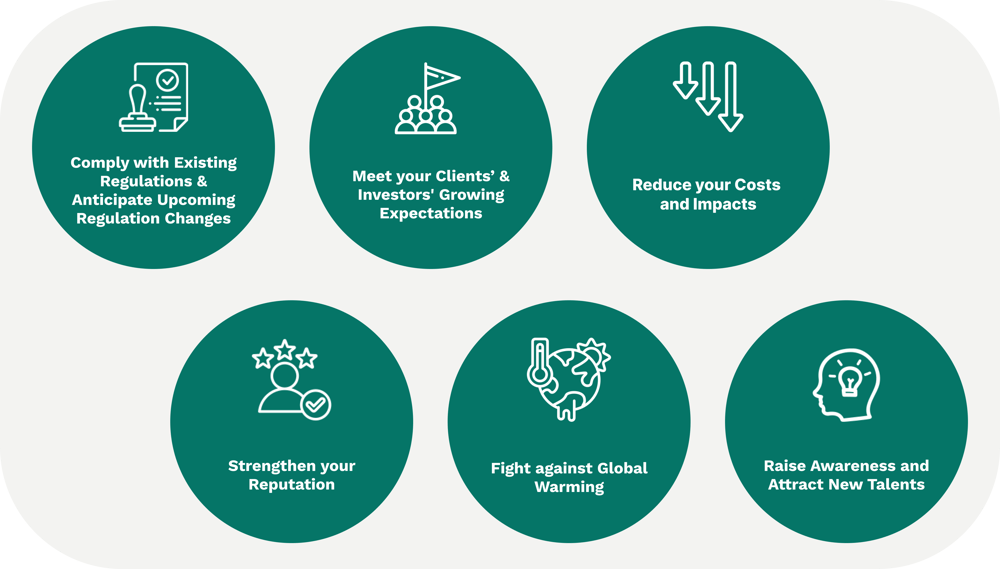
1. Compliance with Regulations
Governments around the world are increasingly implementing
regulations that require companies to disclose their carbon emissions.
Reporting frameworks like the Task Force on Climate-related Financial
Disclosures (TCFD), Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), and various
national policies demand transparency on environmental impact. By measuring and
reporting your carbon footprint, businesses can stay compliant with these
regulations and avoid potential penalties.
For example, the European Union’s Corporate
Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) mandates that companies provide
detailed sustainability and climate-related disclosures. Similarly, countries
like the UK and Canada have introduced carbon tax schemes that incentivize
businesses to reduce emissions. Failing to report or comply with such
regulations can lead to reputational damage and legal ramifications.
2. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Beyond regulatory compliance, reporting on your carbon
footprint is a key aspect of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). CSR
refers to a company’s efforts to assess and take responsibility for its social
and environmental impact. Consumers today are increasingly aware of
environmental issues and prefer to support businesses that are transparent and
committed to sustainability. A study by
Nielsen (2015) found that 66% of global consumers are willing to pay more for
sustainable brands.
By publicly reporting carbon emissions, businesses can
demonstrate their dedication to reducing their environmental impact and taking
part in the fight against climate change. This not only helps the environment
but also strengthens relationships with customers, investors, and other
stakeholders.
3. Transparency and Accountability
Reporting on carbon footprints promotes transparency, which
is critical in building trust with both internal and external stakeholders. As
highlighted by research from the World Economic Forum (2021),
stakeholder expectations for corporate climate action are rapidly increasing. Whether it’s shareholders, employees,
customers, or the wider public, people want to know how organizations are
managing their impact on the environment. Transparency in reporting ensures
that everyone is aware of a company’s carbon footprint, the steps being taken
to reduce it, and the progress made over time.
Moreover, public disclosure helps hold businesses
accountable. By openly reporting carbon emissions, companies create a level of
responsibility and are more likely to stay committed to their environmental
goals.
4. Improved Operational Efficiency
When companies begin to measure and report their carbon
footprint, they often uncover inefficiencies within their operations. For
example, businesses might realize that their energy consumption is higher than
necessary, or that waste management practices can be improved. Reducing
emissions often goes hand-in-hand with reducing costs, especially in areas like
energy consumption, resource management, and waste reduction.
By reporting on your carbon footprint, businesses can identify areas where improvements can be made, leading to cost savings and a more efficient operation overall. This can also result in long-term sustainability benefits that make the business more resilient to market fluctuations and supply chain disruptions caused by environmental factors.
5. Enhancing Reputation and Gaining a Competitive Edge
In today’s market, companies that prioritize sustainability
are more likely to be viewed favorably by consumers, investors, and partners.
Publicly reporting carbon emissions demonstrates a proactive approach to
environmental responsibility, which can enhance a company’s reputation and
differentiate it from competitors who may not be as transparent.
Businesses that report their carbon footprint also position themselves as industry leaders in sustainability. Many large corporations are setting ambitious carbon reduction targets, such as Net Zero by 2050 or sooner. Publicly committing to these goals through reporting not only shows leadership but also attracts like-minded investors, customers, and employees.
6. Long-term Sustainability and Risk Management
Measuring and reporting your carbon footprint allows
businesses to better understand their environmental impact and identify
climate-related risks that could affect their operations in the future. As
extreme weather events and resource scarcity become more common, businesses
need to be aware of their vulnerabilities. Reporting carbon emissions and
taking steps to reduce them can help organizations develop long-term
sustainability strategies that ensure they are prepared for these challenges.
Additionally, businesses that demonstrate leadership in
sustainability are more likely to benefit from future opportunities in a
low-carbon economy. Reporting allows companies to not only reduce risks but
also innovate and find new ways to thrive in a climate-conscious world.
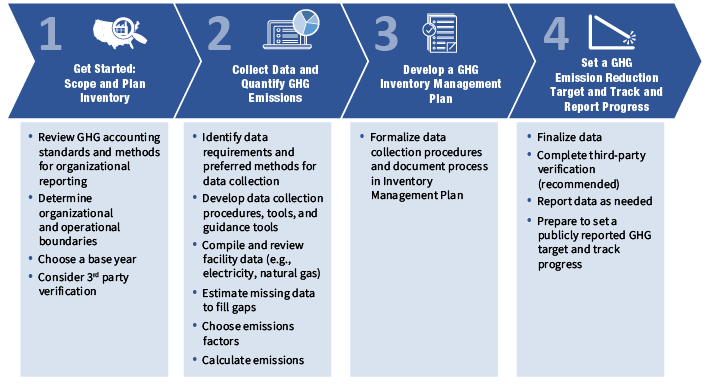
Getting
Started with Measuring & Reporting
Reporting on climate change and your carbon footprint might
seem daunting, but it's a journey you can take step by step.
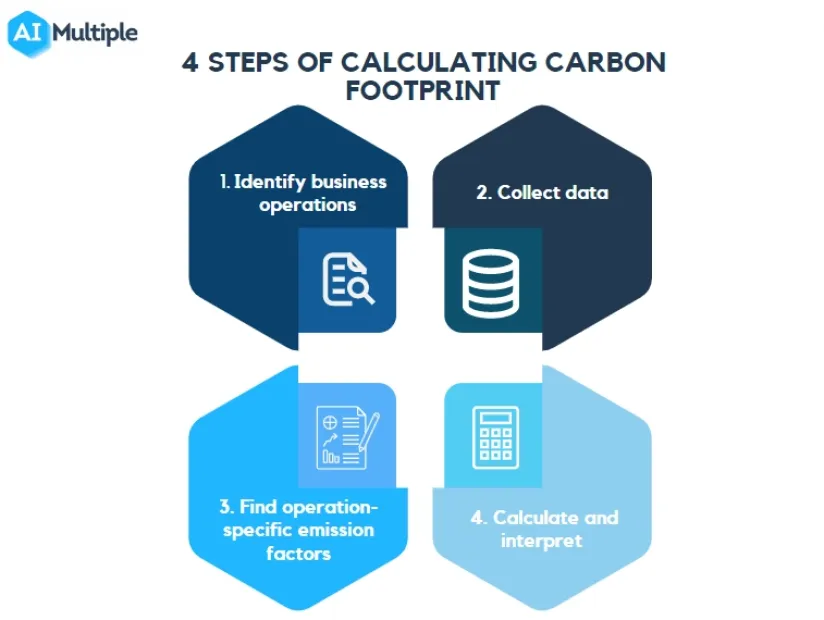
Start by identifying the scope of your carbon footprint
measurement. You can choose to measure:
- Personal
footprint (e.g., your household or individual activities).
- Business
or organizational footprint (emissions from business operations).
- Product
or service footprint (lifecycle emissions from production to
disposal).
For businesses, this will typically involve defining
operational boundaries and selecting which scopes (1, 2, and 3) you will
include in the measurement.
- Identify
Your Emission Sources: Start by identifying the key activities
and processes within your business that generate greenhouse gas emissions.
This could include:
- Energy
consumption: Electricity, heating, cooling, and fuel use.
- Transportation: Company
vehicles, employee commuting, business travel and transportation of
goods.
- Waste
management: Waste generation, disposal, and recycling.
- Upstream and downstream activities: Emissions from your suppliers, transportation of materials, and the use of your products by customers (Scope 3 emissions). When considering Scope 3, businesses must think about their entire supply chain, including product manufacturing, suppliers, distributors, and even customers.
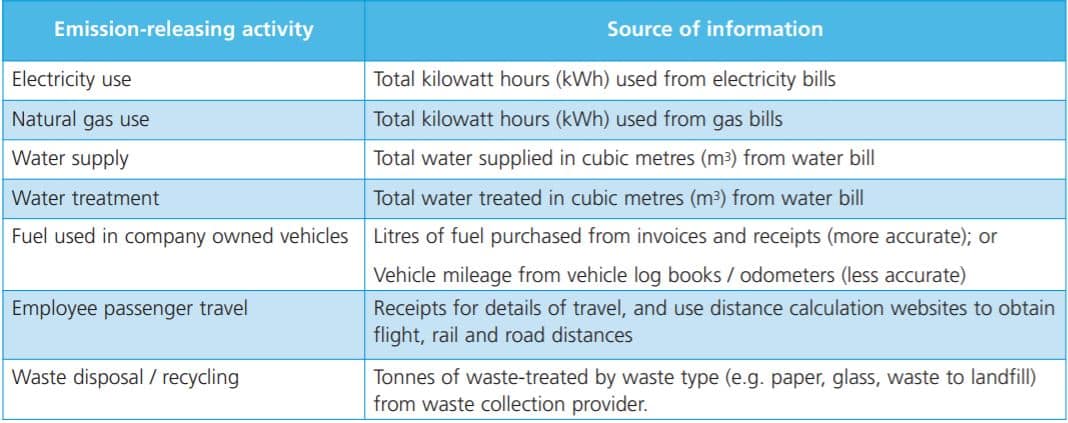
- Gather
Data: Once you've identified your emission sources, you need to
gather data on their emissions. This may involve:
- Reviewing
existing records: Check your energy bills, fuel receipts, and
other relevant documents for information on your energy consumption, fuel
use, and waste generation.
- Conducting
energy audits: Consider hiring an energy auditor to conduct a
thorough assessment of your energy use and identify opportunities for
improvement.
- Engaging with suppliers: Request emissions data from your suppliers to understand your Scope 3 emissions. Calculate emissions related to the materials and products you buy by gathering data on quantities purchased, suppliers, and distribution networks.
- Convert
Data into CO₂ Equivalents. After gathering the raw data, you need to
convert it into CO₂ equivalents (CO₂e) to understand its carbon
impact. This conversion uses specific emission factors, which are
ratios that convert activity data (e.g., energy use) into GHG emissions.
- There are several tools and calculators available online that automatically apply these emission factors to your data:
- For Individuals: Tools like the EPA’s Carbon Footprint Calculator or CoolClimate Network are user-friendly for personal carbon footprint calculations.
- For Businesses: The Greenhouse Gas Protocol Calculator, Carbon Trust Footprint Calculator, and Carbon Footprint Ltd. provide more comprehensive tools for organizations.
- Common
emission factors include:
- Electricity:
X metric tons of CO₂e per kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumed.
- Gasoline:
X metric tons of CO₂e per gallon of fuel burned.
- Flights: X metric tons of CO₂e per mile or kilometer flown, depending on the aircraft and flight class.
Once the data has been converted, you’ll have your total carbon footprint, usually expressed in metric tons of CO₂e.
The next step is to interpret these results:
- What
areas contribute the most to your footprint? For many, energy consumption
and transportation tend to be significant contributors.
- Are
there any “hotspots” where emissions are disproportionately high? For
example, frequent business flights or heavy reliance on fossil fuels for
heating.
Analyzing your carbon footprint helps you prioritize actions to reduce emissions, such as switching to renewable energy sources, optimizing logistics, or changing personal habits like reducing air travel.
3. Set Reduction Targets and Take Action
Now that you understand your carbon footprint, the next step
is to set targets for reducing emissions. Some examples include:
- For
Individuals: Reducing car usage, switching to public transport,
lowering household energy use, or adopting a plant-based diet.
- For
Businesses: Implementing energy efficiency measures, transitioning to
renewable energy, reducing waste, optimizing supply chains, or introducing
carbon offset programs.
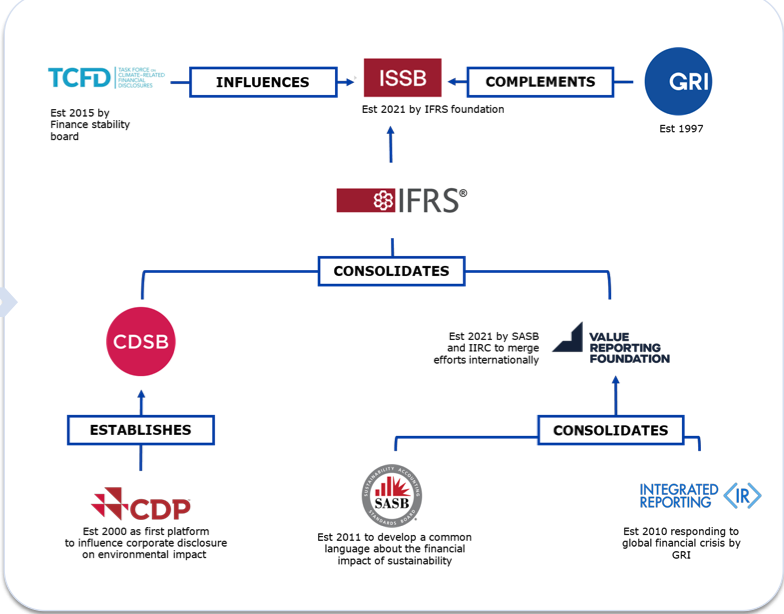
4. Choosing a Reporting Framework
- Greenhouse
Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol): This is the most widely used
framework for measuring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions. It
provides standardized guidance on data collection, calculation, and
reporting.
- CDP
(Carbon Disclosure Project): CDP focuses on environmental reporting,
particularly climate change, water security, and deforestation. Many
businesses use CDP to disclose their carbon footprint to investors,
customers, and regulators. The CDP framework emphasizes climate-related
risks, targets, and progress towards carbon reduction.
- Task
Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): This
framework focuses on disclosing the financial risks and opportunities
associated with climate change. It provides guidance on reporting on
governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets.
- B
Corporation Certification: For businesses interested in holistic
sustainability, B Corp certification focuses on environmental, social, and
governance (ESG) practices. Part of the certification process involves
reporting your carbon footprint and overall sustainability impact.
- Other
Frameworks: There are other frameworks available, such as the
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) and the Global Reporting
Initiative (GRI), which may be relevant depending on your industry and
reporting needs.
5. Reporting Your Findings
Your carbon footprint report should be clear, comprehensive,
and transparent. Whether you're a small business, a large corporation, or an
individual, a well-organized report ensures that your audience understands your
environmental impact and reduction strategies.
- Structure: Your
climate change report should be well-structured and easy to understand. It
should include:
- An
executive summary that highlights your key findings and commitments.
- A
description of your company's approach to climate change and your
emissions reduction efforts.
- A
breakdown of your emissions by category (Scope 1, 2, and 3).
- Your
emissions reduction targets and the actions you are taking to achieve
them.
Example:
“This report details the carbon footprint of XYZ Company for the period from
January to December 2023. Over this period, XYZ Company emitted 2,500 metric
tons of CO₂e, with 70% of emissions coming from transportation and energy use.
The report outlines our reduction strategies and future targets.”
- Transparency
and Clarity: Be transparent about your data collection methods,
assumptions, and limitations. Use clear and concise language to explain
your findings. Avoid jargon and
technical terms where possible, especially if your audience is not
familiar with carbon accounting.
- Visuals: Incorporate
charts, graphs, and infographics to make your data more engaging and
understandable.
- Story-telling.
Your climate change report should
be more than just a dry list of data. It should tell a compelling story
about your company's commitment to reducing its impact on the
environment.
- Use Clear and Engaging Language: Avoid technical jargon and use language that is easy to understand for a general audience.
- Highlight Your Company's Journey: Describe your company's approach to climate change, your motivations for taking action, and the challenges you've faced.
- Showcase Your Achievements: Highlight your successes in reducing emissions, implementing sustainable practices, and contributing to a greener future.
- Emphasize Your Commitment: Clearly communicate your company's commitment to continuous improvement and ongoing efforts to address climate change.
· Actionable Steps: Show What You're Doing: Describe the specific actions your company is taking to reduce its carbon footprint, such as:
o Investing in renewable energy
o Implementing energy efficiency measures
o Reducing waste and promoting recycling
o Partnering with suppliers to reduce their emissions
o Supporting climate-friendly initiatives in your community
- Quantify
Your Impact: Whenever possible, quantify the impact of your
actions. For example, if you've installed solar panels, calculate the
amount of emissions you've avoided.
- Set
Future Goals: Outline your company's future goals for reducing
emissions and addressing climate change. This demonstrates your commitment
to continuous improvement and long-term sustainability. Goals should involve all stakeholders,
including employees, customers, and suppliers. Engage them in your carbon
reduction journey and communicate the role they can play. For instance,
your supply chain partners may need to align with your sustainability
goals, and customers may appreciate eco-friendly initiatives.
Example:
“By 2025, we aim to reduce our total emissions by 30%, primarily by
increasing energy efficiency and transitioning to 100% renewable energy for our
operations. By 2030, we commit to reaching a 50% reduction in emissions, with a
goal of achieving Net Zero by 2050.”
Example of SMART goals:
“Reduce electricity
consumption by 20% within the next 12 months by installing energy-efficient
lighting and optimizing heating and cooling systems.”
“Reduce company-wide air travel by 40% by 2025 by implementing video conferencing solutions.”
·
Track Progress and Adjust: Regularly
monitor your progress towards your goals. Reporting annually or quarterly helps
keep track of your carbon reduction strategies and provides an opportunity to
adjust your approach as needed.
Example:
“After reviewing our first-quarter energy data, we noticed a 15% reduction
in electricity use. We plan to continue implementing these changes and explore
additional ways to decrease our reliance on fossil fuels.”
By following these tips, you can create a compelling climate
change report that engages your audience, builds trust, and inspires action. Reporting
on climate change and your carbon footprint is an ongoing process. You'll need
to update your data and report regularly to demonstrate your commitment to
continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Reducing Carbon Footprint
Once you've measured and reported your carbon footprint, the next step is to take action. Reducing your carbon emissions not only benefits the environment but also improves efficiency, lowers operational costs, and enhances your reputation as a responsible organization or individual.
Below are some of the best practices to adopt in your journey toward reducing your carbon footprint.
1. Energy Efficiency
One of the most effective ways to reduce your carbon
footprint is by improving energy efficiency. Since energy consumption is often
a major source of greenhouse gas emissions (particularly Scope 2 emissions),
enhancing energy efficiency can lead to immediate reductions.
- Upgrade
Lighting: Switch to energy-efficient lighting solutions such as LEDs.
LEDs use significantly less energy and last much longer than traditional
incandescent or fluorescent lights.
- Smart
Thermostats: Install smart thermostats to optimize heating,
ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. These devices learn your
schedule and adjust temperatures automatically, reducing energy waste.
- Energy-Efficient
Equipment: Invest in energy-efficient appliances and equipment that
meet the highest standards (e.g., Energy Star certified products). From
refrigerators to industrial machinery, using efficient models reduces
electricity consumption.
- Building
Insulation: Improve the insulation of your buildings to prevent energy
loss, particularly in colder months. This can reduce the amount of energy
required for heating and cooling.
- Conduct
Energy Audits: Regularly perform energy audits to identify areas of
waste or inefficiency. An energy audit can reveal opportunities to cut
down on energy usage by making simple adjustments or investments in new
technologies.
Switching to renewable energy sources is a powerful way to
significantly reduce your carbon footprint. Fossil fuels like coal and natural
gas produce a large portion of global carbon emissions, so replacing these
energy sources with renewables is critical for long-term sustainability.
- Install
Solar Panels: Depending on your location, installing solar panels can
provide a renewable source of electricity, reducing reliance on the grid
and lowering emissions from electricity use.
- Purchase
Green Energy: Many utility providers now offer options to purchase
green energy generated from wind, solar, or hydroelectric sources. Even if
you can’t install your own renewable energy systems, you can still reduce
your carbon footprint by switching to a green energy provider.
- Utilize
Wind Energy: If possible, consider small-scale wind turbines for
onsite renewable energy generation, especially in windy regions.
- Invest
in Offsets: When renewable energy options are not feasible onsite, you
can purchase carbon offsets by investing in renewable energy projects
elsewhere. This can help neutralize some of your carbon emissions.
Transportation is a major source of greenhouse gas
emissions, especially for businesses with large fleets or employees who
frequently commute or travel for business. Adopting more sustainable
transportation practices can significantly reduce your carbon footprint.
- Electric
Vehicles (EVs): If possible, transition company vehicles or personal
cars to electric vehicles (EVs). EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions and,
when paired with renewable energy, can drastically cut overall carbon
output.
- Carpooling
and Public Transport: Encourage employees to carpool, use public
transportation, or bike to work. Offering incentives such as public
transport subsidies or bike-to-work programs can help promote these
options.
- Remote
Work: Adopt remote work or hybrid work models where feasible. Reducing
daily commutes not only cuts emissions but can also increase employee
satisfaction and productivity.
- Optimize
Business Travel: Limit business travel by encouraging video
conferencing instead of in-person meetings, especially for international
travel, which has a large carbon footprint. When travel is necessary,
choose airlines or modes of transportation with lower emissions.
4. Reduce Waste
Waste contributes to carbon emissions throughout its
lifecycle—from production and transportation to disposal in landfills where it
releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Reducing waste and promoting
recycling can help lower your carbon footprint.
- Reduce,
Reuse, Recycle: Implement the three Rs in your organization or
household. Focus on reducing the amount of waste produced, reusing
materials where possible, and ensuring recyclable materials are properly
sorted and recycled.
- Composting:
Organic waste such as food scraps can be composted instead of being sent
to a landfill. Composting reduces methane emissions from landfills and
produces nutrient-rich soil for gardening or farming.
- Go
Paperless: In offices and businesses, transitioning to digital systems
reduces paper consumption and waste. E-invoicing, cloud storage, and
digital signatures are just a few ways to cut down on paper use.
- Eco-Friendly
Packaging: If your business involves shipping products, switch to
biodegradable or recyclable packaging. Consumers are increasingly
demanding sustainable packaging, and this can also help your company
reduce its environmental impact.
Your carbon footprint isn’t just about your direct
emissions; it also includes the emissions from your suppliers and the products
you purchase. Making sustainability a priority throughout your supply chain is
an effective way to reduce your overall impact.
- Evaluate
Supplier Sustainability: Choose suppliers who have committed to
reducing their carbon footprint and can provide evidence of sustainable
practices. Opt for suppliers that use renewable energy, low-carbon
transportation methods, and sustainable materials.
- Green
Procurement: Implement green procurement policies to prioritize the
purchase of sustainable products, such as recycled materials,
energy-efficient equipment, or eco-friendly chemicals.
- Collaborate
with Suppliers: Work with your suppliers to identify areas where
carbon emissions can be reduced. This can involve everything from
optimizing transport logistics to choosing suppliers that are
geographically closer to reduce shipping distances.
6. Engage Employees in Sustainability
Creating a culture of sustainability within your
organization can amplify efforts to reduce your carbon footprint. Employees can
be valuable contributors to your carbon reduction goals if they are engaged and
motivated to participate.
- Sustainability
Training: Provide training on sustainable practices, such as energy
conservation, waste reduction, and eco-friendly transportation options.
Make sure employees understand how their actions directly impact the
company’s carbon footprint.
- Green
Initiatives: Encourage employee participation in green initiatives
like recycling programs, energy-saving competitions, or volunteer work
with environmental organizations. Setting up "Green Teams"
within the organization can foster ongoing efforts.
- Incentivize Sustainable Behavior: Offer incentives for employees who contribute to sustainability efforts, such as awards, bonuses, or recognition programs. For instance, you could reward employees who reduce their commuting footprint or suggest effective sustainability improvements.
Finally, setting clear, actionable targets is crucial for
making measurable progress in reducing your carbon footprint. Without defined
goals, it’s difficult to gauge success or know where to focus your efforts.
- Short-Term
and Long-Term Goals: Establish both short-term (e.g., a 10% reduction
in emissions within a year) and long-term goals (e.g., reaching Net Zero
by 2050). These targets should be SMART—Specific, Measurable, Achievable,
Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Track
and Report Progress: Regularly track your emissions and compare them
to your targets. Reporting on your progress, both internally and
externally, helps maintain accountability and can boost stakeholder
confidence in your commitment to sustainability.
Conclusion: Join the Movement for a Sustainable Future
Reporting on climate change and your carbon footprint isn't
just a trend; it's a responsibility. By taking action to reduce your emissions
and transparently reporting your progress, you're not only demonstrating your
commitment to environmental responsibility, but also playing a vital role in
mitigating climate change and building a more sustainable future.
The journey to a greener future begins with understanding
your impact. By taking the steps outlined in this guide, you can embark on a
path of continuous improvement, inspiring your stakeholders and contributing to
a world where businesses are a force for positive change.
Ready to take the next step? Explore the
resources mentioned in this blog post to learn more about climate change
reporting and get started on your sustainability journey.
The future of business is sustainable. Let's make your
company part of the solution.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/co-why-is-carbon-dioxide-bad-4864246_V2-4ea7c0936b5a4cd3b8d4f2b41ec02f63.png)






















Comments
Post a Comment