Tech for Good: The Role of Technology in Sustainability Reporting
As the world grapples with unprecedented environmental, social, and governance (ESG) challenges, the imperative for transparency and accountability has never been more pressing. Sustainability reporting, once a niche concern, has emerged as a critical pillar of responsible business practice. Enter Technology – the game-changing catalyst poised to transform the sustainability reporting landscape. Leveraging innovations like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, Tech for Good initiatives are streamlining reporting processes, enhancing data accuracy, and amplifying stakeholder engagement. This convergence of technology and sustainability has the potential to propel organizations towards greater ESG performance, risk mitigation, and long-term resilience. In this blog, we explore the transformative role of technology in sustainability reporting, highlighting cutting-edge applications, best practices, and the future of Tech-enabled sustainable development.
Technology is revolutionizing the way businesses collect and
analyze data related to their sustainability performance. Gone are the days of
manual data entry and spreadsheets. Now, businesses can leverage powerful
software and platforms to automate data collection, track progress, and gain
valuable insights.
Data collection tools are the foundation of effective
sustainability reporting, providing the raw materials for analysis, insights,
and impactful action.
Energy Management Systems (EMS)
Purpose: EMS are software platforms designed to
monitor, manage, and optimize energy consumption within buildings and
facilities. They collect data on energy usage, identify areas of inefficiency,
and provide insights for reducing energy waste.
Key Features:
- Real-time monitoring: Track energy consumption in real-time, allowing for immediate identification of anomalies or unexpected spikes.
- Data visualization: Present energy usage data in easy-to-understand charts, graphs, and dashboards, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
- Alerts and notifications: Set up alerts for exceeding energy consumption thresholds or identifying potential issues.
- Control and optimization: Adjust energy settings, optimize HVAC systems, and implement energy-saving measures based on data insights.
- Examples: Building automation systems, smart lighting controls, and energy-efficient appliances are examples of EMS technologies that collect data for sustainability reporting.
Emissions Tracking Tools
Purpose: These tools are specifically designed
to measure and track greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from various sources within
a company's operations, supply chain, and even product lifecycle.
Key Features:
- Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions: Calculate emissions from direct sources (Scope 1), indirect sources (Scope 2), and the entire value chain (Scope 3), providing a comprehensive view of a company's carbon footprint.
- Emissions factors: Use standardized emissions factors to ensure accurate calculations and consistency across reporting frameworks.
- Data aggregation: Consolidate emissions data from multiple sources, providing a single, centralized view of a company's overall emissions.
- Reporting and analysis: Generate reports and visualizations that showcase emissions trends, identify hotspots, and inform strategies for reduction.
- Examples: Platforms like ClimatePartner, Ecologi, and CarbonNeutral offer emissions tracking tools, often with integrations for data collection from other systems.
Supply Chain Management Platforms
Purpose: These platforms help businesses manage
their supply chains, including tracking materials, products, and logistics.
They can also be used to collect data on the sustainability performance of
suppliers.
Key Features:
- Supplier data collection: Gather data on supplier emissions, social responsibility practices, and environmental certifications.
- Supply chain mapping: Visualize the entire supply chain, identifying key suppliers and potential areas for improvement.
- Performance monitoring: Track supplier performance against sustainability metrics and identify opportunities for collaboration on sustainability initiatives.
- Reporting and communication: Generate reports on supply chain sustainability performance and communicate findings to stakeholders.
- Examples: Platforms like EcoVadis and Sphera offer supply chain management features that can be used for sustainability reporting.
Purpose: These systems track and manage waste
generation, recycling, and disposal within a company's operations.
Key Features:
- Waste tracking: Monitor waste generation by type, source, and disposal method.
- Recycling and diversion: Track the amount of waste diverted from landfills through recycling and other methods.
- Waste audits: Conduct regular waste audits to verify data accuracy and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Reporting and analysis: Generate reports on waste generation, recycling rates, and disposal methods, providing insights for waste reduction strategies.
- Examples: Waste management software, RFID tags for waste containers, and mobile apps for waste reporting can all contribute to data collection for sustainability reporting.
Other Data Sources
Internal databases: Many companies have internal databases that contain relevant data for sustainability reporting, such as energy consumption records, fuel usage logs, and employee travel data.
Surveys and questionnaires: Surveys and
questionnaires can be used to gather data on employee engagement, customer
satisfaction, and other social and governance factors.
Publicly available data: Data on emissions
factors, industry benchmarks, and environmental regulations can be accessed
from publicly available sources, such as the EPA, the GHG Protocol, and the
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI).
Technology enables sophisticated data analysis and
visualization also allow businesses to identify trends, patterns, and areas for
improvement. Interactive dashboards, data modeling tools, and machine learning
algorithms can help businesses gain deeper insights from their data and make
more informed decisions. For example, a manufacturing company might use a
cloud-based platform to track its energy consumption, identify areas of
inefficiency, and set targets for reducing its carbon footprint. The platform
could then generate reports and visualizations that showcase progress towards
these targets, enabling the company to communicate its sustainability efforts
to stakeholders.
Remember: The specific data collection tools you
choose will depend on your company's industry, size, and specific
sustainability goals. It's important to select tools that are reliable,
accurate, and easy to integrate with your existing systems. By leveraging these
tools, you can build a strong foundation for accurate and impactful
sustainability reporting.
Transparency
and Communication: Technology for Engaging Stakeholders
Imagine a sustainability report that's not just a static document,
but a dynamic and interactive experience. That's the power of technology in
enhancing transparency and communication. By leveraging interactive platforms,
social media, and real-time reporting, businesses can engage stakeholders in
meaningful ways, building trust and fostering a shared understanding of their
sustainability journey.
Interactive Reporting Platforms: Beyond the Static Page
Purpose: Interactive reporting platforms go beyond
traditional PDF reports, offering a more engaging and immersive experience for
stakeholders. They allow users to explore data, access multimedia content, and
interact with the information in a dynamic way.
Key Features:
- Interactive dashboards: Display key performance indicators (KPIs), charts, and graphs, allowing users to drill down into data and explore different perspectives.
- Multimedia content: Embed videos, images, and infographics to enhance storytelling and make the report more visually appealing.
- Interactive maps: Visualize geographic data, such as the location of renewable energy projects or the impact of supply chain activities.
- Data filtering and customization: Allow users to filter data based on their interests and customize their view of the report.
- Examples: Platforms like Power BI, Tableau, and Qlik Sense offer interactive reporting capabilities that can be used for sustainability reporting.
Social Media and Digital Channels: Reaching a Wider
Audience
Purpose: Social media platforms and websites provide
a powerful channel for communicating sustainability initiatives and reporting
to a wider audience, including customers, employees, investors, and the general
public.
Key Features:
- Content sharing: Share sustainability reports, blog posts, infographics, and videos on social media platforms to reach a broader audience.
- Engagement and interaction: Use social media to engage with stakeholders, answer questions, and address concerns.
- Storytelling: Use social media to tell compelling stories about your company's sustainability journey, highlighting your achievements and challenges.
- Real-time updates: Share updates on your progress towards your sustainability goals, keeping stakeholders informed about your initiatives.
- Examples: Companies can use platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram to share their sustainability stories and engage with stakeholders.
Real-Time Reporting and Updates: Transparency in Action
Purpose: Real-time reporting enables businesses to
provide continuous updates on their sustainability performance, demonstrating
transparency and accountability.
Key Features:
- Live dashboards: Display key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, allowing stakeholders to track progress towards sustainability goals.
- Progress trackers: Visualize the impact of sustainability initiatives, showcasing the positive changes that are being made.
- Automated updates: Use technology to automate updates and notifications, ensuring that stakeholders are informed about the latest developments.
- Examples: Companies can use platforms like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio to create live dashboards that display real-time data on their sustainability performance.
Examples in Action:
A fashion company: Might use an interactive reporting
platform to showcase its commitment to sustainable materials and ethical
sourcing. The platform could include interactive maps that trace the origin of
its materials, videos that highlight its manufacturing processes, and data
visualizations that show its progress towards its sustainability goals. The
company could also use social media to share stories about its sustainable
practices and engage with customers on these issues.
A technology company: Might use a real-time dashboard
to track its energy consumption and carbon emissions. The dashboard could
display data on its renewable energy use, energy efficiency initiatives, and
progress towards its emissions reduction targets. The company could also use
its website and social media channels to communicate these updates to its
stakeholders.
Remember: The key to effective transparency and
communication is to engage stakeholders in meaningful ways. By leveraging
technology, businesses can create more interactive, accessible, and engaging
experiences that build trust and foster a shared understanding of their
sustainability journey.
Beyond
Reporting: Technology for Driving Sustainability
Technology isn't just about reporting; it's also driving
innovation in sustainable practices. From renewable energy to energy efficiency
and waste reduction, technology is enabling businesses to reduce their
environmental impact and create a more sustainable future. Here's a look at how
blockchain and AI are playing a transformative role:
Sustainable Technology Solutions: From Innovation to Action
Energy Efficiency: Energy efficiency technologies,
such as smart lighting systems, building automation, and energy-efficient
appliances, help businesses reduce their energy consumption and save costs.
These technologies can optimize energy use, reduce waste, and improve building
performance.
Waste Reduction: Waste reduction technologies, such
as waste-to-energy systems, recycling solutions, and composting programs, help
businesses minimize their environmental footprint. These technologies can
reduce landfill waste, recover valuable resources, and create new products from
waste materials.
Water Conservation: Water conservation technologies,
such as low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and smart irrigation
systems, help businesses reduce their water consumption and protect water
resources. These technologies can optimize water use, reduce waste, and improve
water efficiency.
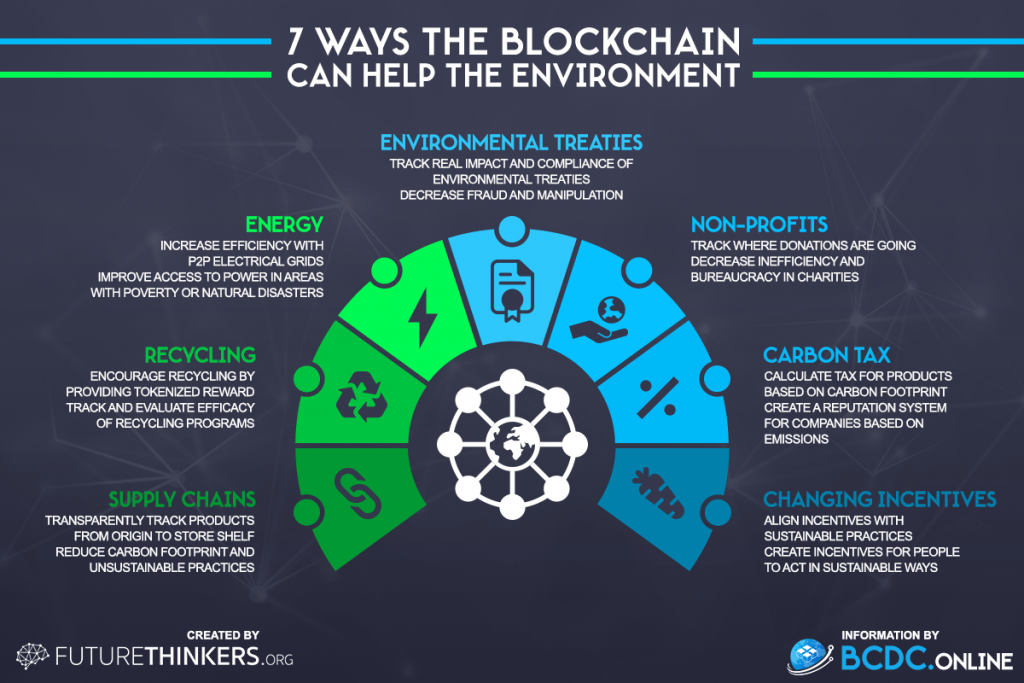
Blockchain for Transparency and Traceability
Purpose: Blockchain technology is a decentralized,
immutable ledger that can track the movement of assets, information, and
transactions across a network. In the context of sustainability, blockchain can
enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, ensuring that products
and materials are sourced ethically and sustainably.
Key Benefits:
- Traceability: Track the origin and journey of products and materials, providing a clear audit trail from source to consumer.
- Transparency: Provide a transparent and verifiable record of sustainability practices, reducing the risk of fraud or misrepresentation.
- Trust and accountability: Build trust with stakeholders by demonstrating the authenticity and sustainability of products and materials.
Examples:
Sustainable sourcing: Track the origin of sustainable
materials, such as recycled plastics or certified wood, ensuring that they meet
ethical and environmental standards.
Carbon offsetting: Track the purchase and retirement
of carbon offsets, ensuring that they are legitimate and verifiable.
Supply chain management: Track the movement of goods
and materials through the supply chain, identifying potential sustainability
risks and opportunities for improvement.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Optimization and
Efficiency
Purpose: AI can analyze vast amounts of data and
identify patterns and insights that humans might miss. This capability can be
harnessed to optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and improve resource
efficiency, leading to significant environmental and cost savings.
Key Applications:
- Energy management: AI-powered systems can analyze energy consumption data and identify opportunities for optimization, such as adjusting lighting schedules, optimizing HVAC systems, and predicting energy demand.
- Waste reduction: AI can analyze waste generation data and identify patterns that can inform waste reduction strategies. It can also be used to optimize recycling processes and improve waste management systems.
- Resource optimization: AI can help businesses
optimize resource use, such as water and materials, by identifying
inefficiencies and recommending solutions.
Smart buildings: AI-powered building management
systems can optimize energy consumption by adjusting lighting, HVAC, and other
systems based on real-time data and occupancy patterns.
Predictive maintenance: AI can analyze sensor data from equipment to predict potential failures, allowing for preventative maintenance and reducing downtime and energy waste.
Supply chain optimization: AI can optimize
transportation routes, reduce delivery times, and minimize fuel consumption,
leading to environmental and cost savings.
Blockchain and AI are just two examples of how technology is driving innovation in sustainability. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more transformative solutions that will help businesses reduce their environmental impact, enhance transparency, and create a more sustainable future.
Challenges
and Opportunities: Navigating the Path Forward
While technology offers tremendous potential for enhancing
sustainability reporting, it's not without its challenges. Businesses need to
be aware of these hurdles and embrace the opportunities to make the most of technology's
transformative power.
Challenges
Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy
of sensitive data is crucial. Businesses need to implement robust data security
measures, comply with relevant regulations (like GDPR), and ensure transparency
in how data is collected, used, and stored.
Access to Technology: Not all businesses have equal
access to technology. It's important to ensure that SMEs and businesses in
developing countries have the resources and support they need to leverage
technology for sustainability reporting. This might involve providing training,
grants, or access to affordable technology solutions.
The Evolving Landscape: Technology is constantly
evolving. Businesses need to stay informed about the latest advancements and
adapt their reporting practices accordingly. This requires ongoing learning,
investment in technology, and a willingness to embrace change.
Data Accuracy and Reliability: Ensuring the accuracy
and reliability of data is essential for meaningful sustainability reporting.
Businesses need to establish robust data management practices, validate data
sources, and implement quality control measures.
Integration and Interoperability: Integrating
different data collection tools and platforms can be challenging. Businesses
need to ensure that their systems are compatible and that data can be
seamlessly shared across different platforms.
Cost and Investment: Implementing sustainable
technology solutions and adopting new data collection tools can require
significant investment. Businesses need to carefully assess the costs and
benefits of different technologies and prioritize investments that align with
their sustainability goals.
Opportunities
Improved Transparency and Accountability: Technology
can enhance transparency and accountability by providing more detailed and
verifiable data on sustainability performance. This can build trust with
stakeholders and foster a more responsible business environment.
Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement: Technology can
enable more interactive and engaging sustainability reporting, allowing
stakeholders to explore data, access multimedia content, and participate in
conversations about sustainability. This can lead to greater understanding and
support for sustainability initiatives.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Technology can provide
businesses with valuable data insights that can inform better decision-making.
This can lead to more effective sustainability strategies, reduced
environmental impact, and improved resource efficiency.
Innovation and Collaboration: Technology can foster
innovation and collaboration in sustainability. Businesses can share data, best
practices, and solutions, driving collective progress towards a more
sustainable future.
New Business Models: Technology can enable new
business models that are based on sustainability principles. This could include
circular economy models, shared resource platforms, and sustainable supply
chains.
By embracing the opportunities and addressing the challenges, businesses can leverage technology to create a more sustainable future. This requires a commitment to innovation, collaboration, and responsible use of technology.
Conclusion: Embracing Technology for a Sustainable Future
In the ever-evolving landscape of sustainability reporting,
technology stands as a powerful ally, driving innovation, enhancing
transparency, and shaping a more sustainable future. From data collection tools
to blockchain, AI, and sustainable technology solutions, businesses have a
wealth of resources at their disposal to navigate the complexities of
sustainability reporting.
As we journey through the realms of interactive reporting
platforms, social media engagement, real-time reporting, and beyond, one thing
becomes clear: technology is not just a tool for data collection—it's a
catalyst for change. It empowers businesses to optimize energy consumption,
reduce waste, track sustainability performance, and foster collaboration
towards a shared goal of environmental responsibility.
Amidst the challenges of data security, accessibility, and evolving technologies, opportunities abound for improved transparency, stakeholder engagement, data-driven decision-making, innovation, and new business models. By embracing these opportunities, businesses can pave the way for a more sustainable future, where sustainability reporting is not just a compliance exercise, but a strategic imperative.
As we navigate the path forward, let us harness the
transformative power of technology to drive sustainability, foster
collaboration, and create a world where businesses thrive in harmony with the
planet. Together, we can build a more sustainable future—one innovation, one
report, and one step at a time.
Embrace technology, embrace sustainability, and let's
forge a path towards a greener, more sustainable tomorrow.







Comments
Post a Comment