Telling Your Sustainability Story: A Guide to Effective Reporting
In today’s business landscape, sustainability is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a critical component of long-term success and corporate responsibility. As stakeholders increasingly demand transparency and accountability, companies are expected to not only implement sustainable practices but also to effectively communicate their efforts through comprehensive sustainability reporting.
Sustainability reports serve as a vital tool for
organizations to showcase their commitment to environmental, social, and
governance (ESG) issues. These reports do more than just highlight a company’s
green initiatives; they tell a compelling story of progress, challenges, and
impact, providing a window into how the company is addressing the most pressing
issues of our time.
However, preparing an effective sustainability report is not
a straightforward task. It requires a deep understanding of your audience,
clear goal-setting, and careful selection of the right reporting framework.
Moreover, the report must be crafted in a way that not only presents data but
also weaves a narrative that resonates with stakeholders, builds trust, and
reinforces your company’s brand.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to
create a sustainability report that not only meets regulatory requirements but
also effectively tells your company’s unique sustainability story. Whether
you’re new to sustainability reporting or looking to refine your approach, this
blog will provide you with the tools and insights needed to communicate your
sustainability journey with clarity and impact.
Step 1:
Define Your Scope and Goals
1.1 Identifying Material Issues
- Conducting a Materiality Assessment: A materiality assessment helps you identify your most important sustainability issues. Here's a simple process:
- Identify Stakeholders: List the key stakeholders who have an interest in your organization's sustainability performance, including investors, customers, employees, suppliers, communities, and NGOs.
- Gather Stakeholder Input: Engage with stakeholders to understand their priorities and concerns related to sustainability. You can use surveys, interviews, focus groups, or workshops to gather this input.
- Identify Potential Issues: Based on stakeholder input and your own knowledge of your operations, create a list of potential sustainability issues. These could include topics like climate change, water management, waste reduction, human rights, labor practices, and diversity and inclusion.
- Prioritize Issues: Prioritize the issues based on their potential impact on your organization and stakeholders. Consider factors like the severity of the impact, the likelihood of occurrence, and the potential for reputational damage.
- Document Your Findings: Document the results of your materiality assessment, including the identified issues, the stakeholder input, and the prioritization criteria.
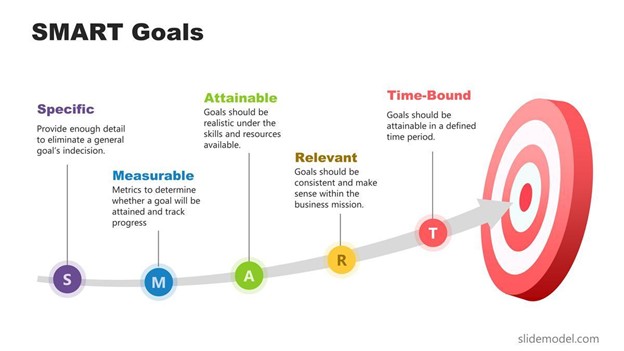
SMART Goals: When setting sustainability goals, use the SMART framework:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve.
- Measurable: Establish metrics to track progress towards your goals.
- Achievable: Set goals that are realistic and achievable within your organization's capabilities.
- Relevant: Ensure that your goals are aligned with your organization's overall sustainability strategy and priorities.
- Time-Bound: Set deadlines for achieving your goals.
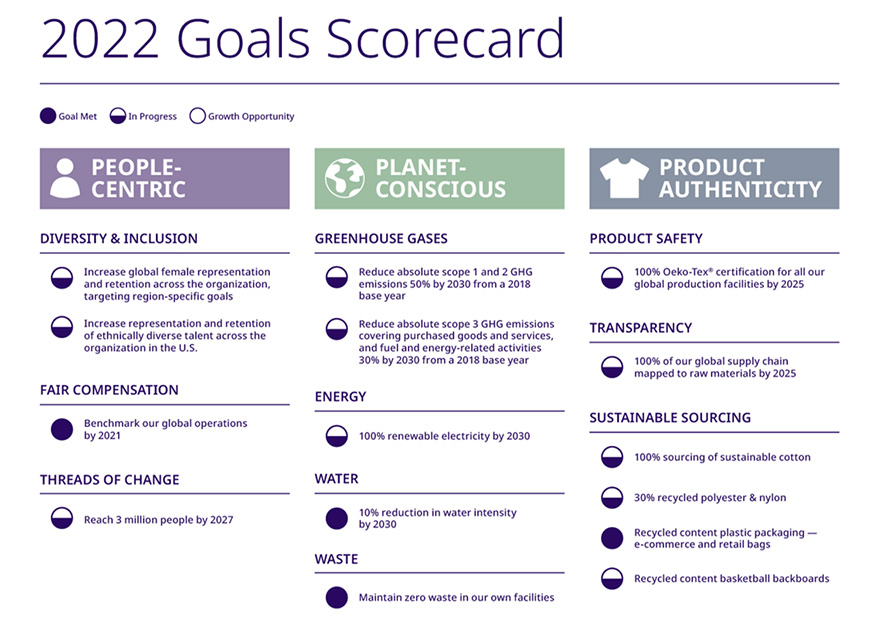
- Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Reduce scope 1, 2, and 3 greenhouse gas emissions by 20% by 2025.
- Increase Renewable Energy Use: Source 50% of electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
- Improve Water Efficiency: Reduce water consumption by 15% per unit of production by 2028.
- Enhance Employee Engagement: Increase employee satisfaction scores to 90% by 2026.
- Time Period: Define the time period covered by your report. This could be a fiscal year, a calendar year, or a specific period related to your goals.
- Geographic Scope: Specify the geographic locations included in your report. This could be your global operations, specific regions, or individual facilities.
- Operations/Activities: Clearly define the operations or activities covered in your report. This could include your entire value chain, specific product lines, or specific business units.
Example Scope:
- Time Period: Fiscal year 2023
- Geographic Scope: Global operations
- Operations/Activities: Manufacturing, supply chain, and distribution
By carefully defining your scope and goals, you'll create a
focused and impactful sustainability report that showcases your organization's
commitment to positive change.
Step 2:
Gather and Analyze Data
2.1 Collect Relevant Data
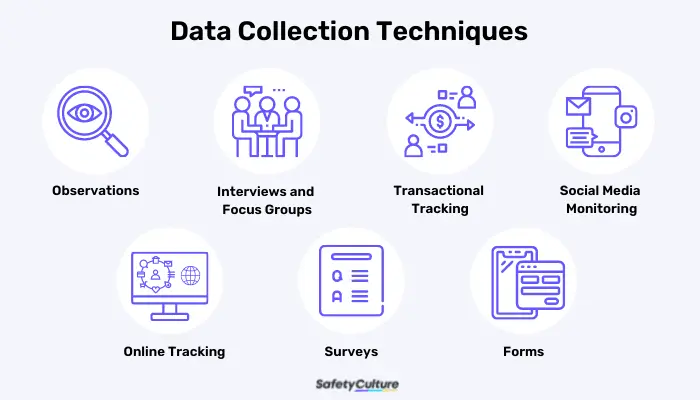
- Identify Data Sources: Identify the sources where you can gather data related to your material issues and goals. These sources could include:
- Internal Systems: Your existing accounting, inventory, energy management, and other systems may contain relevant data.
- Supply Chain Partners: Engage with your suppliers, distributors, and other partners to gather data on their sustainability performance.
- Industry Databases: Utilize industry databases and resources to access benchmark data and best practices.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Conduct surveys or questionnaires to gather data from employees, customers, or other stakeholders.
- Interviews and Focus Groups: Conduct interviews or focus groups to gather qualitative data and insights.
- Data Collection Plan: Develop a data collection plan that outlines the specific data you need, the sources you will use, and the methods you will employ.
- Data Collection Tools: Utilize data collection tools such as spreadsheets, databases, or specialized software to organize and manage your data.
- Data Validation: Validate your data to ensure its accuracy and reliability. This could involve:
- Cross-Checking: Compare data from different sources to verify consistency.
- Data Auditing: Conduct audits to ensure data integrity and completeness.
- Data Reconciliation: Reconcile data from different systems or sources to eliminate discrepancies.
- Data Quality Control: Implement data quality control measures to prevent errors and ensure data consistency.
- Data Standardization: Use consistent metrics and units of measurement across your data to ensure comparability.
2.3 Analyze Your Data
- Data Visualization: Use charts, graphs, tables, and infographics to visualize your data and make it more understandable.
- Trend Analysis: Identify trends and patterns in your data over time.
- Benchmarking: Compare your data to industry benchmarks or best practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigate the root causes of any significant deviations from your goals.
- Data Interpretation: Interpret your data and draw conclusions about your organization's sustainability performance.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Analyze your emissions data to identify the largest sources of emissions and track progress towards your reduction goals.
- Energy Consumption: Analyze your energy consumption data to identify opportunities for efficiency improvements and renewable energy adoption.
- Water Consumption: Analyze your water consumption data to identify areas where you can reduce water usage and implement water conservation measures.
- Waste Management: Analyze your waste generation and diversion data to track progress towards your waste reduction goals.
By gathering and analyzing data rigorously, you can gain a
deeper understanding of your organization's sustainability performance,
identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate your commitment to positive
change.
Step 3:
Structure Your Report
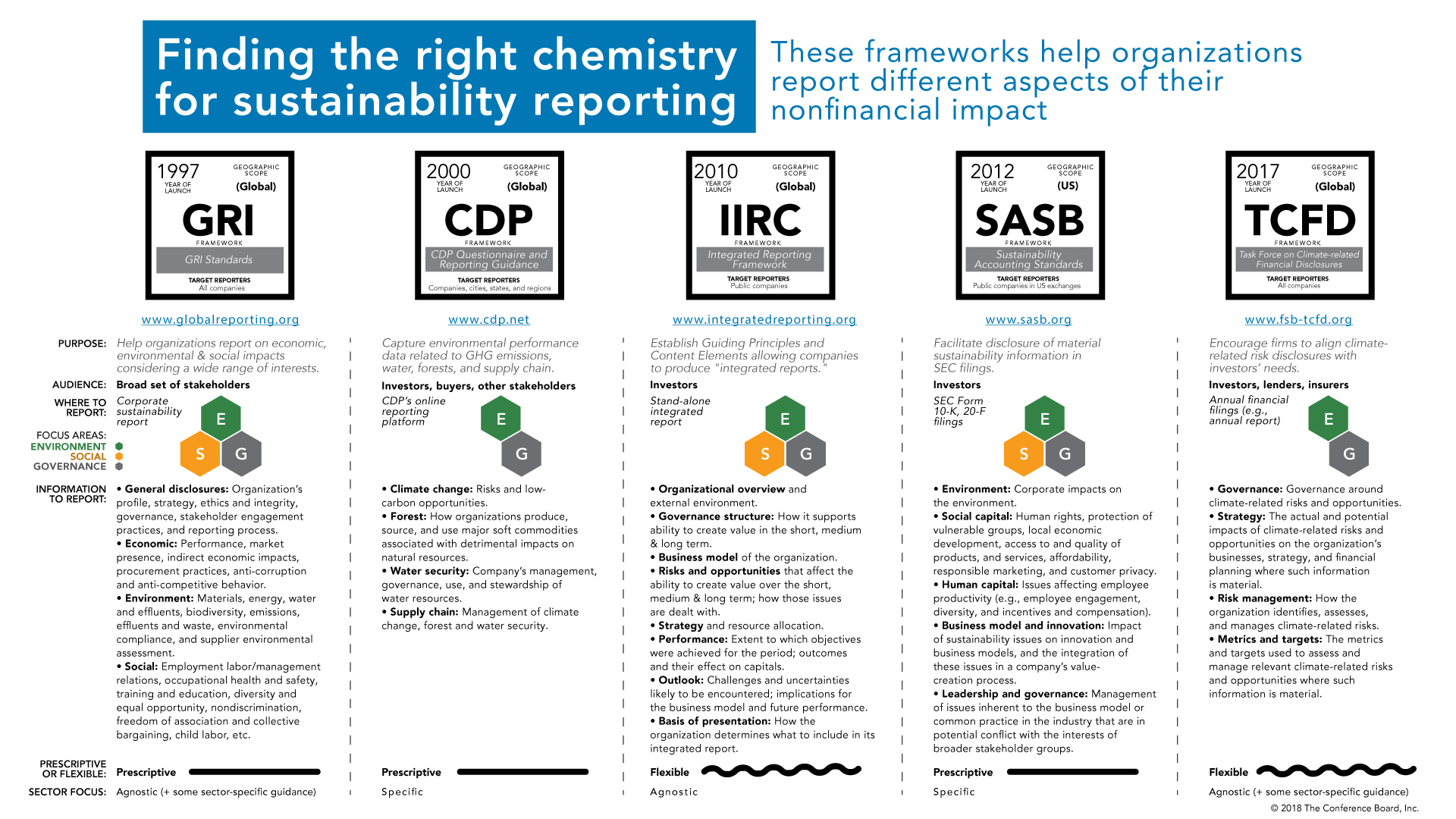
3.1 Choose a Reporting Framework
A reporting framework provides guidance on reporting standards, best practices, and disclosure requirements for sustainability reporting. It helps ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability across reports.
Some popular sustainability reporting frameworks include:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): A widely recognized framework that provides comprehensive guidelines for reporting on economic, environmental, and social performance.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): A framework that focuses on industry-specific sustainability disclosures that are relevant to investors.
- Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): A framework that provides guidance on disclosing climate-related risks and opportunities.
- Integrated Reporting Framework (IIRC): A framework that encourages organizations to integrate financial and non-financial information in their reporting.
Choosing the Right Reporting Framework for Sustainability Reporting
- Identify Your Reporting Needs
- Materiality Assessment: Start by conducting a materiality assessment to identify the most significant sustainability issues for your organization. This will help you understand which aspects of sustainability are most relevant and impactful for reporting.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Consider the interests and expectations of your stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, regulators, and the community. Understanding their priorities will help you align your reporting framework with their needs.
- Industry Standards: Take into account industry-specific standards and regulations that may apply to your organization. Some industries have specific reporting requirements that you need to adhere to.
- Consider Reporting Framework Options
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): GRI is one of the most widely used sustainability reporting frameworks globally. It provides comprehensive guidelines for reporting on economic, environmental, and social performance, offering a flexible and standardized approach to sustainability reporting.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): SASB focuses on industry-specific sustainability disclosures that are material to investors. It provides standards tailored to specific industries, helping organizations report on financially material sustainability issues.
- Integrated Reporting Framework (IIRC): IIRC promotes integrated reporting, encouraging organizations to communicate how their strategy, governance, performance, and prospects create value over time. It emphasizes the connectivity between financial and non-financial information.
- Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): TCFD provides recommendations for disclosing climate-related financial risks and opportunities. It helps organizations assess and disclose the financial implications of climate change on their business.
- Align with Organizational Objectives
- Strategic Alignment: Choose a reporting framework that aligns with your organization's strategic objectives and sustainability goals. The framework should help you communicate your sustainability performance effectively and drive positive change.
- Industry Relevance: Consider the industry-specific focus of the reporting framework and ensure it addresses the key sustainability issues relevant to your sector. Industry-specific frameworks like SASB can provide more tailored guidance.
- Reporting Scope and Complexity
- Reporting Scope: Determine the scope of your sustainability reporting, including the reporting boundaries, geographic coverage, and operational activities included. Ensure that the chosen framework aligns with the scope of your reporting.
- Reporting Complexity: Consider the complexity of the reporting framework and the level of detail it requires. Choose a framework that strikes a balance between comprehensive reporting and practicality for your organization.
- Reporting Maturity and Resources
- Reporting Maturity: Assess your organization's reporting maturity level. If you are new to sustainability reporting, consider frameworks that provide guidance for first-time reporters, such as GRI's 'GRI Standards for Beginners.'
- Resource Considerations: Evaluate the resources, expertise, and capacity available within your organization for sustainability reporting. Choose a framework that matches your resource capabilities and reporting needs.
- Stakeholder Expectations and Transparency
- Stakeholder Expectations: Consider the expectations of your key stakeholders, such as investors, customers, employees, and regulators. Choose a reporting framework that meets their information needs and enhances transparency.
- Transparency and Disclosure: Select a framework that promotes transparency and disclosure of relevant sustainability information. Ensure that the framework enables you to communicate your sustainability performance effectively to stakeholders.
By following these detailed guidelines, you can choose the right reporting framework that aligns with your organization's sustainability goals, meets stakeholder expectations, and enhances transparency in sustainability reporting.
3.2 Develop a Logical Structure
- Clear and Concise: Structure your report in a clear and concise manner, using headings, subheadings, and visuals to enhance readability.
- Logical Flow: Organize your report in a logical flow, starting with an introduction and overview, followed by sections that address your material issues, goals, performance data, initiatives, and future plans.
- Storytelling Approach: Consider using a narrative approach to tell your sustainability story. Use engaging language and compelling visuals to connect with your audience.
Example Structure:
- Introduction: Provide an overview of your organization's sustainability commitment and reporting approach.
- Material Issues: Describe the sustainability issues that are most relevant to your organization.
- Goals and Targets: Outline your sustainability goals and targets.
- Performance Data: Present data on your performance against your goals.
- Initiatives and Programs: Highlight your sustainability initiatives and programs.
- Future Plans: Describe your plans for future sustainability efforts.
- Conclusion: Summarize your key findings and reiterate your commitment to sustainability.
3.3 Include Key Sections
- Letter from the CEO or Sustainability Statement: Include a letter from your CEO or a sustainability statement that outlines your organization's commitment to sustainability and its importance to your business.
- Governance and Management: Describe your organization's governance structure and management systems related to sustainability.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Outline your approach to engaging with stakeholders on sustainability issues.
- Risk and Opportunities: Identify and assess the sustainability-related risks and opportunities facing your organization.
- Metrics and Targets: Present a clear and consistent set of metrics and targets that measure your sustainability performance.
- Performance Data: Provide data on your performance against your metrics and targets.
- Initiatives and Programs: Highlight your sustainability initiatives and programs, including their impact and results.
- Future Plans: Describe your plans for future sustainability efforts.
By carefully structuring your report, you'll create a
well-organized and informative document that effectively communicates your
organization's sustainability story.
Step 4:
Engage Stakeholders
4.1 Identify Your Audience
Understand who your key
stakeholders are, including:
- Investors: They are interested in your financial performance and how sustainability impacts your long-term value.
- Customers: They want to know about your environmental and social impact, and how your products or services align with their values.
- Employees: They are interested in your commitment to ethical and responsible practices, and how sustainability affects their work environment.
- Suppliers: They want to understand your expectations for their sustainability performance and how you are working to create a sustainable supply chain.
- Communities: They are interested in your impact on the local environment and society, and how you are contributing to their well-being.
- Regulators: They are interested in your compliance with environmental and social regulations.
- Tailor your message: Tailor your report to the specific interests and concerns of each stakeholder group. For example, you might focus on financial performance for investors, environmental impact for customers, and employee well-being for employees.
4.2 Use Clear and Concise Language
- Avoid jargon and technical terms: Use simple, clear language that everyone can understand. Avoid using technical jargon or complex terminology that might confuse your audience.
- Focus on the story: Tell a compelling story about your sustainability journey, highlighting your achievements, challenges, and future plans. Use engaging language and compelling visuals to bring your story to life.
- Use active voice: Use active voice to make your report more dynamic and engaging. For example, instead of saying "The company reduced its emissions," say "The company reduced its emissions by 15%."
4.3 Use Visuals to Enhance Engagement
- Charts and graphs: Use charts and graphs to present data in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand way.
- Infographics: Create infographics to illustrate complex information in a simple and engaging way.
- Images and videos: Use images and videos to bring your sustainability story to life. Show real-life examples of your efforts and the impact they are having.
- Interactive elements: Consider incorporating interactive elements, such as maps, timelines, or quizzes, to make your report more engaging and interactive.
Example Engagement Strategies
- Executive Summary: Include a concise executive summary that highlights your key sustainability achievements and future plans.
- Case Studies: Showcase specific examples of your sustainability initiatives and their impact.
- Testimonials: Include testimonials from employees, customers, or community members who have been positively impacted by your sustainability efforts.
- FAQs: Address common questions about your sustainability performance and reporting approach.
Step 5:
Publish and Disseminate Your Report
5.1 Choose a Publication Format
- PDF Document: A traditional and widely accepted format for sustainability reports. It offers a consistent and easily downloadable format for stakeholders.
- Online Platform: A digital platform that allows for interactive elements, multimedia content, and easy sharing. Examples include websites, online reporting platforms, and digital flipbooks.
- Interactive Website: A dedicated website for your sustainability report, allowing for more in-depth content, multimedia features, and user-friendly navigation.
Combine your sustainability report with your annual financial report, showcasing the interconnectedness of your financial and non-financial performance in a integrated reporting methodology.
5.2 Publish Your Report
- Website: Make your report easily accessible on your organization's website, dedicated sustainability page, or a specific reporting section.
- Social Media: Share your report on your social media channels, using relevant hashtags and engaging captions to reach a wider audience.
- Press Release: Issue a press release announcing the publication of your report, highlighting key findings and achievements.
- Email Distribution: Send your report to key stakeholders via email, including investors, customers, employees, and media outlets.
5.3 Promote Your Report
- Targeted Outreach: Reach out to specific stakeholders, such as investors, analysts, and industry influencers, to share your report and engage in discussion.
- Media Relations: Engage with media outlets to promote your report and share your sustainability story.
- Events and Presentations: Present your report at industry events, conferences, and webinars to share your insights and engage with stakeholders.
- Social Media Campaign: Create a social media campaign to promote your report, using engaging visuals, hashtags, and interactive elements.
- Public Relations: Engage in public relations activities to raise awareness of your report and your sustainability efforts.
5.4 Accessibility and Inclusivity:
- Multiple Languages: Translate your report into multiple languages to reach a wider audience.
- Accessible Formats: Provide your report in accessible formats, such as large print, audio, or braille, to cater to individuals with disabilities.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure your report is optimized for mobile devices, allowing stakeholders to access it easily on their smartphones or tablets.
Example Dissemination Strategies:
- Launch Event: Host a launch event to announce the publication of your report, inviting key stakeholders and media representatives.
- Social Media Contest: Run a social media contest to promote your report and encourage engagement.
- Webinar Series: Host a series of webinars to discuss your report and its key findings with stakeholders.
- Partnerships: Partner with industry organizations or NGOs to promote your report and reach a broader audience.
By effectively publishing and disseminating your sustainability report, you can ensure that your message reaches your intended audience and that your sustainability efforts are recognized and celebrated.
Step 6:
Continuously Improve
6.1 Review and Update Your Report
- Regular Reviews: Review your sustainability report regularly, ideally on an annual basis, to ensure it remains current and relevant.
- Data Updates: Update your report with the latest data, including performance metrics, initiatives, and achievements.
- Content Updates: Review and update the content of your report to reflect any changes in your organization's sustainability strategy, goals, or performance.
- Framework Updates: Stay informed about updates to reporting frameworks, such as GRI, SASB, or TCFD, and make necessary adjustments to your report.
6.2 Seek Feedback
- Stakeholder Feedback: Gather feedback from your key stakeholders, including investors, customers, employees, suppliers, and communities, on the content and presentation of your report.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Use surveys, questionnaires, focus groups, or online feedback forms to collect stakeholder feedback.
- Feedback Analysis: Analyze stakeholder feedback to identify areas for improvement and incorporate their suggestions into future reports.
6.3 Embrace Continuous Learning
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on emerging sustainability trends, best practices, and reporting standards.
- Industry Events: Attend industry events, conferences, and webinars to learn from experts and share best practices.
- Professional Development: Invest in professional development opportunities to enhance your knowledge and skills in sustainability reporting.
- Benchmarking: Benchmark your sustainability performance against industry peers and best practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Innovation and Experimentation: Explore new and innovative ways to report on sustainability, such as using interactive elements, multimedia content, or virtual reality.
- Sustainability Committee: Establish a sustainability committee to oversee your reporting process, review your report regularly, and identify areas for improvement.
- Sustainability Reporting Training: Provide training to your team on sustainability reporting best practices, data collection, and stakeholder engagement.
- Reporting Calendar: Develop a reporting calendar to ensure that your report is updated and published on a regular schedule.
- Feedback Loop: Create a feedback loop to gather stakeholder input and incorporate their suggestions into future reports.
By continuously improving your sustainability reporting
process, you can ensure that your report remains relevant, informative, and
impactful, demonstrating your organization's commitment to sustainability and
building trust with stakeholders.
Remember:
- Be Transparent and Honest: Provide accurate and reliable
data, and be transparent about your reporting methodology.
- Focus on Impact: Highlight the positive impact of your sustainability efforts and demonstrate how they contribute to your organization's success.
- Tell a Compelling Story: Use your report to tell a compelling story about your organization's commitment to sustainability and inspire action. Craft your story to resonate with their specific needs and perspectives. For example, investors may be interested in financial performance, while customers may be more interested in environmental impact. Highlight the positive impact of your sustainability efforts on people, communities, and the environment. Show how your actions are making a difference.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively integrating materiality and
scope in sustainability reporting is essential for organizations aiming to
create impactful and credible reports. As companies navigate the complexities
of defining what is material and determining the appropriate scope, they must
balance a range of considerations, from stakeholder expectations to data
collection challenges and competitive sensitivities.
By adopting best practices, engaging stakeholders,
leveraging technology, and staying adaptable to evolving circumstances,
companies can overcome these challenges and produce sustainability reports that
are not only comprehensive but also truly reflective of their environmental,
social, and governance impacts.



















Comments
Post a Comment