The Triple Bottom Line: A Framework for Sustainable Business Success
In today's world, businesses are increasingly being held accountable for their environmental and social impact. Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it's a critical factor in business success. But how can businesses effectively integrate sustainability into their operations and achieve long-term value?
The Triple Bottom Line (TBL) framework provides a powerful
and comprehensive approach to sustainability, emphasizing the
interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic factors. This guide
will provide a clear and accessible overview of the TBL, explaining what it is,
why it's important, and how businesses can use it to achieve sustainable
success.
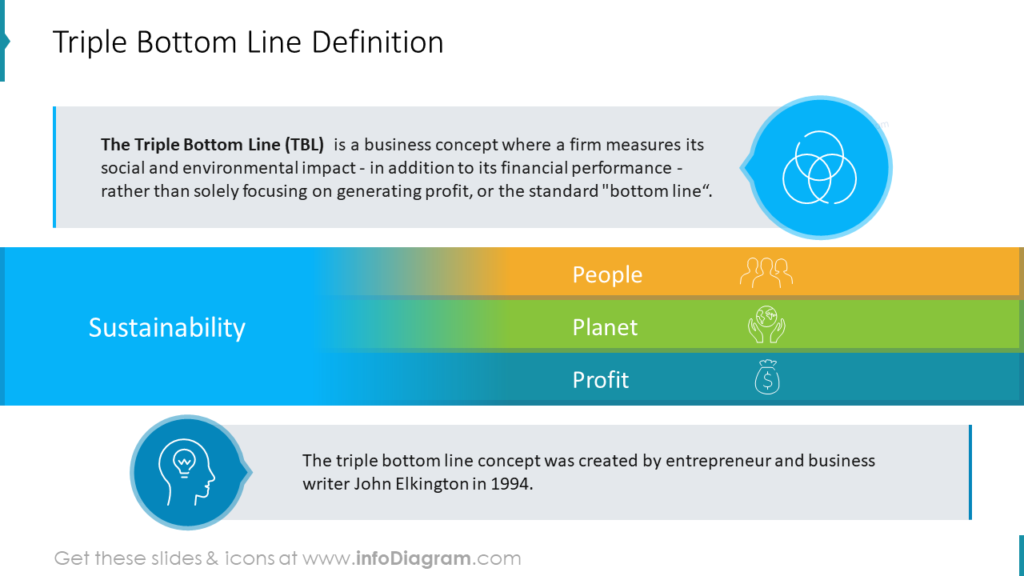
1. What is the Triple Bottom Line?
The Triple Bottom Line (TBL) is a framework that encourages
businesses to consider the impact of their actions on three key areas:
Planet (Environmental): This pillar focuses on minimizing
the company's environmental impact. This includes reducing greenhouse gas
emissions, conserving water and energy, promoting biodiversity, and reducing
waste. Companies committed to the “planet” part of the TBL take proactive steps
to ensure their operations are sustainable and environmentally friendly.
People (Social): This pillar emphasizes ethical and
responsible practices that benefit employees, communities, and society as a
whole. This includes fair labor standards, employee well-being, community
engagement, ethical sourcing, and diversity and inclusion initiatives. Businesses that prioritize the “people”
aspect of the TBL aim to improve the well-being of their employees, customers,
and the broader community.
Profit (Economic): This pillar acknowledges the importance
of financial sustainability and profitability. However, it emphasizes that
profits should be achieved in a way that is consistent with the other two
pillars, ensuring that the business operates in a way that is both profitable
and sustainable. The goal is not just
short-term financial gain but long-term sustainable growth that is achieved
without compromising social and environmental responsibilities. This pillar
ensures that businesses are economically viable while adhering to ethical
practices.
The TBL recognizes that these three pillars are
interconnected and that a focus on one pillar can positively impact the others.
For example, investing in renewable energy can reduce a company's environmental
impact (Planet) while also creating new jobs and boosting economic growth
(Profit).
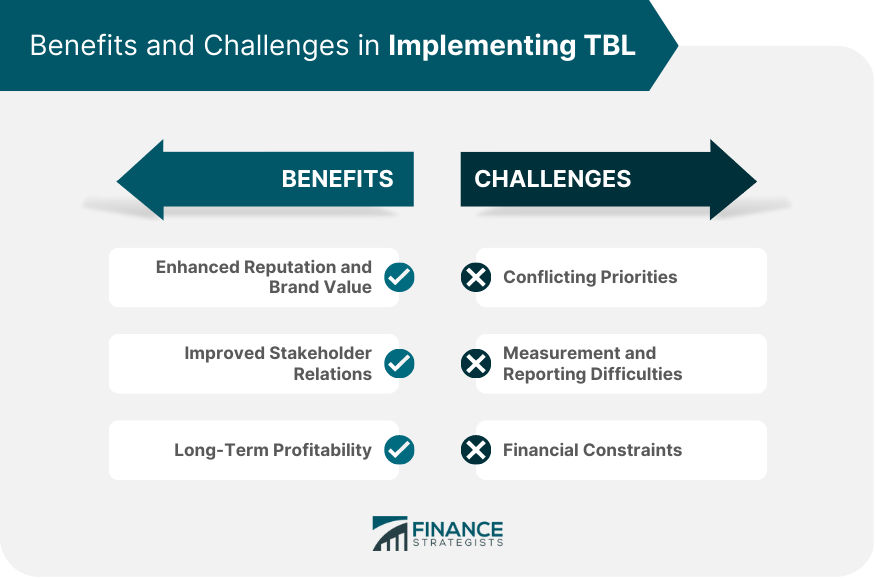
2. Why is the Triple Bottom Line Important?
The Triple Bottom Line is becoming increasingly important for businesses for several reasons:
- Enhanced
Brand Reputation: Businesses that embrace the TBL are often seen
as more trustworthy and ethical, which can attract customers who value
sustainability and enhances brand reputation.
- Reduced
Risks: By addressing environmental and social issues, businesses
can reduce their exposure to risks, such as regulatory fines, reputational
damage, and legal challenges.
- Improved
Employee Engagement: Employees are increasingly attracted to
companies that prioritize sustainability and social responsibility. This
can lead to higher employee morale, retention, and productivity.
- Access
to New Markets and Sustainable Success: The demand for
sustainable products and services is growing rapidly, creating new
opportunities for businesses that embrace the TBL. Businesses that
prioritize social and environmental sustainability are often more
resilient. They manage risks better, innovate more effectively, and
position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly conscious
marketplace.
- Attracting
Investors: Investors are increasingly looking for companies with
strong sustainability practices. The TBL can help businesses demonstrate
their commitment to sustainability and attract investors who are seeking
long-term value. Regulatory
policies around environmental and social governance (ESG) are becoming
stricter, and businesses that embrace the TBL are better prepared for
future regulations.
3. What to Include in Sustainability Efforts Using the Triple Bottom Line
Here are some specific example of key areas of how businesses can
incorporate the Triple Bottom Line into their sustainability efforts:
Planet (Environmental)
- Reduce
Energy Consumption: Implement energy-efficient technologies,
promote telecommuting, and use renewable energy sources.
- Minimize
Waste: Reduce packaging, recycle materials, and compost organic
waste.
- Conserve
Water: Install low-flow fixtures, use rainwater harvesting
systems, and implement water-efficient landscaping.
- Promote
Biodiversity: Protect natural habitats, support sustainable
forestry practices, and reduce pollution.
- Supply
Chain Practices: Encourage sustainability practices among suppliers
and partners to extend your environmental impact.
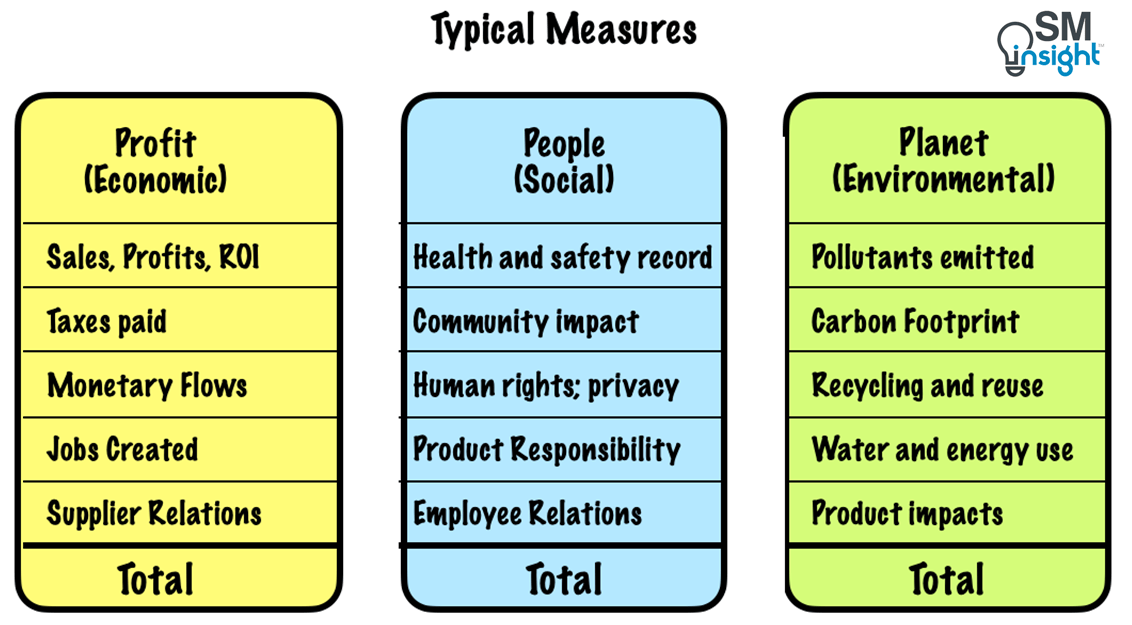
To fully embrace the Triple Bottom Line, companies should track and report on metrics from all three categories and evaluate their interconnectedness. For example, by investing in energy efficiency (Planet), a company can reduce operating costs (Profit) while contributing to a cleaner environment and creating jobs in green energy (People). For example, the following metrics measure a company’s environmental impact, including resource consumption and efforts to mitigate ecological damage.
- Carbon
Footprint:
- Total
Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHG): Measured in tons of CO₂ equivalent
emitted by the company.
- Carbon
Intensity: GHG emissions per unit of revenue or per product sold.
- Energy
Usage:
- Energy
Consumption: Total energy used, measured in megawatts (MW) or
kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Percentage
of Renewable Energy: The share of energy the company sources from
renewable resources like wind, solar, and hydro.
- Water
Usage:
- Water
Consumption: Total water used, measured in liters or cubic meters.
- Water
Recycling Rate: Percentage of water that is reused in the company's
processes.
- Waste
Management:
- Waste
Generation: Total amount of waste produced, measured in tons.
- Waste
Diversion Rate: Percentage of waste that is diverted from landfills
to be recycled or reused.
- Resource
Efficiency:
- Material
Intensity: The amount of raw material used per product unit.
- Sustainable
Sourcing: Percentage of raw materials that are sustainably sourced
(e.g., certified wood, fair-trade coffee).
People (Social)
- Fair
Labor Practices: Pay fair wages, provide safe working conditions,
and promote employee well-being.
- Community
Engagement: Support local communities, invest in education,
healthcare and wellness, and promote social responsibility.
- Diversity
and Inclusion: Create a diverse and inclusive workplace that
values all employees to build a positive corporate culture.
- Ethical
Sourcing: Ensure that suppliers adhere to ethical and sustainable
practices.
- Employee
Satisfaction and Retention:
- Employee
Turnover Rate: The percentage of employees leaving the company within
a given period.
- Employee
Engagement Score: Survey-based metric reflecting employees’
commitment and motivation.
- Average
Length of Employment: Measures how long employees stay with the
company, reflecting job satisfaction.
- Diversity
and Inclusion:
- Diversity
Ratio: The percentage of women, minorities, or other underrepresented
groups in the workforce or leadership positions.
- Equal
Pay Ratio: Compares pay levels between male and female employees in
similar roles.
- Training
and Development:
- Training
Hours per Employee: Measures how much time companies invest in
employee skills and development.
- Internal
Promotion Rate: Percentage of leadership roles filled by internal
hires.
- Community
Engagement:
- Volunteer
Hours: Total hours employees volunteer for community service or
charity work.
- Donations
or Community Investment: Amount of money or in-kind donations to
social causes and local communities.
- Health
and Safety:
- Injury
Rate: The number of workplace accidents or injuries per 1,000
employees.
- Employee Health and Wellness Programs Participation: Percentage of employees enrolled in company health initiatives.
Profit (Economic)
- Invest
in Sustainable Products and Services: Develop innovative products
and services that meet the needs of a growing market for sustainability. Build a business model that balances
profitability with ethical and sustainable practices.
- Optimize
Resource Use: Reduce waste, improve efficiency, and implement
circular economy practices.
- Invest
in Renewable Energy: Transition to renewable energy sources to
reduce costs and improve environmental performance.
- Impact
Investing: Invest in companies and projects that have a positive
social and environmental impact.
- Revenue
and Profitability:
- Revenue
Growth Rate: Year-on-year percentage growth in sales or revenue.
- Net
Profit Margin: Net income as a percentage of total revenue,
reflecting overall profitability.
- Return
on Investment (ROI):
- Return
on Equity (ROE): Measures profitability relative to shareholder
equity.
- Return
on Assets (ROA): Measures how efficiently a company uses its assets
to generate profit.
- Cost
Savings from Sustainability Initiatives:
- Energy
Savings: Reduction in energy costs due to energy efficiency measures
(e.g., LED lighting, solar panels).
- Waste
Reduction Savings: Cost savings resulting from reduced waste
production and improved waste management practices.
- Sustainable
Product Revenue:
- Percentage
of Revenue from Sustainable Products: The portion of total revenue
derived from products or services that contribute to social or
environmental goals (e.g., eco-friendly products, renewable energy
solutions).
- Innovation
and Research Investment:
- R&D
Spending as a Percentage of Revenue: Reflects investment in
innovation, especially in sustainable technologies or solutions.
- Sustainability
Innovation Index: The number of new sustainable products or processes
introduced per year.
Monitoring these metrics helps companies ensure their social, environmental, and financial efforts are aligned, driving sustainable growth and positive impact across all areas of their operations.
4. The Triple Bottom Line in Action
Many businesses are successfully using the Triple Bottom
Line to achieve sustainability and drive business success. Here are a few
examples of companies that have successfully implemented the Triple Bottom
Line (TBL) approach, balancing their impact across people, planet,
and profit:
1. Patagonia (Outdoor Apparel)
- People:
Patagonia is known for its ethical treatment of workers throughout its
supply chain. The company actively promotes fair wages, worker well-being,
and transparent labor practices. It also donates 1% of sales to
environmental organizations.
- Planet:
Sustainability is at the core of Patagonia’s operations. The company uses
recycled materials in its products, runs initiatives to repair and reuse
clothing, and encourages customers to recycle or resell their used gear.
They’re committed to reducing their carbon footprint and advocate for
environmental conservation.
- Profit:
Despite its sustainability commitments, Patagonia remains profitable. Its
business model emphasizes high-quality, long-lasting products, which
appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Patagonia’s loyal customer
base drives its financial success, proving that profitability can go hand
in hand with ethical and environmental responsibility.
2. Unilever (Consumer Goods)
- People:
Unilever has focused on improving the livelihoods of farmers, suppliers,
and workers across its supply chain. The company promotes gender equality
and fair labor practices and is committed to enhancing the well-being of
over 1 billion people through health and hygiene initiatives.
- Planet:
Unilever has set ambitious environmental goals, such as cutting its
environmental impact in half by reducing waste, energy use, and carbon
emissions. The company works toward sourcing 100% of its agricultural
materials sustainably and continuously invests in eco-friendly product
innovations.
- Profit:
Unilever has shown that sustainable business practices can enhance
profitability. Sustainable brands within the company’s portfolio, like
Dove and Ben & Jerry’s, contribute to strong financial performance
while addressing critical social and environmental issues.
3. Tesla (Automotive and Energy)
- People:
Tesla focuses on creating high-quality jobs and supporting the transition
to sustainable energy. It also encourages skills development in clean
energy and manufacturing and maintains a global workforce.
- Planet:
Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable
energy. By producing electric vehicles, solar panels, and battery storage
solutions, Tesla significantly reduces carbon emissions associated with
traditional energy and transportation industries. The company continuously
invests in technologies that reduce its environmental impact.
- Profit:
Tesla’s profitability is evident in its dominance of the electric vehicle
market. Its focus on sustainability has become a key part of its brand
identity, attracting environmentally conscious consumers and investors,
which has contributed to its strong financial growth.
4. IKEA (Furniture and Home Goods)
- People:
IKEA is committed to responsible sourcing, ethical labor practices, and
promoting the well-being of workers in its supply chain. The company also
works to create affordable, sustainable home products that improve the
quality of life for its customers.
- Planet:
IKEA has ambitious sustainability goals, including becoming climate
positive by 2030. The company focuses on renewable energy, sustainable
materials, and circular economy principles, such as creating products that
can be recycled or reused. It has invested heavily in wind and solar
energy to power its stores.
- Profit:
IKEA’s sustainable practices haven’t hindered its profitability. Instead,
the company’s focus on affordable sustainability has resonated with
consumers, driving continued growth. Its commitment to reducing costs
while maintaining a positive environmental impact has positioned it as a
leader in both sustainability and business innovation.
5. Ben & Jerry’s (Ice Cream)
- People:
Ben & Jerry’s has a strong commitment to social justice, fair trade,
and ethical sourcing of ingredients. The company actively supports causes
related to racial equality, climate justice, and LGBTQ+ rights. It ensures
that farmers who supply ingredients receive fair wages and support.
- Planet:
Ben & Jerry’s works to minimize its environmental impact through
sustainable sourcing, reducing energy use, and promoting environmental
stewardship. The company is involved in various climate change
initiatives, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and advocating
for renewable energy policies.
- Profit: Despite being socially and environmentally focused, Ben & Jerry’s remains profitable and continues to grow its business globally. Its commitment to the Triple Bottom Line has attracted customers who care about sustainability and social justice, boosting the brand’s appeal.
These companies demonstrate that it’s possible to achieve
success while maintaining a strong commitment to social responsibility and
environmental stewardship. By embracing the Triple Bottom Line, they
have shown that sustainability can enhance profitability and create long-term
value for businesses.
5. Tips for Implementing the Triple Bottom Line Approach
To successfully implement the Triple Bottom Line, businesses
must be proactive and thoughtful about integrating these principles into their
operations. Here are a few tips to get started:
- Conduct
a Sustainability Audit: Start by assessing your company’s current
social, environmental, and economic impacts. Identify areas where you can
improve.
- Engage
Stakeholders: Involve employees, customers, and other stakeholders in
sustainability planning. They can provide valuable insights into what’s
important and where your company should focus.
- Set
SMART Goals: Ensure that your sustainability goals are Specific,
Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). Clear goals
make it easier to track progress and ensure accountability.
- Monitor and Report Progress: Transparency is key. Regularly measure your progress and communicate it through sustainability reports. This helps to build trust and ensures your company stays on track.
Conclusion
The Triple Bottom Line is a holistic framework that helps
companies achieve sustainable success by balancing people, planet, and profit.
By adopting the TBL approach, businesses not only contribute to a better world
but also strengthen their long-term resilience and profitability. Whether it’s
improving labor conditions, reducing environmental impact, or building a
sustainable business model, the Triple Bottom Line provides a clear guide for
aligning business goals with sustainability.
Now is the time for businesses to think beyond financial
gain and embrace the interconnectedness of social, environmental, and economic
well-being. Incorporating the Triple Bottom Line into your sustainability
strategy is not only good for business—it’s essential for a sustainable future.















Comments
Post a Comment