Your Guide to the SASB Framework: Reporting on Sustainability with Confidence
In today's world, investors, customers, and employees are increasingly demanding that businesses demonstrate their commitment to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Sustainability reporting, which involves communicating a company's impact on these areas, has become a critical tool for building trust and transparency. But with so many different reporting frameworks and standards, it can be challenging for businesses to know where to start.
The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
framework provides a clear and consistent approach to sustainability reporting,
helping businesses communicate their performance on the sustainability issues
that matter most to their investors. This guide will provide a clear and
accessible overview of the SASB framework, explaining what it is, how to use
it, and tips for effective implementation.
1. What is the SASB Framework?
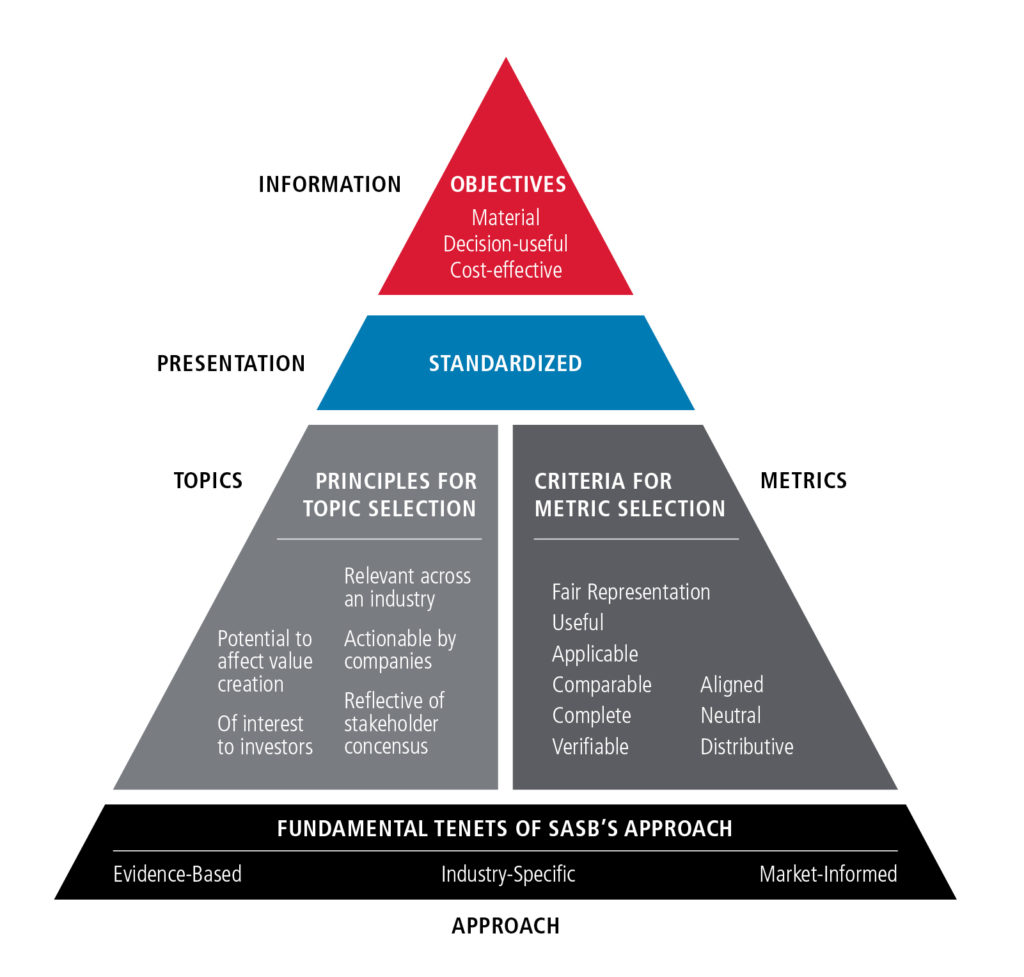
The SASB is a non-profit organization that develops and promotes industry-specific sustainability accounting standards. The SASB framework aims to provide a standardized approach to sustainability reporting, helping businesses identify and disclose the sustainability issues that are most material to their industries and investors.
Two key features of the framework that contribute to this goal are industry-specific standards and the concept of materiality which we shall explain in the following sections.
Industry-Specific Standards
The SASB framework recognizes that not all sustainability
issues are equally important to every industry. Therefore, it provides
industry-specific standards that identify the sustainability issues that are
most likely to impact a company's financial performance within a particular
sector. These standards are developed through a rigorous process that involves
extensive research, stakeholder engagement, and expert review.
The SASB framework provides guidance on the key elements of a sustainability report, including:
- Governance: Describe
your company's governance structure and processes related to
sustainability.
- Strategy: Outline
your company's sustainability strategy and how it aligns with your
business goals.
- Risk
Management: Identify and assess the material sustainability risks
and opportunities facing your company.
- Metrics
and Targets: Set measurable targets for your sustainability
performance and track your progress towards achieving them.
Key Benefits of Industry-Specific Standards
Relevance: By focusing on the sustainability issues that are
most relevant to a specific industry, the SASB framework ensures that
businesses are reporting on the information that is most important to investors
in that sector. This helps investors make more informed decisions and compare
companies within the same industry on a more level playing field.
Efficiency: Industry-specific standards streamline the
reporting process by helping businesses prioritize the sustainability issues
that matter most. This reduces the burden on companies and makes the reporting
process more efficient.
Comparability: The use of industry-specific standards makes
it easier for investors to compare the sustainability performance of companies
within the same sector. This helps investors identify best practices and
understand the relative risks and opportunities associated with different
companies within the same industry.
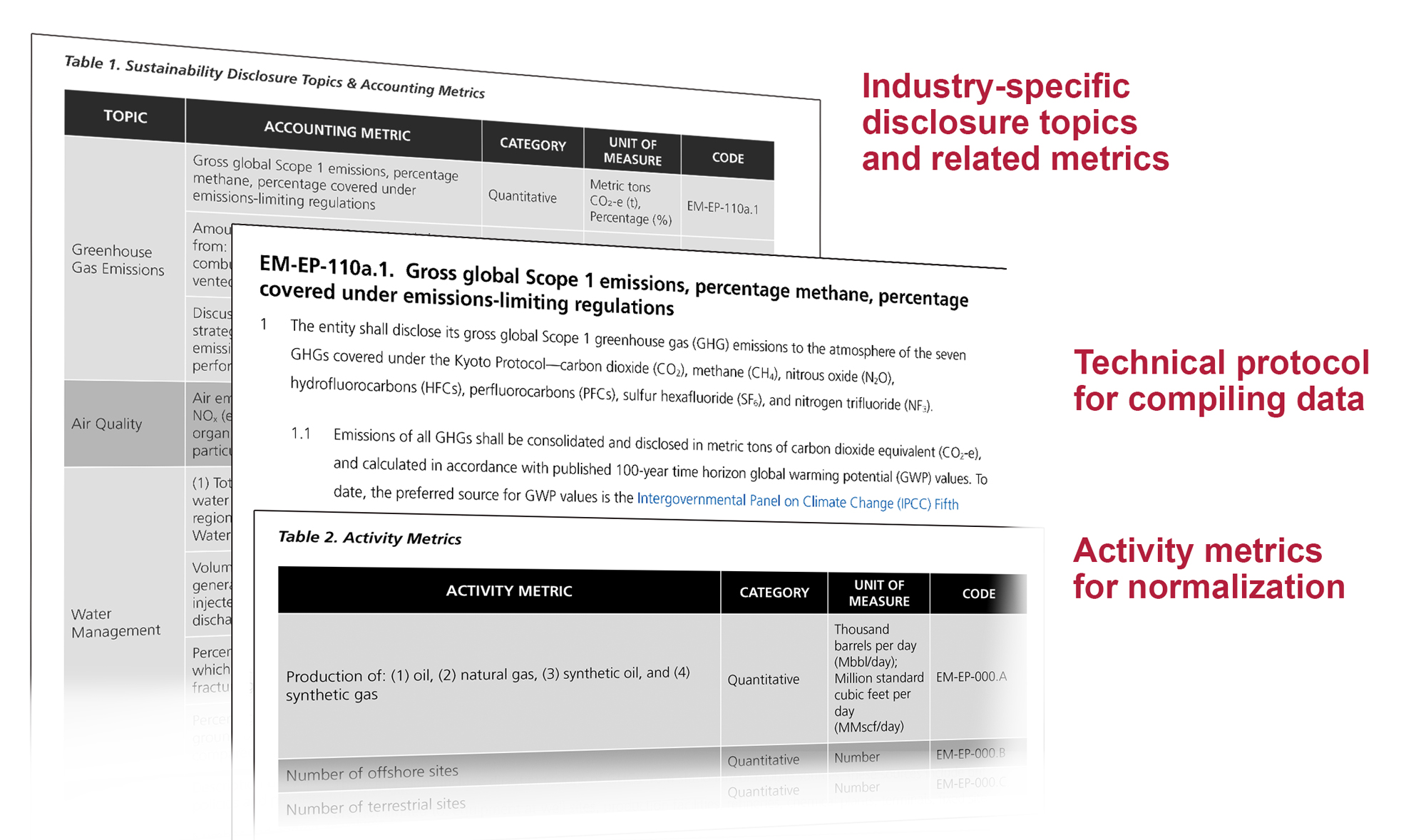
Example: The SASB standard for the electric utilities and power generators industry focuses on issues such as greenhouse gas emissions, water management, and air quality, as these are considered to be the most material sustainability issues for this sector. In contrast, the SASB standard for the healthcare delivery industry focuses on issues such as patient safety, quality of care, and labor practices. This industry-specific approach ensures that companies are reporting on the sustainability issues that are most relevant to their investors and stakeholders.
Materiality: Focusing on the Information That Matters
Most to Investors
Materiality is a fundamental concept in financial reporting,
and the SASB framework applies it to sustainability reporting. Material
information is defined as information that could reasonably be expected to
influence the decisions of investors. In other words, it is the information
that investors need to make informed decisions about a company's financial
performance and future prospects.
Key Considerations for Determining Materiality
Financial Impact: Sustainability issues that have a
significant impact on a company's financial performance, such as revenue
growth, profitability, or risk profile, are considered material. For example, a
company's greenhouse gas emissions might be considered material if they could
lead to increased regulatory costs or damage to the company's reputation.
Investor Interest: Sustainability issues that are of
particular interest to investors are also considered material. For example,
investors might be interested in a company's efforts to reduce its
environmental impact or its commitment to social responsibility.
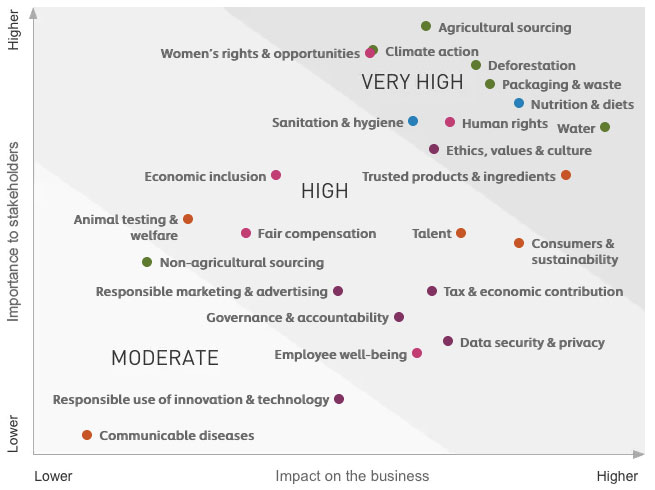
Industry Context: The materiality of sustainability issues can vary depending on the industry. For example, water management might be a more material issue for a company in the agricultural industry than for a company in the technology industry.
How Materiality Guides SASB Reporting
Focus on Key Issues: The SASB framework helps companies
identify and prioritize the sustainability issues that are most material to
their industry and investors. This ensures that companies are reporting on the
information that is most relevant to investors' decision-making.
Transparency and Disclosure: The SASB framework encourages companies to disclose material sustainability information in a clear and concise way. This helps investors understand the risks and opportunities associated with a company's sustainability performance and make informed investment decisions.
Improved Investor Relations: By focusing on material
sustainability issues, companies can improve their communication with
investors, build trust, and enhance their relationships.
Example: A company in the energy sector might consider its greenhouse gas emissions to be material because they could impact its regulatory compliance, operating costs, and brand reputation. Investors in this sector are likely to be interested in a company's plans to reduce its emissions and its commitment to a low-carbon future. Therefore, a company in the energy sector would need to disclose its emissions data and its plans for reducing emissions in its SASB report.
Benefits of Using the SASB Framework
Improved Investor Relations: The SASB framework helps businesses communicate with investors in a clear and consistent way, enhancing investor confidence and trust.
Reduced Risk: By identifying and managing material
sustainability risks, businesses can reduce their exposure to financial and
reputational risks.
Enhanced Sustainability Performance: The SASB framework
encourages businesses to focus on their sustainability performance, leading to
improvements in their environmental, social, and governance practices.
Effectively Implementing the SASB Framework
The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) framework provides a valuable tool for businesses to communicate their sustainability performance in a clear and consistent way. Implementing the SASB framework effectively requires a strategic approach that involves several key steps:
1. Establish a Foundation for Sustainability
Integrate Sustainability into Business Strategy: Sustainability should not be a separate initiative but rather an integral part of a company's core strategy. This means embedding sustainability considerations into all aspects of the business, including operations, supply chains, product development, and marketing.
Identify Material Sustainability Issues: Businesses need to identify the sustainability issues that are most material to their industry and stakeholders. This involves considering the sector's supply chain, regulatory trends, stakeholder concerns, physical location risks, and innovation opportunities. The SASB framework provides guidance on which sustainability issues are most material for a particular industry.
Prioritize Sustainability Metrics: Once material issues are identified, businesses should prioritize the most impactful metrics for reporting. This involves considering both internal factors (operations, areas for improvement) and external factors (stakeholder expectations, regulatory requirements). The goal is to choose metrics that are meaningful, measurable, and aligned with the organization's values and goals.
2. Apply SASB Standards for Enhanced Disclosure
- Identify Relevant SASB Standards: Review the list of SASB standards and select those that are applicable to your industry. The SASB website provides a comprehensive list of industry standards and guidance on selecting the appropriate ones.
- Map Metrics to Business Activities: Map each metric to its corresponding business activity to understand which areas of operations are most impacted by sustainability risks and opportunities.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Gather data on the prioritized metrics and analyze it against internal targets and external benchmarks. This enables tracking progress over time and identifying areas for improvement.
- Disclose Findings in a Comprehensive Report: Produce a clear, concise, transparent, and easily understandable report that discloses findings from the analysis conducted against the prioritized metrics.
3. Leverage the SASB Framework for Investor Engagement
- Communicate Material Sustainability Information: Use the SASB framework to disclose financially material sustainability information that is relevant to investors. This includes information on governance, environmental impact, social capital, human capital, business model and innovation, and customer privacy and data security.
- Create a Common Language: The SASB framework helps create a common language between companies and investors about the risks and opportunities associated with sustainability issues.
- Demonstrate Commitment to Sustainable Growth: By effectively leveraging SASB standards for investor engagement, companies can improve transparency and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable growth strategies.
4. Collaborate with Stakeholders for Sustainability
- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Create clear communication channels and engagement strategies to effectively collaborate with stakeholders. This could involve using platforms like the SASB website or other online tools.
- Gain Valuable Insights: Engaging with stakeholders helps identify and prioritize sustainability issues that are most important to them. This also provides valuable insights into potential risks and opportunities associated with operations.
- Build Trust and Partnerships: Collaboration with stakeholders builds trust, strengthens partnerships, enhances brand reputation, and ultimately improves business performance.
5. Continuously Improve Sustainability Reporting and Disclosure
- Establish a Performance Baseline: Gather data on your organization's sustainability metrics (e.g., greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, water usage) to establish a baseline of current performance.
- Set Targets for Future Progress: Identify areas for improvement and set targets for future progress based on the baseline data.
- Engage with Stakeholders: Incorporate stakeholder feedback into decision-making processes to ensure sustainability efforts are aligned with their expectations and needs.
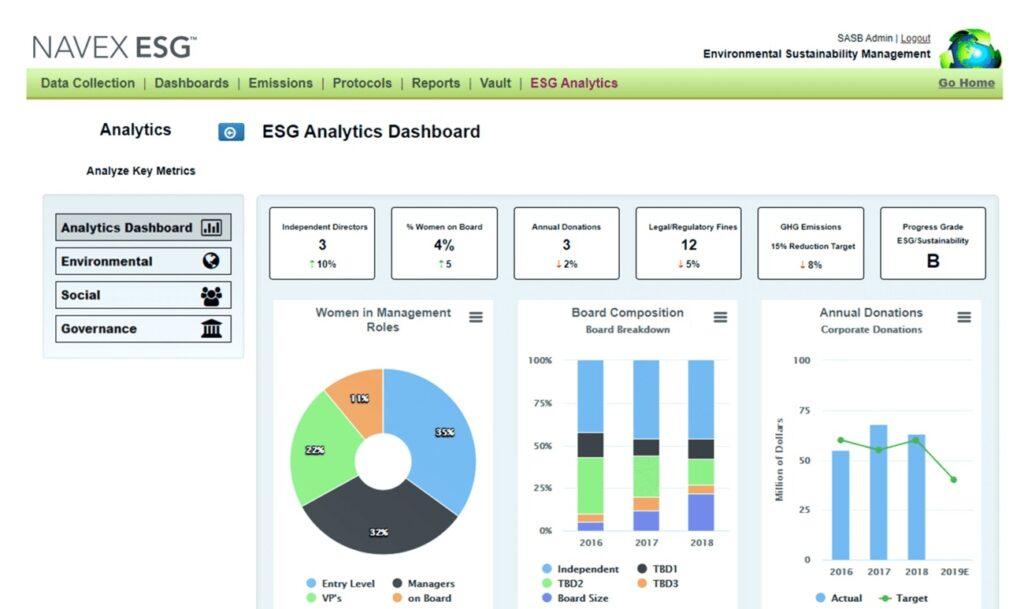
6. Utilize Technology for Efficient Implementation
- Energy and Sustainability Management Platforms: Leverage technology platforms to automate data collection, reporting, and analysis, improving data completeness, accuracy, and quality. These platforms can also integrate directly with the SASB framework for seamless reporting.
- Data Management Tools: Invest in data management tools that can help you collect, organize, and analyze sustainability data efficiently. This will make the reporting process more streamlined and accurate.
7. Seek Expert Guidance and Support
- Consult with Sustainability Professionals: Engage with sustainability professionals or consultants who have experience implementing the SASB framework. They can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the process.
- Attend Workshops and Training: Participate in workshops and training sessions offered by the SASB or other organizations to enhance your knowledge and understanding of the framework.
Here are examples of how companies in different industries
have successfully implemented the SASB framework and achieved positive
outcomes:
1. Technology
Salesforce: Salesforce, a leading cloud-based software company, has been a vocal advocate for the SASB framework and has used it to enhance its sustainability reporting. They have incorporated SASB standards into their annual sustainability report, which focuses on material issues such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and employee diversity. This has helped Salesforce attract investors who are interested in companies with strong sustainability practices. Their commitment to SASB has also led to improved stakeholder engagement and increased transparency in their operations.
2. Financial Services
- Goldman Sachs: Goldman Sachs, a global investment bank, has implemented the SASB framework to improve its disclosure of climate-related risks and opportunities. They have used SASB standards to report on their exposure to climate change, their efforts to reduce their carbon footprint, and their investments in sustainable businesses. This has helped Goldman Sachs demonstrate its commitment to responsible investing and attract investors who are concerned about climate change.
3. Energy
ExxonMobil: ExxonMobil, a major oil and gas company, has used the SASB framework to improve its disclosure of environmental and social risks. They have reported on their greenhouse gas emissions, their water usage, and their efforts to manage their environmental impact. This has helped ExxonMobil address investor concerns about climate change and demonstrate its commitment to responsible energy production. They have also used SASB standards to report on their workforce diversity and their community engagement initiatives.
4. Retail
- Target: Target, a large retail chain, has used the SASB framework to improve its disclosure of social and governance risks. They have reported on their labor practices, their supply chain management, and their efforts to promote diversity and inclusion. This has helped Target address investor concerns about ethical sourcing and demonstrate its commitment to responsible business practices. They have also used SASB standards to report on their environmental impact, including their efforts to reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainable packaging.
5. Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson: Johnson & Johnson, a global healthcare company, has used the SASB framework to improve its disclosure of patient safety and quality of care. They have reported on their efforts to ensure the safety and efficacy of their products, their commitment to patient privacy, and their investments in research and development. This has helped Johnson & Johnson demonstrate its commitment to patient well-being and attract investors who are interested in companies with strong healthcare practices.
Positive Outcomes Achieved through SASB Implementation
- Improved
Investor Relations: Companies that have implemented the SASB
framework have reported improved investor relations, as they are able to
communicate their sustainability performance in a way that is relevant and
understandable to investors.
- Enhanced
Transparency and Disclosure: The SASB framework has helped
companies enhance their transparency and disclosure of material
sustainability information, which has increased investor confidence and
trust.
- Increased
Stakeholder Engagement: Companies that have used the SASB
framework have reported increased stakeholder engagement, as they are able
to communicate their sustainability efforts in a more effective way.
- Improved
Sustainability Performance: The SASB framework has encouraged
companies to focus on the sustainability issues that are most material to
their business, which has led to improvements in their sustainability
performance.
Metrics
for Tracking
Here are some key metrics that companies use to track the success of their SASB implementation.
1. Alignment with SASB Standards
- Percentage of SASB Metrics Reported: Companies can track the percentage of SASB metrics that they are reporting on in their sustainability reports. This metric provides a measure of the extent to which they are adhering to the SASB framework.
- Number of SASB Disclosure Topics Addressed: Companies can also track the number of SASB disclosure topics that they are addressing in their reports. This metric provides a measure of the comprehensiveness of their sustainability reporting.
2. Data Quality and Reliability
- Data Accuracy and Completeness: Companies should assess the accuracy and completeness of the data they are using to report on SASB metrics. This involves verifying the data sources, ensuring consistency across reporting periods, and implementing internal controls to maintain data integrity.
- Data Governance and Assurance: Companies should establish data governance processes to ensure that the data they are reporting is accurate, reliable, and consistent with SASB standards. This may involve engaging with independent third-party auditors to provide assurance over the data.
Investor Feedback and Engagement: Companies should track investor feedback on their SASB reporting. This can involve monitoring investor calls, reviewing investor presentations, and analyzing investor surveys. This feedback can help identify areas for improvement in their reporting and demonstrate the value of their SASB implementation.
- Media Coverage and Brand Reputation: Companies can track media coverage of their SASB reporting and assess its impact on their brand reputation. This can help gauge the effectiveness of their communication efforts and identify areas for improvement.
4. Internal Alignment and Integration
- Alignment
with Business Strategy: Companies should assess the extent to
which their SASB reporting is aligned with their overall business
strategy. This involves ensuring that their sustainability goals and
initiatives are integrated into their core operations and decision-making
processes.
- Integration with Other Reporting Frameworks: Companies should track the extent to which their SASB reporting is integrated with other reporting frameworks, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). This can help streamline their reporting processes and ensure that they are meeting the needs of multiple stakeholders.
- Progress on Sustainability Goals: Companies should track their progress on achieving their sustainability goals, as measured by the SASB metrics. This can help demonstrate the value of their SASB implementation and highlight areas for further improvement.
- Financial Performance and Risk Management: Companies can also track the impact of their SASB implementation on their financial performance, including revenue growth, profitability, and risk management. This can help demonstrate the link between sustainability and financial value creation.
By tracking these key metrics, companies can effectively assess the success of their SASB implementation and demonstrate the value of their sustainability efforts to investors and other stakeholders. This information can also help guide future improvements in their sustainability reporting and practices.
Conclusion
Implementing the SASB framework effectively requires a
commitment to sustainability, a strategic approach, and a willingness to engage
with stakeholders. By following these steps, businesses can enhance their
sustainability reporting practices, build trust with investors, and contribute
to a more sustainable future.


















Comments
Post a Comment